Homework Problem Answers
advertisement
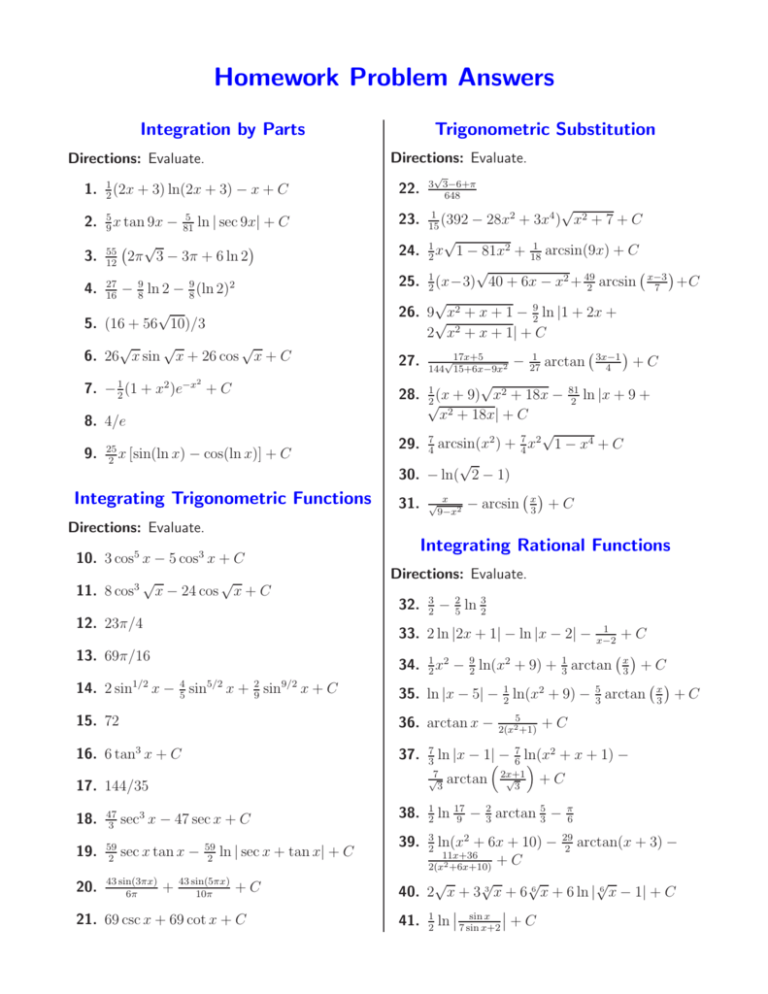
Homework Problem Answers
Trigonometric Substitution
Integration by Parts
Directions: Evaluate.
Directions: Evaluate.
1.
1
(2x
2
+ 3) ln(2x + 3) − x + C
5
x tan 9x
9
5
81
ln | sec 9x| + C
! √
"
55
3. 12
2π 3 − 3π + 6 ln 2
2.
−
27
16
− 98 ln 2 − 98 (ln 2)2
√
5. (16 + 56 10)/3
√
√
√
6. 26 x sin x + 26 cos x + C
4.
22.
√
3 3−6+π
648
23.
1
(392
15
24.
1
x
2
25.
26.
27.
2
7. − 21 (1 + x2 )e−x + C
28.
8. 4/e
9.
25
x [sin(ln x)
2
− cos(ln x)] + C
Integrating Trigonometric Functions
29.
30.
31.
Directions: Evaluate.
10. 3 cos5 x − 5 cos3 x + C
√
√
11. 8 cos3 x − 24 cos x + C
12. 23π/4
√
√
− 28x2 + 3x4 ) x2 + 7 + C
1
arcsin(9x) + C
1 − 81x2 + 18
√
! "
1
2 + 49 arcsin x−3 +C
(x−3)
40
+
6x
−
x
2
2
7
√
9 x2 + x + 1 − 92 ln |1 + 2x +
√
2 x2 + x + 1| + C
! 3x−1 "
1
√17x+5
−
arctan
+C
2
27
4
144 15+6x−9x
√
1
(x + 9) x2 + 18x − 81
ln |x + 9 +
2
2
√
2
x + 18x| + C
√
7 2
7
2
arcsin(x
)
+
x
1 − x4 + C
4
4
√
− ln( 2 − 1)
!x"
√ x
−
arcsin
+C
3
9−x2
Integrating Rational Functions
Directions: Evaluate.
32.
3
2
− 25 ln 32
33. 2 ln |2x + 1| − ln |x − 2| −
13. 69π/16
14. 2 sin1/2 x − 54 sin5/2 x + 29 sin9/2 x + C
+C
! "
34. 21 x2 − 92 ln(x2 + 9) + 31 arctan x3 + C
! "
35. ln |x − 5| − 21 ln(x2 + 9) − 53 arctan x3 + C
5
2(x2 +1)
15. 72
36. arctan x −
16. 6 tan3 x + C
37.
7
2
ln |x − 1|#− 67 ln(x
+
3
$
7
2x+1
√ arctan
√
+C
3
3
38.
1
2
17. 144/35
18.
47
3
sec3 x − 47 sec x + C
19.
59
2
sec x tan x −
20.
43 sin(3πx)
6π
+
59
2
ln | sec x + tan x| + C
43 sin(5πx)
10π
+C
21. 69 csc x + 69 cot x + C
1
x−2
+C
ln 17
− 23 arctan 53 −
9
x + 1) −
π
6
ln(x2 + 6x + 10) − 29
arctan(x + 3) −
2
11x+36
+C
2(x2 +6x+10)
√
√
√
√
40. 2 x + 3 3 x + 6 6 x + 6 ln | 6 x − 1| + C
% sin x %
%+C
41. 21 ln % 7 sin
x+2
39.
3
2
42.
1
1
2x
ln |ex − !9| −
97
" 194 ln(e
9
ex
arctan 4 + C
388
√
√
2
64. 7(ln x − 1) x2 − 16 + 28 arctan x 4−16 + C
+ 16) −
+ a)15/7 − 78 a(x + a)8/7 + C
√
66. 24 arctan x + C
65.
!
"
43. 11 x − 21 ln(x#2 − x$+ 6) − 22x +
√
√
+C
11 23 arctan 2x−1
23
44.
1
4
7
(x
15
Improper Integrals
%
%
%+C
ln % x−2
x+2
Directions: Evaluate.
45. ln |x + 4| + C
# $
1
√
46. 7 arctan √x7 −
67. 2/15
1
2(x2 +7)
+C
68. 1/64
47. 4x2 − 4 ln(x2 + 1) + C
69. 70e−2
48. 7 ln 23 −
70. ln 6
49.
1
6
2
3
71. Diverges
ln 2187
256
72. 7π/8
50. ln(3x2 − 4x + 7) + C
Limits and L’Hôpital’s Rule
Integration Strategies
Directions: Evaluate.
Directions: Evaluate.
51.
51
2
73. 1
tan2 θ + 51 ln | cos θ| + C
74. 0
52. 5eπ/6 − 5e−π/4
# 2 $
√
+1
53. 3 515 arctan 2x√15
+C
75. 1
76. 1/18
54. 4097/45
77. 0
55. −12x + 6x ln(x2 − 25) + 30 ln
56. x − ln(18 + ex ) + C
! x+5 "
x−5
+C
78. e
Infinite Sequences
1 2
θ
2
57. θ tan θ −
+ ln | cos θ| + C
Directions: Determine whether the sequence
!√
"
√
converges or diverges. If it converges, find the
58. 10 9 + ex − 15x + 30 ln ex + 9 − 3 + C
limit.
3
59. − 34 e−x (x3 + 1) + C
%
%√
%
%
60. 71 ln % √6x+49−7
+C
6x+49+7 %
61.
1
2
62. e
ln
−x
63.
#√
2
√4x +1−1
4x2 +1+1
$
79. lim an = 0
n→∞
80. lim an = 1
n→∞
81. Diverges
+C
% x %
%+C
+ ln % eex −1
+1
82. lim an = 0
n→∞
1
2
1
1
ln |x − 7| − 130
ln(x2
65
7
arctan(x/4) + C
260
83. lim an = 1
+ 16) −
n→∞
84. lim an = 0
n→∞
85. Diverges
102. Converges to
cos 1
1 − cos 1
103. Converges to
1 + 2e
e−1
86. lim an = 0
n→∞
87. lim an = 1
n→∞
88. lim an = e12
104. Diverges
89. lim an = ln 3
105. Converges to 3/2
90. Diverges
106. Converges to e − 1
91. lim an = 0
Directions: Determine (a) the values of x for
which the series converges, and (b) the sum of the
series for those values.
n→∞
n→∞
n→∞
92. Converges to 2
Directions: Determine (a) whether the sequence
is increasing, decreasing, or not monotonic; and
(b) whether or not the sequence is bounded.
107. (a) (−4, 4)
(b)
x
4−x
Directions: Answer the questions.
93. (a) not monotonic
94. (a) decreasing
(b) not bounded
(b) bounded
Infinite Series
Directions: Find the sum of the series.
108. No
109. (a) s1 = 1/2, s2 = 5/6, s3 = 23/24, and
(n + 1)! − 1
s4 = 119/120. (b) sn =
(n + 1)!
(c) 1
95. Diverges
Integral Test
96. 5/3
Directions: Determine whether the series
converges or diverges.
97. 40/7
Directions: Determine (a) whether {an } is
∞
110. Converges
&
convergent, and (b) whether
an is convergent.
n=1
111. Converges
98. (a) yes
(b) no
Directions: Determine whether the series
converges or diverges. If it is convergent, find the
sum.
99. Converges to 38/21
112. Converges
113. Converges
114. Converges
Directions: Find the values of p for which the
series is convergent.
100. Diverges
101. Diverges
115. p > 1
Comparison Tests
Directions: Determine whether the series
converges or diverges.
Directions: Approximate the sum of the series
correct to four decimal places.
135. 0.0768
116. Diverges
117. Converges
118. Converges
119. Converges
120. Diverges
121. Converges
122. Diverges
123. Converges
124. Diverges
Alternating Series Test
Ratio and Root Tests
Directions: Determine whether the series is
absolutely convergent, conditionally convergent, or
divergent.
136. Absolutely convergent
137. Divergent
138. Conditionally convergent
139. Absolutely convergent
140. Absolutely convergent
141. Absolutely convergent
142. Absolutely convergent
Directions: Determine whether the series
converges or diverges.
143. Absolutely convergent
125. Converges
145. Conditionally convergent
126. Diverges
146. Absolutely convergent
127. Converges
147. Divergent
128. Diverges
148. Divergent
129. Converges
149. Absolutely convergent
130. Converges
150. Divergent
131. Converges
151. Absolutely convergent
Directions: Show that the series is convergent.
According to the Alternating Series Sum
Estimation Theorem, how many terms of the
series do we need to add in order to find the sum
to the indicated accuracy?
132. 4 terms
144. Divergent
152. Absolutely convergent
153. Divergent
Directions: For each of the following series, is
the Ratio Test conclusive or inconclusive?
(a) Inconclusive
(b) Conclusive (convergent)
133. 4 terms
(c) Conclusive (divergent)
134. 5 terms
(d) Inconclusive
Strategy for Testing Series
(a) Convergent
Directions: Test the series for convergence or
divergence.
(b) Divergent
154. Divergent
(d) Divergent
155. Convergent
(c) Convergent
Representations of Functions as
Power Series
156. Divergent
157. Divergent
Directions: Find a power series representation for
the function and determine the interval of
convergence.
158. Divergent
159. Divergent
174.
160. Divergent
∞
&
(−1)n
n=0
161. Convergent
xn
; i.o.c. (−6, 6)
6n+1
∞
&
9xn
175.
; i.o.c. (−4, 4)
4n+1
n=0
162. Convergent
163. Convergent
176.
164. Convergent
∞
&
(−1)n
n=0
Power Series
Directions: Find the radius of convergence and
interval of convergence of the series.
165. R = 1, I = [−1, 1)
177.
∞
&
x2n+1
; i.o.c. (−7, 7)
49n+1
√
√
(−1)n 5n x2n+1 ; i.o.c. (−1/ 5, 1/ 5)
n=0
Directions: Find a power series representation for
the function and determine the radius of
convergence.
166. R = 1, I = (−1, 1]
167. R = 1, I = [−1, 1]
(a)
168. R = 1, I = (−1, 1)
∞
&
(−1)n (n + 1)
∞
&
(−1)n (n + 1)(n + 2)
n=0
169. R = ∞, I = (−∞, ∞]
(b)
xn
;R=4
4n+2
n=0
170. R = 11, I = (−11, 11]
(c)
171. R = 1, I = [9, 11]
∞
&
n=2
n
(−1) n(n − 1)
xn
22n+3
172. R = 1, I = [−1, 1]
(a)
173. R = 7, I = (−7, 7)
Directions: Suppose that
∞
&
n=0
∞
&
(−1)n−1 xn
n=1
cn xn converges
when x = −4 and diverges when x = 6. What can
be said about the convergence or divergence of
the following series?
n
;R=1
(b)
∞
&
(−1)n xn
(c)
∞
&
(−1)n−1 x2n
n=2
n=1
n−1
n
;R=1
;R=1
xn
22n+7
;R=4
;R=4
∞
&
xn
178. ln 2 −
;R=2
n2n
n=1
179.
∞
&
n−2
n=3
180.
9n−1
189. f (x) =
32n+1 (2n + 1)!
n=0
n
190. f (x) =
x ;R=9
∞
&
n=1
;R=∞
xn
;R=∞
(n − 1)!
191. f (x) =
−7+8(x−2)+18(x−2)2 +8(x−2)3 +(x−2)4
∞
&
(−1)n x2n+1
;R=8
2n+1 (2n + 1)
8
n=0
Directions: Evaluate the indefinite integral as a
power series and determine the radius of
convergence.
192. f (x) =
∞
&
tn
;R=1
181. C −
n2
n=1
∞
&
−6(x + 4)n
4n+1
n=0
193. f (x) =
∞
&
5(−1)n+1 (x − 9π)2n
(2n)!
n=0
∞
182. C +
∞
&
(−1)n+1 x2n−1
;R=1
(2n
+
1)(2n
−
1)
n=1
183. C +
∞
&
n=0
∞
&
(−1)n π 2n+1 x2n+1
(−1)n x4n+3
;R=1
(2n + 1)(4n + 3)
1 & (−1)n (2n)!(x − 16)n
194. f (x) = +
4 n=1
(n!)2 43n+1
195. 0.83527
196. 0.03490
197. f (x) = C +
Directions: Use a power series to approximate
the definite integral to six decimal places.
∞
&
9xn
13n · n!
∞
&
(−1)n x4n+3
(4n + 3)(2n + 1)
n=1
198. f (x) = C +
n=0
184. 0.001111
199. 0.460
185. 0.299969
200. 125/3
Directions: Use the formula
ln(1 − x) = −
∞
&
xn
n=1
n
Curves Defined by Parametric
Equations
to compute the indicated value correct to five
decimal places.
Directions: Eliminate the parameter to find a
Cartesian equation of the curve.
186. 0.08618
201. y = (x + 6)2 , x > −6
Taylor and Maclaurin Series
Directions: Answer the questions.
187. f (x) =
∞
&
(−1)n (x − 2)n
n=0
188. f (x) =
4n (n + 3)
∞
&
(−1)n−1 5n xn
n=1
n
;R=4
; R = 1/5
202. y = ex/2 , x ≥ ln 36
Directions: Determine what curve is represented
by the parametric equations. Be sure to indicate
direction as well as any starting or ending points.
203. It’s the circle x2 + y 2 = 4 traced out
exactly once in the counterclockwise
direction beginning and ending at the
point (2, 0).
204. It’s the parabola y = x2 with −1 ≤ x ≤ 1;
the point (x, y) moves back and forth
infinitely many times along the parabola
from (−1, 1) to (1, 1).
212.
Calculus with Parametric Curves
Directions: Answer the questions.
205. y = x − 1
206. y = 2x − 1
213.
dy
3t + 2
d2 y
3
=
and 2 =
dx
2
dx
4t
(b) (0, ∞)
(a)
(a) (1, −54) and (1, 54)
(b) (10, 0)
√
√
(a) (−3/
2,
−1),
(−3/
√
√2, 1),
(3/ 2, −1), and (3/ 2, 1)
214.
(b) (−3, 0) and (3, 0)
207. y = −2x/5 and y = 2x/5
' 5√
1 √
208.
1 + 4t2 dt = [10 101 + ln(10 +
4
√3
√
√
101) − 6 37 − ln(6 + 37)]
√
209. 20 10 − 2
210. e3 − e−3
215.
Polar Coordinates
Directions: Answer the questions.
√
(a) (2 2, 7π/4)
√
(b) (−2 2, 3π/4)
(c) (2, π/3)
(d) (−2, 4π/3)
211. x2 + (y − 3)2 = 9; the circle with center
(0, 3) and radius 3
Directions: Sketch the graph of the given polar
equation.
216.
217.
222.
223.
218.
Directions: Answer the questions.
219.
√
224. − 3
(a) π/4, 3π/4
(b) 0, π/2
(a) 0, 2π/3, 4π/3
(b) π/3, π, 5π/3
Areas in Polar Coordinates
220.
Directions: Answer the questions.
225. 15π 2 /16
226. 41π/4
227. 507π/2
228. 11
229. 19π/2
221.
230. 9π
231. π/16
√
18π − 27 3
232.
2
√
4π + 6 3
233.
3
234. 9π + 72
√
25(3 3 − π)
235.
3
√
236. 8π + 6 3
π−2
8
√
2− 2
238.
2
237.
Volumes by Cylindrical Shells
Directions: Use the method of cylindrical shells
to find the volume of the solid obtained by
rotating the region bounded by the given curves
about the specified axis.
250. 4π/e
251. 16π 3 ln(4π) − 8π 3 +
√
10π + 9 3
239.
12
252. 64π/3
240. (3/2, π/6) and (3/2, 5π/6)
254. 8π/3
241. (5, π/12), (5, 5π/12), (−5, 7π/12),
(−5, 11π/12), (5, 13π/12), (5, 17π/12),
(−5, 19π/12), and (−5, 23π/12)
255. 256π/15
242. π
257. 23π/10
253. 50π
256. 27π/2
Work
Areas and Volumes
Directions: Find the volume of the solid obtained 258. 40000 ft-lb
by rotating the region bounded by the given
259. 0.96 J
curves about the specified axis.
(a) 7.55 J
243. 49π 2 /4
(b) 120 ft-lb
)
(
√
5
244. 9π 2 2 −
260. 3.83 × 108 J
2
245. 8π
261. 5.37 × 105 ft-lb
246. 50π/9
262. 1058400 J
247. π/6
Directions: Answer the questions.
(a) 750 ft-lb
(b) 562.5 ft-lb
263. 8 cm
248.
1
πh(R2 + Rr + r 2 )
3
(a) 436/3
(b) rectangular solid; V = b2 h
1
(c) square pyramid; V = b2 h
3
249.
e2π − 13
4
π
2
264. 16 ft-lb