Made in China. And Indonesia. And Taiwan
advertisement

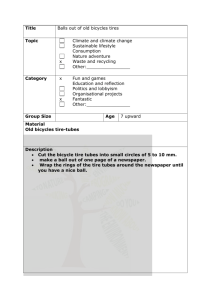
Facts section: imports Made in China. And Indonesia. And Taiwan... Consumer tire imports are up 15.5% C hinese consumer tire imports were down 27.6% last year compared to 2009. Passenger tire imports were hit particularly hard, dropping from 38 million units to 27.4 million units (see Chart 3). It’s easy to pinpoint the reason for the dramatic decreases. A series of tariffs, which went into effect on Sept. 26, 2009, are directly responsible. In the 15 months since they were implemented, consumer tire demand in the United States has outpaced domestic supply. After depleting their inventories in 2009, some domestic tire manufacturers have tried to catch up by returning to 24/7 schedules. They also increased plant capacity by 1%. It wasn’t enough. Because the tariffs — which dropped from 39% to 34% on Sept. 26, 2010 — drastically reduced Chinese produced tires, tire manufacturers and marketers Chart 3 U.S. CONSUMER TIRE IMPORTS FROM CHINA (in millions) Year Units Yr./yr. change 2010 31.1 -27.6% 2009 43.0 -7.5% 2008 46.5 +14.8% 2007 40.5 +50.0% 2006 27.0 +28.0% Source: U.S. government, MTD figures Chart 4 U.S. CONSUMER TIRE IMPORTS BY COUNTRY 2010 Rank/ country 2009 rank % change vs. 2009 1. China 1 -27.6% 2. S. Korea 4 +81.0% 3. Canada 2 +10.0% 4. Japan 3 +34.0% 5. Indonesia 5 +78.0% 6. Thailand 8 +77.5% 7. Mexico 6 +44.5% 8. Brazil 7 +9.6% 9. Taiwan 9 +118.0% 10. Germany 11 +17.0% The top 10 countries account for 92% of all passenger tire imports in the U.S. 32 turned to countries such as South Korea and Indonesia (see Chart 4). The result? Overall consumer tire imports to the U.S. were up 15.5% in 2010 vs. 2009. Still, China remained the number one importer. “Tire production in the U.S. increased 15%, or about 25 million tires, in 2010 vs. 2009, and employment increased slightly, but at a much lower rate than the increase in production,” says Saul Ludwig, a managing director with Northcoast Research Holdings LLC. “So the USW can certainly claim victory. “However, because imports from countries other than China increased even more than those from China decreased, there were other influences that may better explain the increase in production. Inventories (in units) that had been chopped by 30% in 2009 had to be rebuilt, and actual tire demand also increased. In my opinion, those factors trumped the tariffs as the principal reason for the increase in production and employment.” Both the United Steelworkers union and the Alliance for American Manufacturing (of which the USW is a member) say domestic tire production is up and jobs have been created because of the tariffs. The Tire Industry Association believes there is no reliable data to support the claim that the tariff has protected tire manufacturing jobs. Either way, the production of low-cost radial consumer tires in the U.S. has not increased, and may never return. In addition, consumer shipment numbers from China are not anywhere near as low as predicted. The International Trade Commission estimated the tariffs would decrease shipments anywhere from 38.2% to 58.4%. Many opponents of the tariff legislation claimed shipments would drop to almost nothing. ■ Chart 5 U.S. TRUCK TIRE IMPORTS FROM CHINA 440,000 bias (11%) 3.56 million radial (89%) Source: U.S. government, MTD figures MTD January 2011