Acronyms/Abbreviations/
Root Words/Prefixes/Suffixes
A majority of medical terms are composed of
Greek and Latin word parts and are broken
down into different elements. One element
is the root word. The root word is the
foundation of the medical term and contains
the fundamental meaning of the word. All
medical terms have one or more roots.
Examples:
hydr = water
lith = stone
path = disease
Combining forms (or vowel, usually “o”)
links the root word to the suffix or to
another root word. This combining vowel
does not have a meaning on its own; it only
joins one part of a word to another.
Prefixes and suffixes are two of the other
elements used in medical terminology and
consist of one or more syllables (prepositions
or adverbs) placed before or after root
words to show various kinds of relationships.
Prefixes are before the root word and suffixes
are after the root word and consist of one or
more letters grouped together. They are
never used independently; however, they
can modify the meaning of the other word
parts. Many prefixes and suffixes are added
to other words with a hyphen, but medical
dictionary publishers are opting to drop
the hyphen on many of the more common
prefixed medical words.
Examples:
Root Words/Combining Forms
abdomin/oabdomen
acous/ohearing
extremities, top,
acr/o
extreme point
aden/ogland
fat
adip/o
andr/omale
ankyl/o
stiff, bent, crooked
anter/ofront
arthr/ojoint
yellowish, fatty plaque
ather/o
audi/o
hearing
aur/o
ear
aut/o
self
armpit
axill/o
balan/o
glans penis
life
bi/o
blast/o
developing cell
blephr/oeyelid
brach/oarm
bronchial tubes
bronch/o
carcin/ocancer
card/o
heart
cheil/olip
chol/o
gall, bile
cholangi/o bile duct
chondr/ocartilage
to cut
cis/o
colp/o
vagina
coron/oheart
cost/o
ribs
crani/oskull
cry/o
cold
cutane/oskin
cyan/oblue
cyt/o
cell
cyst/o
urinary bladder
dacry/o
tear duct, tear
derm/oskin
dermat/oskin
Acronyms /
Abbreviations
Prefixes:
micro = small
peri = surrounding
Suffixes:
algia = pain
an = pertaining to
The following are lists of prefixes and
suffixes typically seen in coding:
1
Plain English Descriptions for Coding Terms
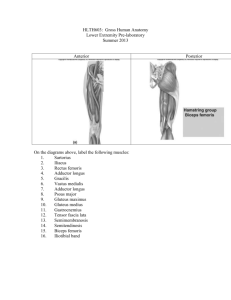
Muscular System
(Anterior View)
Masseter m.
Buccinator m.
Sternocleidomastoid m.
Trapezius m.
Deltoid m.
Frontalis m.
Anatomy
Temporalis m.
Orbicularis oculi m.
Zygomaticus minor m.
Zygomaticus major m.
Orbicularis oris m.
Depressor anguli oris m.
Levator scapulae m.
Pectoralis minor m.
Pectoralis major m.
Internal intercostal mm.
Coracobrachialis m.
Brachialis m.
Serratus anterior m.
Biceps brachii m.
Rectus sheath
Rectus abdominus m.
Linea alba
Brachialis m.
External abdominal
oblique m.
Brachioradialis m.
Extensor carpi
radialis longus m.
Internal abdominal oblique m.
Transversus abdominus m.
Palmaris longus m.
Flexor pollicis longus m.
Palmaris longus m.
Flexor carpi radialis m.
Superficial inguinal ring
Flexor digitorum
superficialis m.
Tensor fasciae
latae m.
Abductor pollicis
brevis m.
Sartorius m.
Adductor longus m.
Rectus femoris m.
Iliopsoas m.
Pectineus m.
Vastus lateralis m.
Iliotibial tract
Vastus medialis m.
Adductor brevis m.
Adductor magnus m.
Vastus lateralis m.
Flexor pollicis
brevis m.
Abductor digiti
minimi m.
Gracilis m.
Lateral patellar retinaculum
Tibialis anterior m.
Gastrocnemius m.
Peronius longus m.
Peronius brevis m.
Soleus m.
Extensor digitorum longus m.
Vastus medialis m.
Patella
Patellar ligament
Medial patellar retinaculum
Tibia
Flexor digitorum longus m.
Extensor hallucis longus m.
Extensor hallucis brevis m.
Abductor hallucis m.
© Fairman Studios, LLC, 2002. All Rights Reserved.
13
Terminology
2D Echocardiography A feature of the echocardiogram
abdominal aorta The portion of the aorta (main blood
vessel) in the abdomen.
abdominal cavity The hollow space of the body between
the diaphragm and pelvis containing the abdominal organs.
abdominal delivery Delivery of an infant through an
incision made into the intact uterus through the abdominal
wall.
abdominal hysterectomy Surgical removal of all or part
of the uterus through an incision in the abdominal wall.
abdominohysterectomy Surgical removal of all or part of
the uterus through an incision in the abdominal wall.
abdominoplasty Plastic surgery of the abdomen in which
excess fatty tissue and skin are removed, usually for cosmetic
purposes.
abduction Movement of a body part away from the medial
plane.
Abelcet Drug used to help the body overcome serious
infections caused by fungus.
aberrant 1) Deviating from the usual course, as certain
ducts, vessels, or nerves. 2) Out of place; ectopic.
aberration Deviation from the normal or usual.
abiotrophy Progressive loss of the ability of certain
tissues to live, leading to disorders; applied to degenerative
hereditary disease of late onset.
ablation Removal of a body part of the destruction of its
function, as by surgery, disease, or noxious substance.
ABLC (amphotericin B lipid complex) Drug used to help
the body overcome serious fungal infections.
ablutomania Morbid preoccupation with thoughts about
cleanliness, exhibited by frequent washing, as seen in
obsessive-compulsive disorder.
ABO A, B, and O are the three major blood types. ABO
incompatibility is a reaction of the immune system that
occurs if two different and incompatible blood types are
mixed together.
abocclusion Condition in which the upper teeth do not
touch the lower teeth when biting.
aborted systole A weak contraction of the heart, usually
premature.
abortifacient A substance that causes pregnancy to end
prematurely and cause an abortion.
aboulomania Pathological indecisiveness and the inability
to act independently.
abrachia Congenital absence of the arms.
29
A–D
machine which allows imaging of the heart structure.
3D conformal radiotherapy Radiation delivery that is
performed using three dimensional scans to directly treat a
tumor with less destruction of healthy tissue.
3D rendering The application of computer software to give
a two dimensional object depth and texture.
4D imaging The application of computer software to give a
three dimensional object motion.
A-hydroCort Drug used as a corticosteroid-type hormone
when the body is not producing enough cortisol. Also used to
suppress the immune system in order to treat conditions such
as allergies, rejection of transplanted organs, or rheumatoid
arthritis.
A-MethaPred Drug used to provide relief for inflamed
areas of the body and to treat severe allergies, skin problems,
asthma, or arthritis.
A-mode A one-dimensional representation of a reflected
sound wave in a diagnostic ultrasound.
A-Spas Drug used for relief from spasms of the
gastrointestinal tract, the bladder, and the biliary tract, and
in controlling conditions such as colitis, spastic bladder,
diverticulitis, infant colic, renal and biliary colic, peptic ulcer,
irritable bowel syndrome , splenic flexure syndrome, and
pancreatitis.
Aarskog-Scott syndrome A syndrome of wide spaced
eyes, front facing nostrils, a broad upper lip, a malformed
scrotum, and looseness of the ligaments resulting in bending
back of the knees, flat feet, and overly extensible fingers.
abarelix Drug used in the palliative treatment of advanced
prostate cancer.
abarognosis Loss of the ability to sense weight.
abasia Inability to walk.
abatacept Drug used to treat arthritis.
Abbe-Estlander procedure Procedure in which lower lip
is used to reconstruct upper lip. Also known as lip switch.
Abbokinase Drug used to dissolve blood clots that have
formed in certain blood vessels.
Abbokinase, open cath Drug used to dissolve blood clots
that form in tubes that are placed in the body.
abciximab Drug used to lessen the chance of heart attack in
people who need percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI), a
procedure to open blocked arteries of the heart.











![MMT,_Goniometry,_Prime_movers[1]](http://s3.studylib.net/store/data/008618461_1-74306e0c1ef005cd8edb0aef500304e8-300x300.png)