Tissues and Membranes
advertisement

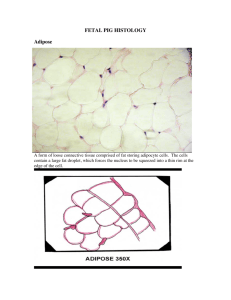
Tissues and Membranes Objectives • Describe the characteristics of each of the four major categories of tissue. • Describe the functions of the types of epithelial tissues • Describe the functions of connective tissue • Explain the differences between skeletal muscle, smooth muscle and cardiac muscle. • Name the 3 parts of the neuron and the function of each. • Describe locations and types of membranes and the functions of serous fluid in these locations • State the location of mucous membranes and the purpose of mucus. • Explain the difference between exocrine and endocrine glands and give an example of each. Tissues and Membranes • Four basic tissue types – Epithelia – Muscle – Nervous – Connective Epithelia • Act as linings and coverings • Absorption and secretion Connective • Connective and supportive • Bind body structures together • Fluid tissue types – Liquid media for transport, exchange, defense Muscle • Ability to contract • Support • Movement Nervous • • • • Conduction Telecommunications network Sensory Motor Epithelial Tissue • Found on surfaces – Coverings of outer surfaces – Linings of inner surfaces • Lack capillaries • Depend on blood supply from supporting connective tissues • Many are capable of secretion Epithelial Tissue • Classification based: – on type of cell – Characteristic shape – Number of layers of cells Epithelial Tissue • Three distinctive shapes – Squamous – Cuboidal – Columnar • Layers – Simple= 1 layer – Stratified= many layers Simple Squamous Epithelium • Simple squamous epithelia consist of only a single layer of flattened cells resting on connective tissues. These flattened cells are specifically found in thin barriers where exchange of nutrients, wastes, or respiratory gases occurs Simple Cuboidal Epithelia Due to larger cytoplasmic volumes, cuboidal cells can undertake more complex functions such as absorption and secretion. Most secretory cells of glands are cuboidal epithelial cells. In addition, the ducts of most exocrine glands are lined by cuboidal cells as are most of the tubules in the kidneys. Simple Columnar Epithelia Simple columnar epithelium is found in: ducts of exocrine glands larger tubules or collecting ducts of the kidney stomach, small intestine, and large intestine, smaller respiratory tubes or bronchioles, fallopian tubes, Goblet cells Pseudostratified Epithelium As the name implies, pseudostratified epithelium is "falsely stratified". Cells are columnar but tall and thin. All cells rest on the basement membrane. The unique appearance of pseudostratified epithelia occurs because the tall, thin cells intertwine. Nuclei appear at various levels but there is no distinct layering Nasal Pseudostratified Epithelium Stratified Squamous Epithelium • Many layers • Lower cells rounded • Barrier to microorganisms Stratified Squamous Epithelium Non-keratinized or mucous type, stratified squamous is found in: the oral cavity Esophagus to the stomach junction anus and rectum vagina and cervix Transitional Epithelium Transitional epithelium is only found in the urinary tract! Bladder Urethra Stratified Columnar and Cuboidal Epithlia Glands • Organs that secrete something • Secretion may function at the site of secretion or at a distant location • Classified as endocrine or exocrine Exocrine Glands • Have ducts • Connect to the surface Modes of Secretion • Most glands Modes of Secretion Modes of Secretion Endocrine • • • • • Hormone producing Lack ducts Hormones enter bloodstream Circulate throughout body Target organs • What kind of gland is the thyroid gland? • Question: Where is ciliated epithelium found? • Question: Where are goblet cells found? Connective Tissue • • • • • • • Areolar Adipose Fibrous Elastic Bone Blood Cartilage Blood • Cells – RBC – Platelets – WBC • Plasma – Transport medium • What are the functions of the blood cells? • Question: What other cells are found in areolar connective tissue, and where is this tissue found? • Question: For which organs is adipose tissue a cushion? Areolar Connective Tissue Adipose • • • • Cells called adipocytes Store fat Excess caloric intake stored as fat Small matrix: tissue fluid and few collagen fibers • Stored between dermis and muscle • Endocrine functions: leptin, estrogen, cytokines Fibrous Connective Tissue • Parallel collagen fibers • Few fibroblasts • Flexible strength • Poor blood supply Elastic Connective Tissue • Primarily elastin fibers • Walls of large arteries • Alveoli of lungs Bone • • • • • support - for muscles, organs, and soft tissues leverage and movement - the synovial joints protection - for critical organs calcium phosphate storage - mineral balance hemopoiesis - formation of blood cells Compact Bone • Compact bone is a very dense tissue forming the outer layer of all bones and the thickened shafts or diaphyses of long bones. In a microscopic view, compact bone always contains numerous osteons or Haversian Systems. Each consists of a central canal through which blood vessels and nerves pass. Surrounding this canal are multiple concentric lamellae or layers of bone. Haversian systems are only found in compact bone. Their specific arrangements within compact bone contribute to the strength of this osseous tissue type. Spongy bone • Cancellous or bone is found forming the core of most flat and irregular bones. It is also very prevalent in the epiphyses(ends) of long bones. The construction of this osseous tissue type is quite different than that of compact bone. One key difference is the absence of osteons! Spongy bone as the name implies is more open and in cross-section offers a compartmentalized appearance not unlike that of a sponge. Consisting of interconnecting "struts" of bone called trabeculae, spongy bone has abundant spaces typically occupied by bone marrow and adipose tissues. Spongy bone Cartilage • • • • • • Protein-carbohydrate matrix More water than bone No Calcium salts Firm, smooth, flexible Chondrocytes nourished by diffusion Repair very slow if at all Muscle Tissue • Specialized for contraction • Three types – Skeletal – Smooth – Cardiac Skeletal • • • • • • • AKA: Striated, voluntary Cylindrical cells Have several nuclei Appear striated or striped Attach to bones Produce heat Skeletal muscle is the most abundant muscle type in the body. Smooth Muscle • Involuntary or visceral muscle • Cells have tapered ends • Functions of organs Cardiac • Only in the heart • Branched with one nucleus each • Cell membranes folded and lock cells together • Forms the myocardium • Inherent ability to beat • What are the other names for skeletal muscle and smooth muscle? • Which type of muscle tissue must receive nerve impulses to contract? • What movement does cardiac muscle produce? Nerve Tissue • Neurons • Two divisions classically named – CNS: brain and spinal cord – PNS • Neurons capable of transmitting impulses Neuron Structure • In which direction do the dendrites and axon carry impulses? • What is the name for the space between two neurons? Membranes • • • • • Sheets of tissues Cover or line surfaces Separate organs May produce secretions Two main categories – Epithelial – Connective tissue Epithelial Membranes • Two divisions – Serous • Produces serous fluid – Mucous • Produces mucus Mucous membranes line the digestive, respiratory, urinary, and reproductive tracts. • Serous membranes occur in pairs, with a parietal and visceral layer. • The heart also has a set of serous membranes, the parietal and visceral pericardia. Serous Membranes • Simple squamous epithelium • Line some closed body cavities – – – – – – – Pleural membranes: thorax Parietal pleura: line chest wall Visceral pleura: cover lungs Parietal pericardium: lines pericardium Visceral pericardium: covers heart Peritoneum lines abdominal cavity Mesentery or visceral peritoneum covers abdominal organs • Serous fluid prevents friction Mucous Membranes • Line body tracts – Respiratory – Digestive – Urinary – Reproductive • Mucus keeps epithelial cells wet • What is the function of serous fluid? • What is the function of mucus? • What do the mucous membrane tracts all have in common? Connective Tissue Membranes • • • • • • • Superficial fascia Periosteum Perichondrium Synovial Deep fascia Meninges Fibrous pericardium