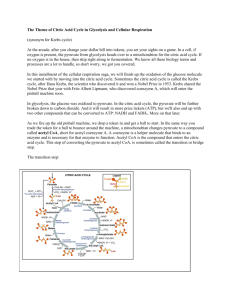
NAD + H-S-CoA CH3 C C O O NADH CH3 O C S CoA O + CO2
advertisement

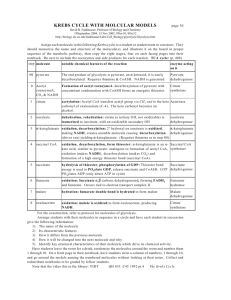
Conversion of Pyurvate Ion to Acetyl CoA Dr. Gergens - Mesa College The decarboxylation and oxidation of pyruvate to produce acetyl CoA: O C CH3 O C NAD+ O- + NADH O CH3 C H-S-CoA pyruvate ion Coenzyme A dehydrogenase complex + S CoA CO2 acetyl coenzyme A Pyruvate is decarboxylated, which liberates a molecule of CO 2 . It is also oxidized, and hydride anion, H:– , that is removed is accepted by NAD+ . Finally, the remaining acetyl group, CH3 CO2 – , is linked to coenzyme A by a thioester bond. The pyruvate dehydrogenase complex that carries out this reaction is actually a cluster of three enzymes and five coenzymes. Acetyl coenzyme A is a central character in cellular metabolism. The principle function of acetyl CoA in energygenerating pathways is to carry the acetyl group to the citric acid cycle (the Krebs Cycle), where it will be used to produce large amounts of ATP energy. Lipids Polysaccharides Proteins monosaccharides Fatty Acids Amino Acids GLYCOLYSIS Acetyl CoA Fatty Acids CITRIC ACID CYCLE Cholesterol Ketone bodies Triglycerides CO2 + H2O ATP Bile salts Phospholipids Steroids NH2 CH3 O C S acetate CH2 CH2 O N C H N CH3 O C CH2 O OH CH3 P H C O- O P O CH2 O- O P O- N O O acetyl coenzyme A N O OH O- N