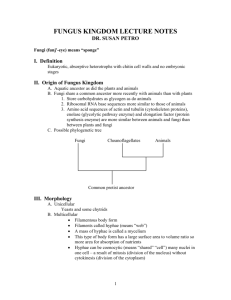
Characteristics of Fungi Hyphae and Mycelium Multi vs Unicellular
advertisement

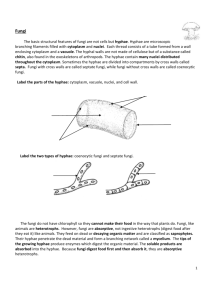
You should be able to answer these questions after reviewing the notes. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. Fungi Characteristics of Fungi Mycology- study of fungi Eukaryotic Heterotrophic decomposers Multicellular except yeast (unicellular) • Lack true roots, stems, & leaves • Reproduce by sexual & asexual spores • Warm, moist environments (shade) List 6 characteristics of fungi. What is the difference between Hyphae and Mycelium? What two traits make yeast different from most fungi (like mushrooms)? What are the three different reproductive structures used by fungi? What is a spore? What is budding and what type of fungus employs budding for reproduction? Define Mycorrhizae. How are fungus used to makes food and how are fungus harmful? Structure Draw this in you notes • • • • Recent molecular evidence suggests fungi are closely related to animals than to the plants. Hyphae and Mycelium Multi vs Unicellular Hypha Mycelium Yeast- unicellular Multicellular- fungi is composed of hyphae No hyphae 1 Classification • Fungi are classified according to structures used during reproduction Fungus Reproduction • Asexual (identical clones) and Sexual Cup Fungi Thread-Like Club Fungi Asexual • • Reproductive cells divide to form spores. Spores –cells with dehydrated cytoplasm & a protective coat capable of developing into new individuals • Budding – Wind, animals, water, & insects spread spores – When spore lands on moist surface, new hyphae form an identical parent. – (a small yeast cell grows from the body of a fungus. Eventually breaks away. Cycle repeats) Sexual • Sexual – Hyphae of two fungi grow together and genetic material is exchanged. New structure grows from joined hyphae How do they Eat? • Absorptive heterotrophs – fungus grow hyphae into a food source. – Digestive juices ooze from the tips of the hyphae. – These juices break down the food. – The hyphae then absorb the dissolved food • Some fungi – break down decaying organisms. – live as parasites on other living organisms (athlete's foot) Ecological Roles • Lichens – a symbiotic relationship between a fungus and a photosynthetic partner, usually algae • The fungi hyphae provide protection and hold moisture while food is provided by the photosynthetic partner. – Can be used as pollution indicators • retain and accumulate nutrients from air and rainfall-heavy metals, sulfur, radioactive elements, NO2, and ozone Do you know what “symbiotic” means? 2 Ecological Roles cont… • Mycorrhizae: Economic Role • Used directly as food… – a symbiotic relationship between a fungus and plant roots. – mushrooms • Over 90% of plants have fungi associated with their roots. • Fungus absorbs and concentrates phosphates for delivery to the plant roots. In return, the fungus receives sugars synthesized by the plant during photosynthesis • …or to make food – – – – Cheeses (Blue Cheese) wine, beer, and whiskey (Yeast) bread rise soy sauce from soy beans • Used to break down materials and recycle wastes and dead organisms • Used to make certain drugs (ex. Penicillin) Harmful Fungus • Food spoilage • Plant disease such as rusts and smuts • Human diseases (ring worm athlete’s foot) • Destroy leather, fabrics, plastics, etc. In athlete’s foot, hyphae actually penetrate the skin and grow through the cells.This is why you can’t scrape the fungus off your foot. 3