Print › Ancient Greek Drama and Theater Vocabulary | Quizlet
advertisement
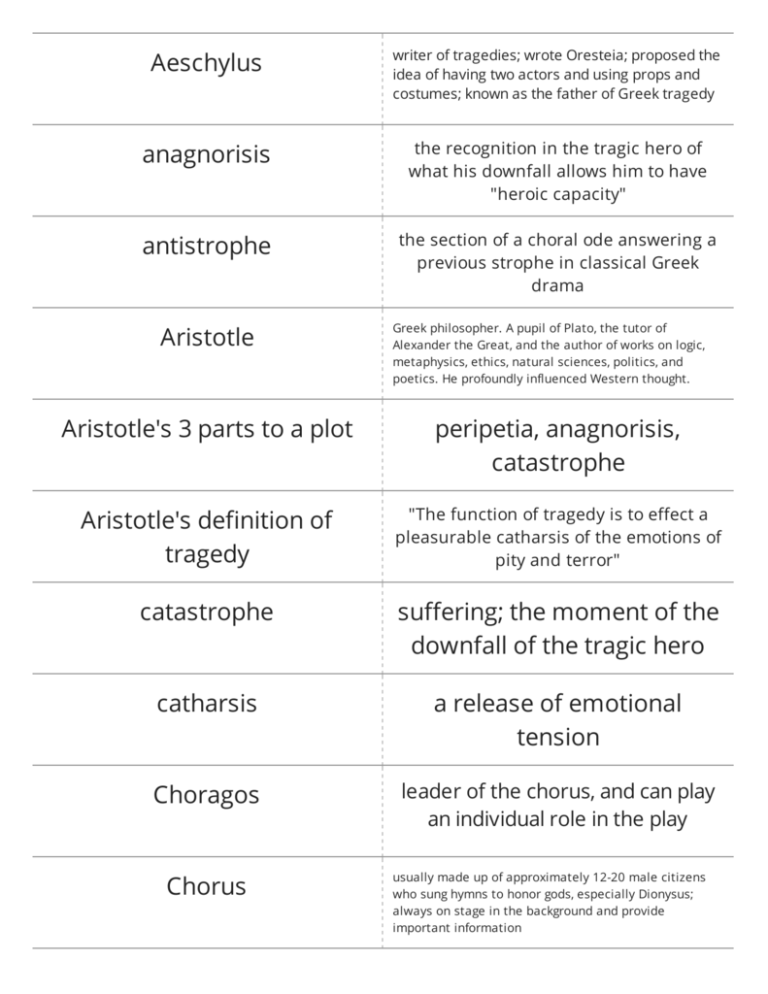
Aeschylus writer of tragedies; wrote Oresteia; proposed the idea of having two actors and using props and costumes; known as the father of Greek tragedy anagnorisis the recognition in the tragic hero of what his downfall allows him to have "heroic capacity" antistrophe the section of a choral ode answering a previous strophe in classical Greek drama Aristotle Greek philosopher. A pupil of Plato, the tutor of Alexander the Great, and the author of works on logic, metaphysics, ethics, natural sciences, politics, and poetics. He profoundly influenced Western thought. Aristotle's 3 parts to a plot peripetia, anagnorisis, catastrophe Aristotle's definition of tragedy "The function of tragedy is to effect a pleasurable catharsis of the emotions of pity and terror" catastrophe suffering; the moment of the downfall of the tragic hero catharsis a release of emotional tension Choragos leader of the chorus, and can play an individual role in the play Chorus usually made up of approximately 12-20 male citizens who sung hymns to honor gods, especially Dionysus; always on stage in the background and provide important information city of Dionysia contained the festival in which playwrights would contribute tragedies and a satyr comedy comedy light and humorous drama with a happy ending, focuses on the fortunes of a community, aims at showing a remaking of society conflict opposition in a work of drama or fiction between characters or forces (especially an opposition that motivates the development of the plot) deus ex machina any active agent who appears unexpectedly to solve and insoluble difficulty dialogue a literary composition in the form of a conversation between two people; more than one person talking back and forth Dionysus god of fertility, wine, music, and drama who created the festival b/c he brought Spring to the Greeks each year drama the creation, development, and resoultion of tension in an audience episode plot develops through action here; central scenes in the play where Oedipus interacts with other characters and the chorus exodus the final choral ode; after the last stasimon, the final action foil characters that reflect each other hamartia the character flaw or error of a tragic hero that leads to his downfall heroic capacity at the end of the tragedy, the hero shows his recognition of his mistakes, acts upon his new wisdom, and gives the audience hope for the future; it inspires the audience to also be heroic hubris overbearing pride or presumption monologue a (usually long) dramatic speech by a single actor; speaking alone; a speech you make to yourself nemesis punishes hubris and cannot be escaped; avenger of the Gods; (Greek mythology) the goddess of divine retribution and vengeance odes moments where the chorus talks to us/ speaks. Designed to represent the audience literal & metaphorical bridge Oedipal complex a pattern described by Freud in which a boy has a desire for his mother and wants to eliminate his father's competition for her attention Oedipus (Greek mythology) a tragic king of Thebes who unknowingly killed his father Laius and married his mother Jocasta orchestra seating on the main floor in a theater parados entrance of the chorus; chanting lyrics to establish the main theme parados first choral ode peripeteia the reversal of fortune peripetia reversal of fortune, a sudden and unexpected change of fortune or reverse of circumstances (especially in a literary work) plot forward motion of the drama from scene to scene prologue the first episode of the play or opening scene, sets forth the meaning of the play, establishes background protagonist main character relief of tension designed to give the reader a break from the main conflict and give a moment of reflection skene color painted scene, background Sophocles respected and award winning Greek playwright; used three actors; wrote Oedipus Rex, Oedipus at Colonus, and Antigone stasimon choral ode sung at the end of each episode by the chorus strophe a series of lines forming a system whose structure is repeated in a following system theater taking drama and putting it on a stage; a publicized act; from the Greek word theatron, which means "seeing place" tragedy a work in which the protagonist, a person of high degree, is engaged in a significant struggle and which ends in ruin or destruction; drama in which the protagonist is overcome by some superior force or circumstance tragic hero a literary character who makes an error of judgment or has a fatal flaw that, combined with fate and external forces, brings on a tragedy tragos Greek word meaning goat; it is the root of the word tragedy





















