Physical Fitness Notes
advertisement

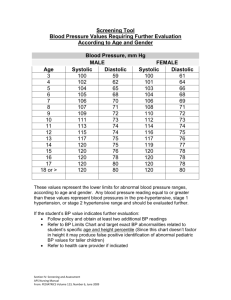
Physical Fitness Unit Physical activity- any form of movement that causes your body to use energy. (Includes all kinds of activities that you do on a daily basis, such as walking to school, cleaning your room, or playing sports with your friends) Physical fitness- The ability to carry out daily tasks easily and have enough reserve energy to respond to unexpected demands. Exercise- Purposeful physical activity that is planned, structured, and repetitive, and that improves or maintains physical fitness. Mental and emotional benefits: -Stress relief -Mood enhancement -Better Sleep -Improved self-esteem How could being physically active affect your social health?? -Can make new friends and spend time with friends you already have -Can use abilities to work with others as a team -Can help you learn skills that will improve your relationships like teamwork and sportsmanship Sedentary- Involving little physical activity Health Problems that may result from being sedentary include: -unhealthful weight gain and obesity -cardiovascular disease, such as heart attack and stroke -certain types of cancer -asthma and other breathing problems -osteoporosis, a condition in which the bones become porous and fragile, making them much more likely to break -osteoarthritis, a condition caused by the breakdown of cartilage and bone in the body’s joints -psychological problems such as stress, anxiety, and depression Cardiorespiratory endurance- the ability of your heart, lungs, and blood vessels to send fuel and oxygen to your tissues during long periods of moderate to vigorous activity. Muscular strength- The amount of force your muscles can exert. Muscualr endurance- the ability of your muscles to perform physical tasks over a period of time without tiring. Flexibility- The ability to move your body parts trough their full range of motion. Aerobic exercise- Includes all rhythmic activities that use large muscle groups for an extended period of time. Anaerobic exercise- Involves intense, short bursts of activity in which the muscles work so hard that they produce energy without using oxygen. Three types of resistance exercises: 1. Isometric exercises- Joint angle and muscle length do not change. 2. Isotonic exercises- Tension is unchanged and the muscle’s length changes. 3. Isokinetic exercises- Exercise performed using a machine. Machine stays at a constant speed. Building a fitness plan: Effective fitness plans focus on four principles: 1. Specificity- choosing the right types of activities to improve a given element of fitness. 2. Overload- exercising at a level that’s beyond your regular daily activities. 3. Progression- gradually increasing the demands on your body. 4. Regularity-working out on a regular basis. Stages of a workout: Warm-up- gentle cardiovascular activity that prepares the muscles for work. 2 Types of Stretching: 1. Static- holding a position/stretch for 10-15 seconds. 2. Dynamic- Functional based exercises that use sportspecific movements. Ex) butt kicks, high knees, carioca Workout- The part of an exercise session when you are exercising at your highest peak. (F.I.T.T) formula F: Frequency of workouts I: Intensity of workouts T: Type of activity T: Time (duration) of workouts Cool-down- low-level activity that prepares your body to return to a resting state. Resting heart rate- The number of times your heart beats per minute when you are not active. Target Heart Rate- The heart rate at which exercise is recommended. Step One: 220- Age = Maximum Heart Rate (Max HR) Step Two: Max HR X .60= a Max HRX .80= b Step Three: Target Heart Rate Range= a to b Example: 16 year old 220-16= 204 204X .60=122 204X .80= 163 Target Heart Rate Range for a 16 year old= 122-163 bpm Blood Pressure: The pressure the blood exerts against the inner walls of the blood vessels. 1. Systolic Pressure- the pressure in the arteries at the peak of ventricular contraction. (The top number of the blood pressure reading). 2. Diastolic Pressure- the pressure when the ventricles are relaxed. (The bottom number of the blood pressure reading). Steps to Taking Blood Pressure Reading: 1. Locate the brachial artery 2. Place cuff above elbow (same level as heart). Rest arm 3. Place stethoscope over brachial artery 4. Close the air release valve attached to the inflation bulb and inflate the cuff until it reaches 20-30 mmHg ABOVE known systolic reading (200 mmHg is probably good). 5. SLOWLY open the air release valve 6. The first sound heard is the SYSTOLIC BP reading 7. Continue to release the air, the last sound you hear is the DIASTOLIC BP reading -For teenage boys, a systolic reading over 130 or a diastolic reading over 80 generally indicates high blood pressure. -For teenage girls, a systolic reading over 125 or a diastolic reading over 80 generally indicated a high blood pressure. Hypertension- High blood pressure. 140/90 mmHg or higher Hypotension- Low blood pressure, a systolic blood pressure below 100 mmHg Injuries and prevention: Hot-Weather Risks- Overexertion, heat exhaustion, heatstroke Cold-Weather Risks- Frostbite Minor Injuries: -Blisters -Muscle cramps -Strains -Sprains -Tendonitis Major Injuries: -Fractures -Dislocations -Concussion Ways to treat minor injuries: (PRICE) P-protect the affected area with a bandage or splint to prevent further injury R-Rest the muscle or joint for at least a day I- ice the affected area for 10 to 15 minutes at a time, three times a day C-Compress the affected area to reduce swelling E- Elevate the injured area to keep the swelling down. (Raised above level of your heart) Skeletal System: Cartilage- Strong, flexible connective tissue that can act as a cushion between two bones to reduce friction. Ligament- Connective tissue that attaches one bone to another. Tendon- Fibrous cord that attaches muscle to the bone. Osteoporosis- Condition in which there is a progressive loss of bone tissue. Muscular System: Smooth muscles- Muscles that act on the lining of the body’s passageways and hollow internal organs. Involuntary. Skeletal muscles- Muscles attached to bone that cause body movements. Voluntary. Flexor- Muscle that closes a joint. Extensor- Muscle that opens a joint. Cardiac Muscle- Type of muscle that forms the wall of the heart.