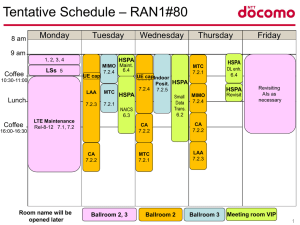
100 mb s × 1,000,000 b 1 mb × 1 B 8 b × 1 mB 1,000,000 B = 12.5
advertisement

Math 202 4G or Not 4G? Prof. Kyhn Sue Beauregard February 25, 2015 1. Convert 100 mb/s (megabits/s) to the following units: a) mB/s: 100 mb 1,000,000 b 1 B 1 mB mB × × × = 12.5 s 1 mb 8 b 1,000,000 B s (The highlighted abbreviations cancel each other out leaving the remaining units 𝑚𝐵 𝑠 .) b) kB/s (kilobytes/s): 12.5 mB 1,000 kB 𝑘𝐵 × = 12,500 s 1 mB 𝑠 c) B/s (bytes/s): 100 mb 1,2500 kB 1,000 B 12,500,000 kB = × = s s 1B s d) b/s (bits/s): 100 mb 12,500,000 B 8 b 100,000,000 b = × = s s 1B s 2. How many times faster is a 4G phone that downloads at 100 Mb/sec compared with the first dial-up modem commonly used a decade ago, which operated at a rate of 56 Kb/sec? (100 Mb×1,000,000)=100,000,000 b⁄s 100 Mb 4G is approximately 1786 𝑏⁄𝑠 times faster than dial-up. 56 Kb = Change into bits (5,600 Kb)×1,000)=56,000 b⁄s ≈ 1786 b⁄s 3. The Generation Partnership Project sets rates for HSPA and HSPA+. Determine to the nearest tenth how many times faster the downlink speed is than the uplink speed for each of the following: HSPA (downlink) HSPA+(downlink) HSPA (uplink) HSPA+ (uplink) 14.4 𝑀𝑏𝑖𝑡𝑠 = 5.76 𝑀𝑏𝑖𝑡𝑠 = 21 Mbits 11.5 Mbits ≈ 2.5𝑀𝑏𝑖𝑡𝑠 𝑓𝑎𝑠𝑡𝑒𝑟 𝑝𝑒𝑟 𝑠𝑒𝑐𝑜𝑛𝑑. ≈ 1.8Mbits faster per second. 4. Speculate on why downlink speed is faster for cell phones than for uplink speed. Downlink speed is faster because people in general downlink more than they uplink! 5. How many times more speed is needed for true 4G capability of 100 Mb/s than what some phone companies were advertising at 14.4 Mb/s? (True 4G) (Companies call 4G) = Mb per second Mb 14.4 per second 100 = 6.9 times more speed 6. A kilobyte might be expected to be 1000 bytes. In reality, computer capacity is based on powers of 2. The number 1000 cannot be written as an integer power of 2; therefore, 1 KB (sometimes written as 1 binary KB, or 1 KiB) is actually 210 bytes, which equals 1024 bytes. The terms megabyte, gigabyte, and terabyte use metric prefixes—that is, powers of 10. Determine what power of 2 is the closest to the following numbers: 𝑎) 220 𝑏) 230 𝑐) 240 7. The percentage error between the decimal (base-10) and the actual binary (base-2) value of 1 KB is (210 − 102 )/210 × 100 the percentage error for the following units: (a) 1 MB (b) 1 GB (c) 1 TB a) 1 MB: 1 million (1 mega − unit) = ( 220 − 106 ) × 100 ≈ 4.6% 220 230 − 109 𝑏) 1 GB: 1 billion (1 giga − unit) = ( ) × 100 ≈ 6.9% 230 240 − 1012 c) 1 TB: 1 trillion (1 tera − unit) = ( ) × 100 ≈ 9.1% 240