MEDICAL SURGICAL NURSING FLASH CARDS
advertisement
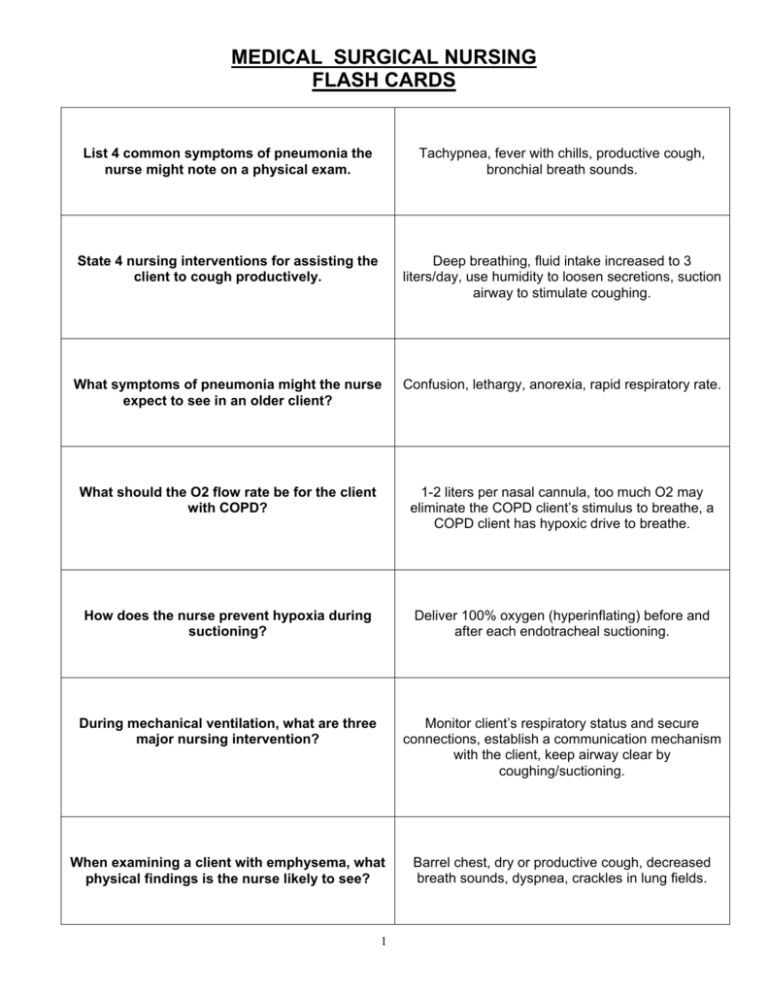
MEDICAL SURGICAL NURSING FLASH CARDS List 4 common symptoms of pneumonia the nurse might note on a physical exam. Tachypnea, fever with chills, productive cough, bronchial breath sounds. State 4 nursing interventions for assisting the client to cough productively. Deep breathing, fluid intake increased to 3 liters/day, use humidity to loosen secretions, suction airway to stimulate coughing. What symptoms of pneumonia might the nurse expect to see in an older client? Confusion, lethargy, anorexia, rapid respiratory rate. What should the O2 flow rate be for the client with COPD? 1-2 liters per nasal cannula, too much O2 may eliminate the COPD client’s stimulus to breathe, a COPD client has hypoxic drive to breathe. How does the nurse prevent hypoxia during suctioning? Deliver 100% oxygen (hyperinflating) before and after each endotracheal suctioning. During mechanical ventilation, what are three major nursing intervention? Monitor client’s respiratory status and secure connections, establish a communication mechanism with the client, keep airway clear by coughing/suctioning. When examining a client with emphysema, what physical findings is the nurse likely to see? Barrel chest, dry or productive cough, decreased breath sounds, dyspnea, crackles in lung fields. 1 What is the most common risk factor associated with lung cancer? Smoking Describe the pre-op nursing care for a client undergoing a laryngectomy. Involve family/client in manipulation of tracheostomy equipment before surgery, plan acceptable communication method, refer to speech pathologist, discuss rehabilitation program. List 5 nursing interventions after chest tube insertion. Maintain a dry occlusive dressing to chest tube site at all times. Check all connections every 4 hours. Make sure bottle III or end of chamber is bubbling. Measure chest tube drainage by marking level on outside of drainage unit. Encourage use of incentive spirometry every 2 hours. What immediate action should the nurse take when a chest tube becomes disconnected from a bottle or a suction apparatus? What should the nurse do if a chest tube is accidentally removed from the client? Place end in container of sterile water. Apply an occlusive dressing and notify physician STAT. What instructions should be given to a client following radiation therapy? Do NOT wash off lines; wear soft cotton garments, avoid use of powders/creams on radiation site. What precautions are required for clients with TB when placed on respiratory isolation? Mask for anyone entering room; private room; client must wear mask if leaving room. List 4 components of teaching for the client with tuberculosis. Cough into tissues and dispose immediately into special bags. Long-term need for daily medication. Good handwashing technique. Report symptoms of deterioration, i.e., blood in secretions. 2 Differentiate between acute renal failure and chronic renal failure. Acute renal failure: often reversible, abrupt deterioration of kidney function. Chronic renal failure: irreversible, slow deterioration of kidney function characterized by increasing BUN and creatinine. Eventually dialysis is required. During the oliguric phase of renal failure, protein should be severely restricted. What is the rationale for this restriction? Toxic metabolites that accumulate in the blood (urea, creatinine) are derived mainly from protein catabolism. Identify 2 nursing interventions for the client on hemodialysis. Do NOT take BP or perform venipunctures on the arm with the A-V shunt, fistula, or graft. Assess access site for thrill or bruit. What is the highest priority nursing diagnosis for clients in any type of renal failure? Alteration in fluid and electrolyte balance. A client in renal failure asks why he is being given antacids. How should the nurse reply? Calcium and aluminum antacids bind phosphates and help to keep phosphates from being absorbed into blood stream thereby preventing rising phosphate levels, and must be taken with meals. List 4 essential elements of a teaching plan for clients with frequent urinary tract infections Fluid intake 3 liters/day; good handwashing; void every 2-3 hours during waking hours; take all prescribed medications; wear cotton undergarments. 3 What are the most important nursing interventions for clients with possible renal calculi? Strain all urine is the MOST IMPORTANT intervention. Other interventions include accurate intake and output documentation and administer analgesics as needed. What discharge instructions should be given to a client who has had urinary calculi? Maintain high fluid intake 3-4 liters per day. Follow-up care (stones tend to recur). Follow prescribed diet based in calculi content. Avoid supine position. Following transurethral resection of the prostate gland (TURP), hematuria should subside by what post-op day? Fourth day After the urinary catheter is removed in the TURP client, what are 3 priority nursing actions? Continued strict I&O; continued observations for hematuria; inform client burning and frequency may last for a week. After kidney surgery, what are the primary assessments the nurse should make? Respiratory status (breathing is guarded because of pain); circulatory status (the kidney is very vascular and excess bleeding can occur); pain assessment; urinary assessment most importantly, assessment of urinary output. 4 How do clients experiencing angina describe that pain? Described as squeezing, heavy, burning, radiates to left arm or shoulder, transient or prolonged. Develop a teaching plan for the client taking nitroglycerin. Take at first sign of anginal pain. Take no more than 3, five minutes apart. Call for emergency attention if no relief in 10 minutes. List the parameters of blood pressure for diagnosing hypertension >140/90. Differentiate between essential and secondary hypertension. Essential has no known cause while secondary hypertension develops in response to an identifiable mechanism. Develop a teaching plan for the client taking antihypertensive medications Explain how and when to take med, reason for med, necessary of compliance, need for follow-up visits while on med, need for certain lab tests, vital sign parameters while initiating therapy. 5 Describe intermittent claudication. Pain related to peripheral vascular disease occurring with exercise and disappearing with rest. Describe the nurse’s discharge instructions to a client with venous peripheral vascular disease. Keep extremities elevated when sitting, rest at first sign of pain, keep extremities warm (but do NOT use heating pad), change position often, avoid crossing legs, wear unrestrictive clothing. What is often the underlying cause of abdominal aortic aneurysm? Atherosclerosis. What lab values should be monitored daily for the client with thrombophlebitis who is undergoing anticoagulant therapy? PTT, PT, Hgb, and Hct, platelets. When do PVCs (premature ventricular contractions) present a grave danger? When they begin to occur more often than once in 10 beats, occur in 2s or 3s, land near the T wave, or take on multiple configurations. 6 Differentiate between the symptoms of leftsided cardiac failure and right-sided cardiac failure . Left-sided failure results in pulmonary congestion due to back-up of circulation in the left ventricle. Right-sided failure results in peripheral congestion due to back-up of circulation in the right ventricle. List 3 symptoms of digitalis toxicity. Dysrhythmias, headache, nausea and vomiting What condition increases the likelihood of digitalis toxicity occurring? When the client is hypokalemic (which is more common when diuretics and digitalis preparations are given together) What life style changes can the client who is at risk for hypertension initiate to reduce the likelihood of becoming hypertensive? Cease cigarette smoking if applicable, control weight, exercise regularly, and maintain a low-fat/low-cholesterol diet. What immediate actions should the nurse implement when a client is having a myocardial infarction? Place the client on immediate strict bedrest to lower oxygen demands of heart, administer oxygen by nasal cannula at 2-5 L/min., take measures to alleviate pain and anxiety (administer prn pain medications and anti-anxiety medications) 7 What symptoms should the nurse expect to find in the client with hypokalemia? Dry mouth and thirst, drowsiness and lethargy, muscle weakness and aches, and tachycardia. Bradycardia is defined as a heart rate below ___ BPM. Tachycardia is defined as a heart rate above ___ BPM. bradycardia 60 bpm; tachycardia 100 bpm What precautions should clients with valve disease take prior to invasive procedures or dental work? Take prophylactic antibiotics. 8 GASTROINTESTINAL SYSTEM: List 4 nursing interventions for the client with a hiatal hernia. Sit up while eating and one hour after eating. Eat small, frequent meals. Eliminate foods that are problematic. List 3 categories of medications used in the treatment of peptic ulcer disease Antacids, H2 receptor-blockers, mucosal healing agents, proton pump inhibitors. List the symptoms of upper and lower gastrointestinal bleeding. Upper GI: melena, hematemesis, tarry stools. Lower GI: bloddy stools, tarry stools. Similar: tarry stools. What bowel sound disruptions occur with an intestinal obstruction? Early mechanical obstruction: high-pitched sounds; late mechanical obstruction: diminished or absent bowel sounds. List 4 nursing interventions for post-op care of the client with a colostomy. Irrigate daily at same time; use warm water for irrigations; wash around stoma with mild soap/water after each colostomy bag change; pouch opening should extend at least 1/8 inch around the stoma. List the common clinical manifestations of jaundice Sclera-icteric (yellow sclera), dark urine, chalky or clay-colored stools. What are the common food intolerances for clients with cholelithiasis? Fried/spicy or fatty foods. 9 List 5 symptoms indicative of colon cancer Rectal bleeding, change in bowel habits, sense of incomplete evacuation, abdominal pain with nausea, weight loss. In a client with cirrhosis, it is imperative to prevent further bleeding and observe for bleeding tendencies. List 6 relevant nursing interventions. Avoid injectons, use small bore needles for IV insertion, maintain pressure for 5 minutes on all venipuncture sites, use electric razor, use soft-bristle toothbrush for mouth care, check stools and emesis for occult blood. What is the main side effect of lactulose, which is used to reduce ammonia levels in clients with cirrhosis? Diarrhea List 4 groups who have a high risk of contracting hepatitis. Homosexual males, IV drug users, recent ear piercing or tattooing, and health care workers. How should the nurse administer pancreatic enzymes? Give with meals or snacks. Powder forms should be mixed with fruit juices 10 ENDOCRINE SYSTEM: What diagnostic test is used to determine thyroid activity? T3 and T4 What condition results from all treatments for hyperthyroidism? Hypothyroidism, requiring thyroid replacement State 3 symptoms of hyperthyroidism and 3 symptoms of hypothyroidism. Hyperthyroidism: weight loss, heat intolerance, diarrhea. Hypothyroidism: fatigue, cold intolerance, weight gain. List 5 important teaching aspects for clients who are beginning corticosteroid therapy. Continue medication until weaning plan is begun by physician, monitor serum potassium, glucose, and sodium frequently; weigh daily, and report gain of >5lbs./wk; monitor BP and pulse closely; teach symptoms of Cushing’s syndrome Describe the physical appearance of clients who are Cushinoid. Moon face, obesity in trunk, buffalo hump in back, muscle atrophy, and thin skin. 11 Which type of diabetic always requires insulin replacement? Type I, Insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus (IDDM) What type of diabetic sometimes requires no medication? Type II, Non-insulin dependent diabetes mellitus (NIDDM) List 5 symptoms of hyperglycemia. Polydipsia, polyuria, polyphagia, weakness, weight loss List 5 symptoms of hypoglycemia. Hunger, lethargy, confusion, tremors or shakes, sweating Name the necessary elements to include in teaching the new diabetic. Teach the underlying pathophysiology of the disease, its management/treatment regime, meal planning, exercise program, insulin administration, sick-day management, symptoms of hyperglycemia (not enough insulin) In less than ten steps, describe the method for drawing up a mixed dose of insulin (regular with NPH). Identify the prescribed dose/type of insulin per physician order; store unopened insulin in refrigerator. If opened, may be kept at room temperature for up to 3 months. Draw up regular insulin FIRST. Rotate injection sites. May reuse syringe by recapping and storing in refrigerator. 12 Identify the peak action time of the following types of insulin: rapid-acting regular insulin, intermediate-acting, long-acting. Rapid-acting regular insulin: 2-4 hrs. Immediateacting: 6-12 hrs. Long-acting: 14-20 hrs. When preparing the diabetic for discharge, the nurse teaches the client the relationship between stress, exercise, bedtime snacking, and glucose balance. State the relationship between each of these. Stress and stress hormones usually increase glucose production and increase insulin need; exercise can increase the chance for an insulin reaction, therefore, the client should always have a sugar snack available when exercising (to treat hypoglycemia); bedtime snacking can prevent insulin reactions while waiting for long-acting insulin to peak. When making rounds at night, the nurse notes that an insulin-dependent client is complaining of a headache, slight nausea, and minimal trembling. The client’s hand is cool and moist. What is the client most likely experiencing? Hypoglycemia/insulin reaction. Identify 5 foot-care interventions that should be taught to the diabetic client. Check feet daily & report any breaks, sores, or blisters to health care provider, wear well-fitting shoes; never go barefoot or wear sandals, never personally remove corns or calluses, cut or file nails straight across; wash daily with mild soap & warm water. 13 MUSCULOSKELETAL SYSTEM: Differentiate between rheumatoid arthritis and degenerative joint disease in terms of joint involvement. Rheumatoid arthritis occurs bilaterally. Degenerative joint disease occurs asymmetrically. Identify the categories of drugs commonly used to treat arthritis. NSAIDs (nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs) of which salicylates are the cornerstones (used when arthritic symptoms are severe). Identify pain relief interventions for clients with arthritis. Warm, moist heat (compresses, baths, showers), diversionary activities (imaging, distraction, selfhypnosis, biofeedback), and medications. What measures should the nurse encourage female clients to take to prevent osteoporosis? Estrogen replacement after menopause, high calcium and vitamin D intake beginning in early adulthood, calcium supplements after menopause, and weightbearing exercise. What are the common side effects of salicylates? GI irritation, tinnitus, thrombocytopenia, mild liver enzyme elevation. What is the priority nursing intervention used with clients taking NSAIDs? Administer or teach client to take drugs with food or milk. List 3 of the most common joints that are Hip, knee, finger. 14 replaced. Describe post-op stump care (after amputation) for the 1st 48 hours. Elevate stump first 24 hours. Do not elevate stump after 48 hours. Keep stump in extended position and turn prone three times a day to prevent flexion contracture. Describe nursing care for the client who is experiencing phantom pain after amputation. Be aware that phantom pain is real and will eventually disappear. Administer pain medication; phantom pain responds to medication. A nurse discovers that a client who is in traction for a long bone fracture has a slight fever, is short of breath, and is restless. What does the client most likely have? Fat embolism, which is characterized by hypoxemia, respiratory distress, irritability, restlessness, fever and petechiae. What are the immediate nursing actions if fat embolization is suspected in a fracture/orthopedic client? Notify physician STAT, draw blood gas results, assist with endotracheal intubation and treatment of respiratory failure. List 3 problems associated with immobility. Venous thrombosis, urinary calculi, skin integrity problems. List 3 nursing interventions for the prevention of thromboembolism in immobilized clients with musculoskeletal problems. Passive range of motion exercises, elastic stockings, and elevation of foot of bed 25 degrees to increase venous return. 15