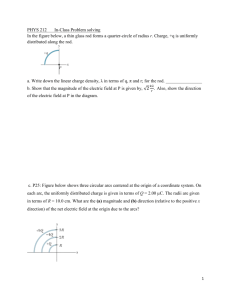
Obtaining a Charge
advertisement
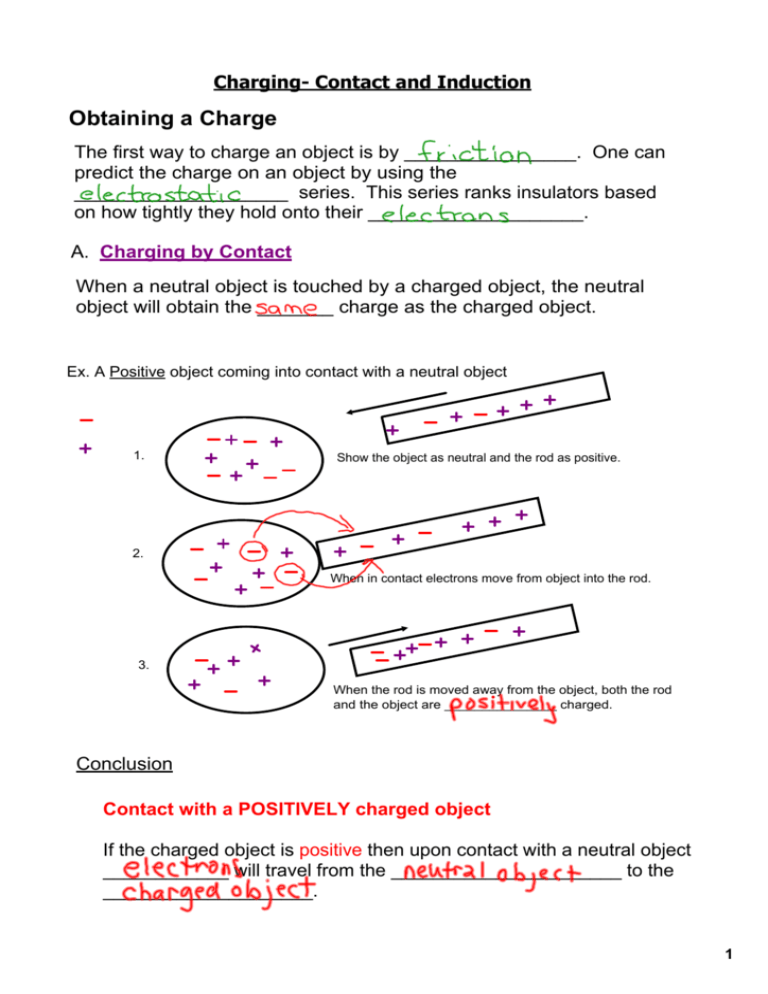
Charging­ Contact and Induction Obtaining a Charge The first way to charge an object is by ________________. One can predict the charge on an object by using the ____________________ series. This series ranks insulators based on how tightly they hold onto their ____________________. A. Charging by Contact When a neutral object is touched by a charged object, the neutral object will obtain the _______ charge as the charged object. Ex. A Positive object coming into contact with a neutral object 1. Show the object as neutral and the rod as positive. 2. When in contact electrons move from object into the rod. 3. When the rod is moved away from the object, both the rod and the object are _______________ charged. Conclusion Contact with a POSITIVELY charged object If the charged object is positive then upon contact with a neutral object ____________ will travel from the ______________________ to the ____________________. 1 Ex. A Negative object coming into contact with a neutral object 1. Show the object as neutral and the rod as negative. 2. When in contact electrons move from _______ into the _________________. 3. When the rod moves away the object, both the rod and the oval are ______________charged. Conclusion Contact with a NEGATIVELY charged object If the charged object is negative then upon contact with a neutral object ____________ will travel from the ____________________ to the ____________________. B. Induction As you bring a charged object near a neutral object, depending upon the freedom of the electrons, often a ________________ _______________ is created. Although the neutral object is still neutral, it has regions at opposite ends that can be considered ____________ and _______________. Ex. A negatively charged rod is brought close (but does not make contact) to the neutral object 1. Show the oval as neutral and the rod as positive. 2. When the rod comes close to the oval the electrons move _____________ rod. http://phet.colorado.edu/en/simulation/balloons 2 Has the charge on the oval object really changed? Is the object really charged? Conclusion : Charging Through Induction : C. Charging through Grounding With this temporary realignment of charge, the neutral object can be charged by ___________ some other neutral object such as the earth (ground). negative rod moves close to a neutral oval with a ground attached positive rod moves close to a neutral oval with a ground attached Note ­ the earth is considered a huge conductor ­ a place that can give or take millions upon millions of electrons. Charge Transfer Now that an object is charged, we must be concerned with how this charge behaves. A. Charge distribution is usually uniform Show each object as neutral with uniform charge distribution 3 B. Arcing or Lightining ­ the jumping of a charge build up Three conditions are involved in the transfer of charge • Charge difference ­ depends upon the properties of the objects and the size of the friction which created the imbalance • Distance between opposite charges ­ one charged object will induce a charge separation in any conductor • Conductivity of the medium ­ reduces the significance of the other 2. Example ­ lightning Points to note • Current Electricity adapts these 3 factors to do work on various appliances. The charge difference is created by the _____________________ and the distance and medium is controlled by the _________________ which allows for an easy transfer • The dangerous part of static electricity is the transfer, not the build up. When playing with the van der Graff, students feel the "shock" of the transfer. A bird landing on a charged wire feels nothing unless a transfer occurs. Most common examples of dangerous transfers occur when the charged object is given a path to the ground. If you become part of the path, you could be seriously injured. Homework­ 1) Read grounding on page 311 2) Use pg 311 to answer the following questions: A) Describe what grounding is B) Why is the Earth a good ground? C) What is the symbol for a ground? 3)Read pg 313­318­ answer questions #1­3 on pg 318 4