Mitosis & Meiosis Quiz Study Guide Vocabulary List: The vocabulary
advertisement

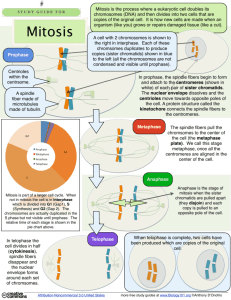
Mitosis & Meiosis Quiz Study Guide Vocabulary List: The vocabulary presented here is specific to your quiz. Obviously we studied more terms than this throughout our lectures and labs… Mitosis Prophase Crossing Over Anaphase 1 Kinetochore Gamete Checkpoint Reduction Division 46 Meiosis Prophase 1 Metaphase Anaphase 2 Chromosome MPF Polar Body Somatic Cell 23 Meiosis 1 Prophase 2 Metaphase 1 Telophase Chromatid G1 Homologous Germ Cell Binary Fission Meiosis 2 Synapsis Metaphase 2 Telophase 1 Diploid S Tetrad Sexual Asexual Independent Assortment Anaphase Telophase 2 Haploid G2 Nucleus Circular Chromosome Questions to think about for this quiz… 1. What is a prokaryote and how does it reproduce? 2. What is a eukaryote and how does it reproduce? 3. What happens during each part of the cell cycle? 4. Which checkpoint during the cell cycle gives the go-ahead for cell division? 5. What are the comparative lengths of each major portion of the cell cycle? 6. What is independent assortment and what does it mean for a cell in meiosis? 7. How do mitosis, meiosis 1, and meiosis 2 differ in how the chromosomes are arranged? 8. Be able to generally describe what occurs during prophase, prometaphase, metaphase, anaphase & telophase. 9. When do synapsis and crossing over occur? How are they beneficial? 10. What is a polar body? How is the production of polar bodies beneficial? Other questions to further your course of study… Match each term with its description. a. cytoplasm apportioned between the two daughter cells b. final phase of mitosis; daughter nuclei reform c. two sister chromatids are joined here d. chromosomes condense and mitotic spindle begins to form e. chromosomes line up at spindle equator f. sister chromatids separate, move to opposite spindle poles now g. about 25 nm in diameter; form mitotic spindle h. half of a chromosome in prophase i. in pairs in some eukaryotic cells; move to poles during spindle formation ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. centriole centromere chromatid cytokinesis metaphase microtubules prophase telophase anaphase Eukaryotic Cell Cycle Answer the following questions in reference to the eukaryotic cell cycle. Each question has only one BEST answer. a. G2 b. mitosis c. S d. G1 e. cytokinesis 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. 19. Period when DNA is duplicated Period when interphase ends in the parent cell Event that forms two daughter cytoplasmic masses Period of cell growth before DNA duplication Period after DNA is duplicated Period of nuclear division Period when interphase begins in a daughter cell\ Period commonly followed by cytokinesis The period in which metaphase occurs The period prior to mitosis Stages of Mitosis Plus Interphase The stages of mitosis plus interphase are listed under a-e below. Answer the following questions with reference to these phases. a. interphase b. prophase c. metaphase d. anaphase e. telophase 20. During this stage, homologous pairs of chromosomes are lined up on the equatorial plate. 21. Chromosomes replicate during this phase. 22. Genes replicate during this phase. 23. DNA replicates during this phase. 24. Condensation and shortening of chromosomes occurs during this phase. 25. Spindle fibers first appear during this stage. 26. During this phase, the centromeres break apart as the separated sister chromatids begin to move to opposite poles. 27. The microtubular spindle develops during this phase. 28. Sister chromatids joined at their centromeres are attached to spindle fibers during this phase. 29. Cytokinesis occurs as this phase of mitosis proceeds. 30. New daughter nuclear membranes form during this phase. Stages of Meiosis Some of the stages of meiosis are listed under a-e below. Answer the following questions with reference to these phases of meiosis. a. prophase I b. prophase II c. metaphase II d. anaphase I e. telophase I 38. The formation of tetrads by synapsis occurs during this stage. 39. Recombination via crossing over occurs during this stage. 40. By the end of this phase, the number of homologous chromosomes is reduced in half. 41. During this stage, the sister chromatids begin to separate. 42. Following this phase, each individual cell is haploid. 43. Chiasmata are present during this stage. 44. During this phase, the centromeres separate. 45. New genetic combinations, upon which natural selection can act, is present after this stage. Other 46. Four of the five answers listed below are stages of actual nuclear division. Select the exception. a. Anaphase b. Prophase c. Interphase d. Telophase e. Metaphase 47. a. b. c. d. e. Four of the five answers listed below are related by a common phase of mitosis. Select the exception. beginning of microtubule assembly outside the nucleus division of centromere disappearance of nucleolus disappearance of nuclear membrane shortening and condensation of chromosomes make them more visible 48. a. b. c. d. e. G1 M R S G2 49. a. b. c. d. e. Four of the five answers listed below are related by a common phase of mitosis. Select the exception. chromosomes decondense spindle microtubules disappear nucleolus reappears chromosomes separate nuclear envelope re-forms Four of the five answers listed below are periods of the same cycle. Select the exception. 50. Four of the five answers listed below are events occurring during mitosis. Select the exception. a. chromosome replication b. division of centromere c. lining up of chromosomes at the cellular equator d. e. attachment of spindle microtubules to centromeres migration of chromosomes to opposite ends of the cell 51. a. b. c. d. e. Four of the five answers listed below assist in chromosome movement. Select the exception. centromere spindle microtubules kinetochores centriole nuclear envelope 52. a. b. c. d. e. Four of the five answers listed below are related by a common phase of mitosis. Select the exception. chromosomes align at the spindle equator sister chromatids become individual chromosomes centromeres divide chromosomes move apart spindle microtubules shorten, pulling chromosomes toward the poles 53. a. b. c. d. e. Four of the five answers listed below are related by a common division association. Select the exception. mitochondria chromosomes ribosomes plastids microbodies 54. a. b. c. d. e. Four of the five answers listed below concern cells with two chromosome sets. Select the exception. zygote somatic cells gamete diploid two full chromosome sets 55. a. b. c. d. e. Four of the five answers listed below are related to pairing of chromosomes. Select the exception. synapsis crossing over exchange of genes pairing of homologues interkinesis 56. a. b. c. d. e. Four of the five answers listed below are related to the process of synapsis. Select the exception. genetic recombination increase in variability exchange of genes identical daughter cells chiasmata 57. a. b. c. d. Four of the five answers listed below are characteristic of meiosis. Select the exception. involves two divisions reduces the number of chromosomes results in producing genetically identical cells produces haploid cells e. involves synapsis 58. a. b. c. d. e. Four of the five answers listed below are terms describing haploid cells. Select the exception. Ovum primary spermatocyte Spermatid polar body secondary spermatocyte 59. a. b. c. d. e. Four of the five answers listed below are haploid. Select the exception. Zygote Meiospore Egg Sperm Gametophyte ANSWERS MATCHING 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. I C H A E G D B F SHORT ANSWER 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. 19. 20. 21. 22. 23. 24. 25. c a e d a b d b b a c a a a b b 26. 27. d b 28. 29. 30. c e c 38. 39. 40. 41. 42. 43. 44. 45. a a d c e a c a OTHER 46. 47. 48. 49. 50. 51. 52. 53. 54. 55. 56. 57. 58. 59. C B C D A E A B C E D C B A