From Dose to Effect
advertisement

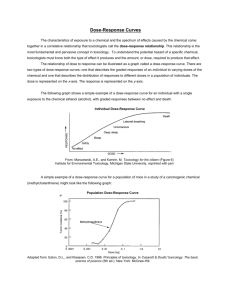
Life History of A Drug DRUG REPONSE RELATIONSHIP M. Imad Damaj, Ph.D. Associate Professor Pharmacology and Toxicology Smith 656A, 828-1676, mdamaj@hsc.vcu.edu Drug-Receptor Interactions DrugDrugReceptor Complex Drug LigandLigandbinding domain Hypothetical Drug in Receptor Site k1 Effector domain k2 Receptor Effect From Dose to Effect Dose Effect site Concentration Pharmacokinetics DOSE EFFECT RELATIONSHIP Effect Pharmacodynamics Dose-Response Curve Type of Dose-Response Curves Graded • Measured in a single biologic unit • Continuous scale (↑ (↑dose → ↑effect) • Relates dose to intensity of effect Quantal • Population studies • AllAll-oror-none pharmacologic effect • Relates dose to frequency of effect Types of Dose-Response Curves: Graded Types of Dose-Response Curves: Quantal Dose related to % of subjects showing a specified “all-or-non” response 100 Relaxation 80 50 100 PDE Inhibition 40 Graded: Dose related to magnitude on a graded scale 20 0 # of Subjects % Control 30 20 10 0 1 10 100 Cumulative % of Subjects 40 60 1 3 1000 5 7 9 11 13 15 80 60 40 20 0 1 Dose 3 5 7 9 11 13 15 Dose Theophylline [µM] Characteristics of A Dose-Response Curve POTENCY • Amount of a drug needed to produce a given effect • Determined mainly by the affinity of the receptor for the drug Variability • Potency affects drug dosage • Relatively unimportant in clinical use of drugs • Are more potent drugs superior therapeutic agents? • Expressed as EC50 (µM) or ED50 (mg/kg) • Graded= 50% of the maximal effect • Quantal = 50% population studied (LD50, TD50) Potency: Graded Responses Potency: Quantal Responses 100 ED90 = 490 mg 80 % of Maximal Effect % 60 Achieving Complete Analgesia 40 EC50 [Drug] ED50 or EC50 = Dose needed to produce 50% of the maximal effect. ED50 = 400 mg 20 0 100 Total Lidocaine Dose (mg) 1000 Ferrante et al. Anesth Analg 82:9182:91-7, 1996 Potency: Quantal Responses EFFICACY • The maximal effect that can be produced by a drug • Determined mainly by the properties of the drug and its receptor-effector system • Important clinical measure • Partial agonist have lower maximal efficacy than full agonists Dose-Response Curves and Efficacy Dose-Response Curves and Partial Agonists Dose-Response Curves and Efficacy Dose-Response Curves Showing Efficacy & Potency SLOPE Slopes of Dose-Response Curves ¾The shape of the curve describe drug binding to receptors ¾Indicator of useful dosage range (steepness of the curve) ¾The slope have more theoretical than practical use VARIABILITY Curves usually represent the mean response of a sample of population Effect may vary considerably “Start Low, Go Slow” Expressed as 95% Confidence limits Confidence Limits of Dose-Response Curves Comparing Dose-Response Curves Value of Dose-Response Curves 100 ⇒ Determining if a drug produces a certain desired effect Drug A 80 ⇒ Determining potency or dose required in producing effect Drug B % of 60 Maximal Effect 40 ⇒ Comparing one drug with others: Drug C 20 1. Efficacy 2. Potency 0 3. Safety Relative Safety of A Drug 1 10 100 [Drug] 100 1000 Therapeutic Index ¾ Dose-response curves help estimating the safety of a drug ¾ Therapeutic Index: TI= LD50/ED50 * LD50= the median lethal dose of a drug in animals * Statement on selectivity of desired effects vs toxic ¾ More general concept: The Median Toxic Dose (TD50) * No drug produce a single effect: example of Codeine * Severity of the disease * Concentration vs dose Examples of TI Certain Safety Factor ¾ Substance safety margin Alcohol 1:4 - 1:10 Aspirin 1:50 Caffeine 1:100 Marijuana 1:400-1:1800 Problems with TI: o o ¾ Comparison of the mid-points of DRC Overlap of DRC Determination of Certain Safety Factor: o Compare the extremes of the DRC Important concept: used to determine a Therapeutic Window o 99% and 1% are not absolutes o Certain Safety Factor = LD1 ED99 Therapeutic and Toxic Effects 100 80 % Responding Drug Interaction & Dose-Response Curves Agonist Therapeutic Toxic Partial agonist 60 Effect 40 20 ED99 0 TD50 TD1 ED50 70 80 90100 Antagonist 200 Inverse Agonist 300 Log [Drug] Dose Agonist Antagonist Receptors, Agonists & Antagonists A) Competitive Antagonists Receptor Receptor Activated Receptor Inactive Receptor Receptors, Agonists & Antagonists Antagonist Effects on Dose-Response Curves A) Non-Competitive Antagonists A) Competitive Antagonists Antagonist Effects on Dose-Response Curves Antagonist Effects on Dose-Response Curves A) Competitive Antagonists C) Non-Competitive Antagonists Acetylcholine (µg/ml) Antagonist Effects on Dose-Response Curves C) Non-Competitive Antagonists Percentage Maximum Contraction 100 Epinephrine Epinephrine + 2 x 10-7 Dibenamine 50 Epinephrine + 4 x 10-7 Dibenamine 0 0.6 4.8 38.4 [Epinephrine] (µM) Non-Competitive Antagonist Effects on Dose-Response Curves Thank you for your attention




![[CLICK HERE AND TYPE TITLE]](http://s3.studylib.net/store/data/006813114_1-9723864d334d1785b63f331f9ef8e2fd-300x300.png)
