Planned order release
advertisement

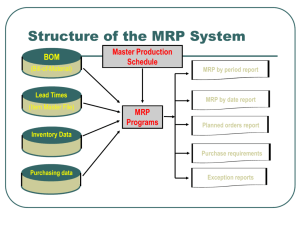
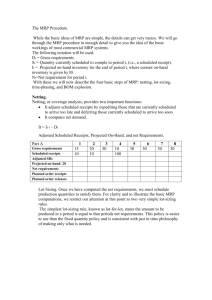
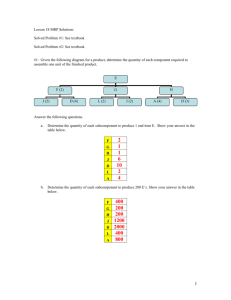
Material Requirements Planning MRP MRP Scheduling Terminology • Gross Requirements: needed during each period. • Scheduled Receipts: Existing orders that arrive at beginning of period. • On-hand or available balance: • (depending on software convention, could be at the beginning of each period or end): • Book: Inventory balance at end of each period. • Net requirements: What is need to meet requirements and safety stock. • Planned order receipt: arrives at beginning of period. • Planned order release: Addresses lead time. MRP Table – determine the Project Available Balance (Inventory) 1 Gross Requirements 10 Scheduled receipts (begin) Projected Available Balance (ending) Net Requirements Planned Order Receipts Planned Order Releases 2 3 4 5 40 10 50 4 54 44 44 4 6 MRP Table – determine the Project Available Balance (Inventory) 1 Gross Requirements 3 10 Scheduled receipts (begin) Projected Available Balance (ending) 2 4 5 40 10 50 4 54 44 44 4 Net Requirements 6 Planned Order Receipts Planned Order Releases 6 units short MRP Table – determine the Project Available Balance (Inventory) In week 5, The project available balance (inventory) SMALLER THAN the Gross Requirement. Therefore, Net requirement = the shortage quantity = 4 (inventory) – 10 (Gross requirement) =6 MRP Table – determine the Ending Inventory in period 5. If given a Standard Lot Size, The Plan Order Receipts = the Standard Lot Size (e.g. lot size = 50) Thus in week 5, The Ending Inventory = Plan Order Receipts – Net requirement = 50 – 6 = 44 MRP Table – determine the Ending Inventory in period 5. 1 Gross Requirements 10 Scheduled receipts (begin) Projected Available Balance (ending) 2 3 4 5 40 10 50 4 54 44 44 4 44 Net Requirements 6 Planned Order Receipts Planned Order Releases Ending inventory 50 50 MRP Table – determine the Plan Order Receipts and Plan Order Release REMARKS: The quantity of Plan Order Receipts always equal to Net Requirement if there is no restriction on Standard Lot Size. The quantity of Plan Order Release always similar to Plan Order Receipt. But, the allocation of the order has referred to Lead Time (LT). MRP Table – determine the Plan Order Receipts and Plan Order Release Example: Given a standard lot size = 50 Lead Time (LT) = 1 week Therefore, Plan Order Receipts for week 5 = 50 Plan Order Release = 50 that allocate at week 4 MRP Table – determine the Plan Order Receipt and Plan Order Release. 1 Gross Requirements 10 Scheduled receipts (begin) Projected Available Balance (ending) 2 3 4 40 10 50 4 54 44 44 4 44 Net Requirements 6 Planned Order Receipts Planned Order Releases 5 50 50 Example of MRP Logic and Product Structure Tree Given the product structure tree for “A” and the lead time and demand information below, provide a materials requirements plan that defines the number of units of each component and when they will be needed. Product Structure Tree for Assembly A A B(4) D(2) C(2) E(1) D(3) F(2) Lead Times A 1 day B 2 days C 1 day D 3 days E 4 days F 1 day Demand Day 10 50 A Day 8 20 B (Spares) Day 6 15 D (Spares) First, the number of units of “A” are scheduled backwards to allow for their lead time. So, in the materials requirement plan below, we have to place an order for 50 units of “A” in the 9th week to receive them in the 10th week. Day: A Required Order Placement 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 50 LT = 1 day 10 50 Next, we need to start scheduling the components that make up “A”. In the case of component “B” we need 4 B’s for each A. Since we need 50 A’s, that means 200 B’s. And again, we back the schedule up for the necessary 2 days of lead time. Day: A 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 R e q u ire d 50 R e q u ire d 20 O rd e r P la c e m e n t 20 LT = 2 A B(4) D(2) 10 50 O rd e r P la c e m e n t B 9 D(3) 200 Spares 4x50=200 C(2) E(1) 200 F(2) Finally, repeating the process for all components, we have the final materials requirements plan: Day: A LT=1 B LT=2 C LT=1 D LT=3 E LT=4 F LT=1 1 Required Order Placement Required Order Placement Required Order Placement Required Order Placement Required Order Placement Required Order Placement 2 3 4 5 6 20 7 8 9 20 50 200 10 50 200 100 55 20 400 55 400 20 200 100 300 300 200 200 200 A Part D: Day 6 40 + 15 spares B(4) D(2) C(2) E(1) D(3) F(2) 14 MRP for Level 0 - the BOM structure - Example of the MRP for Level 0 The Master Production Schedule shows we have to make 400 scissors (SC) during the 3rd week, in the 4th week 600, in the 6th week 800, and in the 7th week 300 scissors. This is called as Gross Requirements, GR to the demand of fabrication of the products. . . Example of MRP Explosion 150 0 EPO is the Plan Order Release