8:National 4 Everyday Consumer Products
advertisement

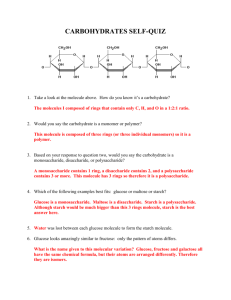
Topic 8 – National 4 Chemistry Summary Notes Everyday Consumer Products In this topic you will learn about two new groups of compounds called alcohols and carbohydrates. Carbohydrates from Plants LI 1 Carbohydrates are a high energy group of compounds that are made by plants through a process called PHOTOSYNTHESIS. Carbohydrates are high energy compounds which contain carbon, hydrogen and oxygen. They include substances you might have heard about called sugars and starch. Carbohydrates are important to us because they provide energy for us in many foods and can be burned as fuels. There are many plants that supply us with carbohydrates: Type of Food High in Sugar (tick) High in Starch (tick) Crisps Plant Source potatoes Fruit juice Pasta Cereal bars Bread wheat 1 LI 2 Formulae of Carbohydrates The two main carbohydrates we are interested in are the simple carbohydrate called glucose and the complex carbohydrate called starch. All carbohydrates contain carbon, hydrogen and oxygen with a ratio of hydrogen and oxygen of 2:1. Glucose is described as a simple carbohydrate because it is a small molecule with the formula: C6H12O6 Glucose Starch is described as a complex carbohydrate because it is formed by joining many glucose molecules together: Plants convert glucose into starch for storing energy. Activity- carry out solubility tests on starch and glucose and then see if you can explain why plants store energy as starch not as glucose: Results Starch_____________ dissolve well in water but glucose _________. Plants do not store glucose because when it rains ________________________________________________________________ 2 LI 3 Chemical Tests For Carbohydrates Starch and glucose are both white powders full of chemical energy. We know that starch is insoluble and glucose is soluble but there are other tests we can do to distinguish between starch and glucose: The Benedict’s Test If a blue solution called Benedict’s solution is added to a carbohydrate solution and it is then heated in a hot water bath the solution will turn orange only if sugar is present and glucose is a sugar. ( other sugars like fructose also change Benedict’s orange) Starch has no effect on Benedict’s solution. The Iodine Test If a carbohydrate is tested with iodine solution the brown iodine will turn blue/black only if starch is present! 3 Summary of Properties of Starch and Glucose Type of Carbohydrate Starch Formula Solubility Reaction with Iodine Reaction with Benedicts Glucose LI 4 Breaking Down Starch Starch is a high energy compound but although it is in food we cannot use it directly in our cells for energy. The starch must be broken back down into glucose so that it can be transported around the body and get into our cells. This break down of starch happens in your digestive system and is part of the digestion process. The Model Gut Experiment You will carry out an experiment to prove that only glucose is small enough to pass through the gut wall and on into the bloodstream. Draw a labelled diagram below of the method you used: 4 The Amylase Experiment You will carry out an experiment to prove that starch is broken down into simple sugar during digestion, in your gut, by an enzyme called amylase. Enzymes are biological catalysts used by your body to speed up reactions. The type of reaction that breaks starch down is called HYDROLYSIS. Draw a labelled diagram below to show the method you used: Acid Hydrolysis Starch can also be broken down by heating with acid. Your teacher will demonstrate it. 5 LI 5 Getting Energy Out Of Glucose Once in body cells the glucose molecules release their energy by going through a process called RESPIRATION. We would not normally show energy as a product in a reaction, it isn’t a substance, but we have left it in to emphasise that respiration is all about releasing energy from food. Respiration is the opposite of photosynthesis Making Alcohol LI 6 Making alcohol is big business in Scotland! There are nearly 20,000,000 barrels of whisky sitting maturing in warehouses at any one time all made by fermenting barley. Many different alcoholic drinks are made from different plant sources. The process for making alcohol is called FERMENTATION where enzymes present in yeast are responsible for converting glucose into ethanol. These alcoholic drinks all contain the alcohol called ethanol but have many other flavour molecules to give distinctive drinks: Type of alcoholic drink Whisky Plant source of carbohydrate Barley Beer Wine Cider 6 Percentage Alcohol Content Fermentation We can make ethanol by fermentation in the school laboratory: C6H12O6 2C2H5OH + 2CO2 Glucose ethanol + carbon dioxide We can prove we made carbon dioxide by bubbling it through limewater because it will _________________________. Q. How can we prove we have made ethanol? Answer- Ethanol has a lower boiling point than water ( 78 °C) so we can separate it out by distillation and show that it burns. Ethanol burns very well. (it also smells!!) The maximum % of alcohol we can produce by fermentation is around 14% because the ethanol is a poison and yeast, a living organism, is killed by high levels of ethanol. Distillation has to be used to produce drinks of a higher alcohol content. Distillation apparatus 7 LI 7 Enzyme Optimal Conditions Not only do high levels of ethanol stop yeast working, the activity of the enzymes in yeast ( and all enzymes) are easily affected by the conditions they are working in. They are sensitive to changes in temperature and pH and work best within a narrow range of pH and temperature. Each individual enzyme has its own set of ideal conditions called “optimal conditions”. Enzymes in yeast work best at around body temperature of 37 0C and a pH of about 7. Units of Alcohol LI 8 As mentioned ethanol is a poison and it is important not to take too much. You will research as a home work how many units of alcohol we should be drinking and what volume of each drink contains one unit of alcohol: Alcoholic Drink Alcohol Content % What volume equals ONE unit (cm3) Whisky Gin Beer Vodka Wine There are many health issues associated with drinking too much alcohol. Write below two of the issues that you think are most important: 1. 2. 8 Carbohydrates as Food or Fuel? LI 9 http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Food_vs._fuel Food vs. fuel is a big concern regarding the risk of using farmland or crops for biofuels production instead of for food supply on a global scale. The "food vs. fuel" or "food or fuel" debate is an international one. There is disagreement about how significant the issue is, what is causing it, and what can or should be done about it. Using the link above to start you off you will research this issue by answering the questions below to help you. 1. Name two crops that could be used as biofuels. 2. Which country( in South America) relies heavily on Bioifuels. 3. What does it grow in order to make the biofuel ethanol. 4. What affect does using so much land to produce biofuels seem to have on food prices. 5. What crops does the UK grow in order to make biofuels. 6. In your reading did you find any other problems with using so much land for biofuels? 9 Topic 8 National 4 – Pupil Self-evaluation Learning Intention Success Criteria “ I can:” 1 I am going to find out that plants are a source of carbohydrates which can be used for fuels or food Name two plants that provide carbohydrates Name two foods high in starch Name two foods high in sugar 2 I am going to find out about the formulae of carbohydrates State that carbohydrates are compounds containing the elements carbon hydrogen and oxygen in a ratio of 2:1 “H” to “O and C” State that starch is a complex carbohydrate State that glucose is a simple carbohydrate State that starch is formed from many glucose molecules State that Starch is insoluble so it can be stored safely in plants State that glucose is very soluble so could be easily washed away I can draw a labelled diagram to show how Benedicts can be used to test for simple sugars I can give the colour change when Benedicts reacts with simple sugars I can give the colour change when Iodine reacts with starch State that enzymes are biological catalysts State that digestion produces small, soluble molecules like glucose, that can pass through the gut wall then into the bloodstream and on into cells 3 4 I am going to find out about the chemical tests for carbohydrates I am going to find out that in our gut we use acid and enzymes to help hydrolysis reactions go fast and that digestion of starch is an example. 10 5 6 I am going to find out about the process called respiration I am going to find out how enzymes in yeast convert glucose to ethanol in a process called fermentation 7 8 9 I am going to find out that enzymes only work well under certain conditions I am going to find out about the alcohol content of different drinks and discuss health issues associated with drinking too much alcohol. I am going to research the issues around using carbohydrates as fuel as well as fuel State that respiration is a process that the cells in our body use to get energy out of glucose State that the products of respiration are water and carbon dioxide State that alcohol is produced in a fermentation reaction Describe what “enzyme optimal conditions” means State that enzymes stop working when the concentration of alcohol gets too high Give examples of different plants used to make alcoholic drinks State that distillation is a process used to separate liquids of different boiling points State that the word optimal mean the best State that pH and temperature affect enzyme activity State the units of alcohol in wine, beer and spirits State two serious health issues brought on by drinking too much alcohol Give examples of two crops used as both food and fuel Give a disadvantage of using so much land to produce crops for fuel rather than food 11 12