Financial Accounts Profit Prior to Incorporation
advertisement
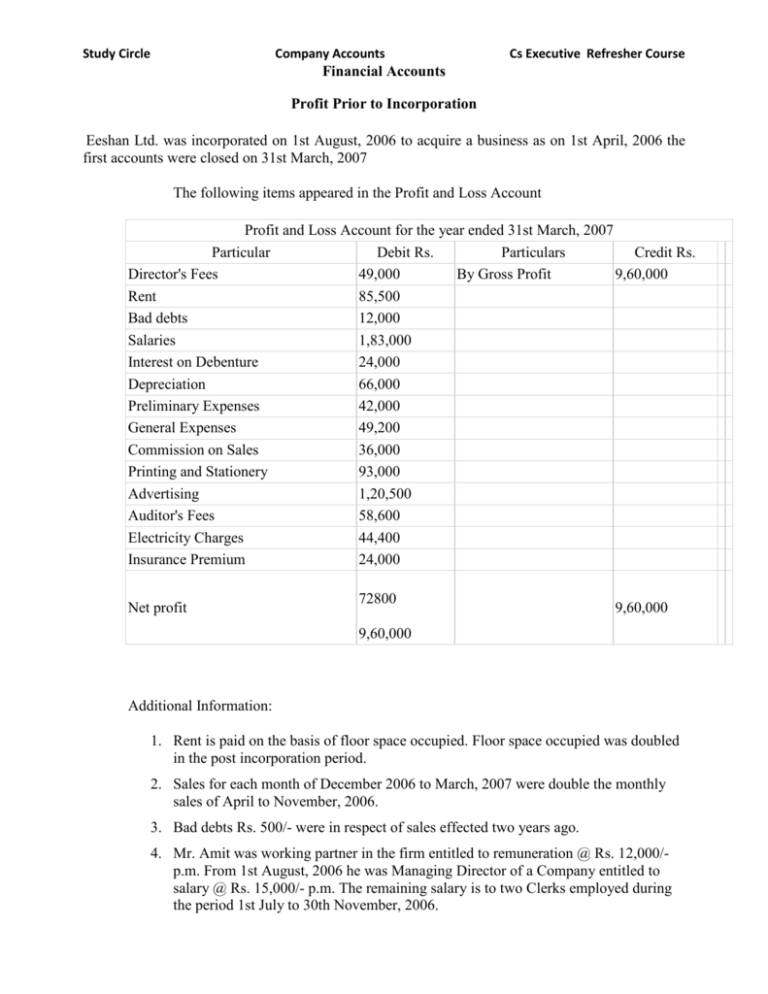
Study Circle
Company Accounts
Cs Executive Refresher Course
Financial Accounts
Profit Prior to Incorporation
Eeshan Ltd. was incorporated on 1st August, 2006 to acquire a business as on 1st April, 2006 the
first accounts were closed on 31st March, 2007
The following items appeared in the Profit and Loss Account
Profit and Loss Account for the year ended 31st March, 2007
Particular
Debit Rs.
Particulars
Credit Rs.
Director's Fees
49,000
By Gross Profit
9,60,000
Rent
85,500
Bad debts
12,000
Salaries
1,83,000
Interest on Debenture
24,000
Depreciation
66,000
Preliminary Expenses
42,000
General Expenses
49,200
Commission on Sales
36,000
Printing and Stationery
93,000
Advertising
1,20,500
Auditor's Fees
58,600
Electricity Charges
44,400
Insurance Premium
24,000
Net profit
72800
9,60,000
9,60,000
Additional Information:
1. Rent is paid on the basis of floor space occupied. Floor space occupied was doubled
in the post incorporation period.
2. Sales for each month of December 2006 to March, 2007 were double the monthly
sales of April to November, 2006.
3. Bad debts Rs. 500/- were in respect of sales effected two years ago.
4. Mr. Amit was working partner in the firm entitled to remuneration @ Rs. 12,000/p.m. From 1st August, 2006 he was Managing Director of a Company entitled to
salary @ Rs. 15,000/- p.m. The remaining salary is to two Clerks employed during
the period 1st July to 30th November, 2006.
Study Circle
Company Accounts
Cs Executive Refresher Course
You are required to prepare profit and loss account for the year ended 31st March, 2007 and
show 'Pre' and 'Post' incorporation period profit or loss.
Underwriting of Shares
Emeses Ltd. Issued 40,000 shares which were underwritten as:
P : 24,000 shares Q : 10,000 shares and R : 6,000 shares. The underwriters made applications for
firm underwriting as under:
P: 3,200 shares; Q: 1,200 shares; and R: 4,000 shares. The total subscriptions excluding firm
underwriting (including marked applications) were 20,000 shares.
The marked applications were – P: 4,000 share; Q: 8,000 shares; and R: 2,000 shares.
Prepare a statement showing the net liability of underwriters.
Study Circle
Company Accounts
Cs Executive Refresher Course
Valuation of Shares & Intangible Assets
Following is the summarised Balance Sheet of M/s. Vijay Engineers as on 30.9.2006.
LIABILITIES
Rs.
ASSETS
Rs.
Share Capital
30,000 Equity shares of
Plant
Rs. 10 each
3,00,000
Reserve and surplus
50,000
Property
1,20,000
Stock
3,10,000
General
1,20,000
Debtors
2,03,000
Capital
1,40,000
Bank
1,17,000
Profit & Loss A/c
1,20,000
Cash
1,700
Total
8,01,700
2,80,000
Current Liabilities &
Provision
Creditors
93,700
I.T. payable
11,500
Proposed Dividend
34,000
Provision for Taxes
82,500
2,21,700
Total
8,01,700
Net Profit before taxation for three years ended 30th September, 2004 Rs. 1,38,000 30th Sept.,
2005, Rs. 1,83,000; and 30th September, 2006, Rs. 1,98,000; freehold property was valued at Rs.
1,60,000. Average yield in this type of business is 10% capital employed. You are required to find
out the value of each equity share on :
(i)
Net Assets basis
(ii)
Yield basis.
(iii)
Fair value basis
The company has a practice of transferring 20% of its yearly profit after tax to General
reserve.
Assume tax at 50%.
Study Circle
Company Accounts
Cs Executive Refresher Course
Valuation of shares
(i)
Intrinsic value method
Rs.
All Assets (AV) including Goodwill,
Investments but excluding Fictitious
Assets
Less: All Outside Liabilities (AV)
Net assets Available for Shareholders
Less: Preference Shareholders Claim
a) Preference Share Capital
b) Arrears of Preference Dividend
Net Assets available for ESH’s
Intrinsic value of shares (each share) = Net Assets
No. of shares
Yield value method
Total profit of last three year
Add/Less: Any other Adjustment
Average profit before Tax
Less: Tax @ ----%
Average Profit After Tax
Less: Transfer to reserve @ __%
Rs.
Study Circle
Company Accounts
Cs Executive Refresher Course
Less: Current Year Preference Dividend
Earnings Available for ESH
ERR =
EAESH
X 100
Equity Share Capital
Yield Value of each share=
ERR / N.R.R X paid up value of each shares
(iii)Fair value method
Fair value of each shares = Intrinsic value + Yield value
2
Study Circle
Company Accounts
Cs Executive Refresher Course
ISSUE OF SHARES
Journal Entries
1) For Equity Share Application Money Received
Cash/Bank A/c
Dr
To Equity Share Application A/c
2) For Equity Share Application Money Transferred to Share Capital
Equity Share Application A/c
Dr
To Equity Share Capital A/c
3) For Equity Share Allotment Due
At Par:
a) Equity Share Allotment A/c
Dr
To Equity Share Capital A/c
At Premium
b) Equity Share Allotment A/c
Dr
To Equity Share Capital A/c
To Securities Premium
At Discount
c) Equity Share Allotment A/c
Discount on issue of Shares A/c
Dr
Dr
To Equity Share Capital A/c
4) For Equity Share Allotment Money Received
Cash/Bank A/c
Dr
To Equity Share Allotment A/c
5) For Equity Share 1st Call Due
Equity Share 1st Call A/c
Dr
To Equity Share Capital A/c
6) For Equity Share 1st Call Money Received
Study Circle
Company Accounts
Cash/Bank A/c
Dr
To Equity Share 1st Call A/c
7) For Equity Share 2nd & Final Call Money Due
Equity share 2nd & Final Call A/c
Dr
To Equity Share Capital A/c
8) For Equity Share 2nd Call money Received
Cash/Bank A/c
Dr
To Equity Share 2nd & Final Call A/c
For Forfeiture of Shares
If Premium is received
1) Equity Share Capital A/c
Dr
To Calls in Arrears A/c
To Share Forfeiture A/c
If Premium is not received
2)
Equity Share Capital A/c
Dr
Securities Premium A/c
Dr
To Calls in Arrears A/c
To Share Forfeiture A/c
For Re-issue of Shares
1) Cash/Bank A/c
Dr
Share Forfeiture A/c Dr
To Equity Share Capital A/c
2) Share Forfeiture A/c Dr
To Capital Reserve A/c
For issue of Shares for Consideration other than Cash
1) When Assets are acquired from Vendors
Sundry Assets A/c
Dr
Cs Executive Refresher Course
Study Circle
Company Accounts
Cs Executive Refresher Course
To Vendors A/c
2) When Shares are issued to Vendors
Vendors A/c Dr
To Equity Share Capital
3) When Shares are issued to Promoters
Goodwill A/c
Dr
To Equity Share Capital A/c
Other Entries
1) Interest on Calls in Arrears
Sundry Shareholders A/c
Dr
To Interest on Calls in arrears A/c
2) Interest on Calls in Advance
Interest on Calls in Advance A/c
Dr
To Sundry Shareholders A/c
Practical Problem
The quality product Ltd. issued 12, 000 Equity shares of Rs. 15 each at par. The amount is
payable as under:
On Application
Rs.3 per share
On Allotment
Rs.7 per share
On First Call
Rs. 3 per share
On Second Call
Rs. 2 per share
The company received application for 20, 000 shares. The Directors rejected application for
1000 shares and allotted shares on pro-rata basis to the remaining applicants. 120 shares were
allotted to Sachin who failed to pay first call and his shares were forfeited. 240 shares were
allotted to saurav who failed to pay second call his shares were also forfeited.
Journalize the above transaction in the book of kwality product Ltd.
Study Circle
Company Accounts
Cs Executive Refresher Course
REDEMPTION OF PREFERNCE SHARES
POINTS TO BE NOTED
(1) Preference shares can be redeemed only if it is fully paid up. If the shares are partly paid up
make them fully paid up by making a call.
(2) Preference shares can be redeemed either out of proceeds of fresh issue or divisible profits.
(2a) Fresh issue means issue of equity shares or preference shares but not debentures.
(2b) Face value
100
100
100
Issue Price
100
110
90
(2b)
DIVISIBLE PROFITS
(Available for dividend redemption)
(1) General Reserve
(2) Revenue Reserve
(3) Dividend equalization Reserve
(4) Reserve Fund
(5) Sinking Fund
(6) Profit & Loss
FACE VALUE OF
PREF. SHARES TO
Be REDEEMED
=
Proceeds
100
100
90
PROFITS.
NON DIVISIBLE PROFITS
(1) Capital Reserve
(2) Capital Redemption Reserve
(3) Security Premium
(4) Share forfeited A/c
(5) Revaluation Reserve
PROCEEDS OF FRESH ISSUE + Divisible Profits
(C.R.R)
(3) Face value of preference shares redeemed out of divisible profit should be transferred to a
special Reserve called “ CAPITAL REDEMPTION RESERVE “ (C.R.R)
(4) C.R.R. can be used only for the issue of fully paid BONUS SHARES.
(5) Preference shares can be redeemed either at par or at premium. If redeemed at premium
such premium on Redemption (loss) will be met either out of SECURITIES
PREMUIM OR DIVISIBLE PROFITS.
PREMUIM ON
REDEMPTION =
SECURITIES PREMUIM + DIVISIBLE PROFITS
(B/S + FRESH ISSUE)
Study Circle
Company Accounts
Cs Executive Refresher Course
JOURNAL ENTRIES
(A) IF THE SHARES ARE PARTLY PAID UP.
(1) Making the final call.
Final call A/C
Dr.
To Pref. Share capital
(2) Receiving the final call
Cash /Bank A/c
Call in arrears
To Final Call A/c.
Dr.
Dr.
(3) Receiving the calls in arrears
Cash / Bank A/c
Dr.
To Calls in arrears A/c.
(4) Forfeiture of shares
Preference share Capital (F. V)
To call in arrears A/c (amt. unpaid)
To Share forfeited A/c ( bal.fig.)
(5) Re issue of Forfeited share
Cash/ Bank A/c (amt recd)
Shares forfeited A/c (Amt unpaid)
To Share Forfeited A/c
Dr.
Dr.
(6) Transfer to Capital Reserve.
Share forfeited A/c
Dr.
To Capital Reserve A/c.
(B) IF THE SHARES ARE FULLY PAID UP.
(7) Sale of investment
Cash/ Bank A/c
Dr.
To Investment A/c.
(Any diff will be transferred to profit & loss A/c)
(Bal fig)
Study Circle
Company Accounts
(8) For Fresh issue of shares.
Cash /Bank A/c
Dr.
To equity share Capital A/c
To security premium A/c
(9) Redemption of Preference shares
Preference share capital A/c
Dr.
Premium on Redemption A/c
Dr.
To Preference shareholder A/c.
(10)
(11)
(12)
(13)
Meeting the Premium on redemption.
Security Premium A/c
Dr.
Divisible Profits A/c
Dr.
To Premium on redemption A/c
Transfer to C.R.R.
Divisible Profit A/c
Dr.
To C.R.R
A/c.
Pay off
Preference Shareholder A/c
Dr.
To Cash / Bank A/c
Declaration of Bonus.
C.R.R A/c
Dr.
Security Premium A/C
Dr.
Capital Reserve A/c
Dr.
Divisible Profit A/c
Dr.
To Bonus to shareholder A/c.
Cs Executive Refresher Course
Study Circle
Company Accounts
Cs Executive Refresher Course
The Balance Sheet of M. Ltd. as on 31.12.2006 is given below :
LIABILITIES
Rs.
ASSETS
Rs.
9% Redeemable Preference
Sundry Assets
9,50,000
Shares of Rs.100 each,
Investments
2,75,000
fully paid up
6,50,000
Cash at Bank
67,500
Equity Shares of
Rs.5 each fully paid up
2,25,000
General Reserve
1,00,000
Profit & Loss Account
2,60,000
Sundry Creditors
57,500
12,92,500
The
Preference
Shares
are
to
be
12,92,500
redeemed
on
1.1.2007,
at
a
premium
of 7½%. In order to facilitate redemption, the company has decided :
i)
To sell the Investments for Rs. 2,60,000.
ii)
To finance part of the redemption from company’s fund; and
iii)
To issue sufficient equity shares at a premium of Rs1/- per share to raise
the balance of funds required.
iv)
Minimum Bank Balance to be retained at Rs. 10,500. The investments were
sold, equity shares are fully subscribed and the shares were duly redeemed.
Show the entries and prepare the Balance Sheet.
Note : Minimum reduction is to be made against Reserve.
Study Circle
Company Accounts
Cs Executive Refresher Course
Buy Back of Equity Shares
Buy back of equity shares can be done only if it is fully paid up.
If the shares are partly paid up they should be made fully paid up by making a final call.
Buy back of shares can be done either out of proceeds of fresh issue or out of free reserve
(a) Free Reserve means securities premium and divisible profit.
(b) Fresh Issue Means :(i)
If equity shares have to be bought back fresh Issue means Issue of Preference
shares or Debentures.
(ii)
If Preference shares have to be bought back fresh Issue means Issue of Equity
shares or Debenture
Formula:Face value of Equity Shares to be bought back = Proceeds of Fresh Issue + Securities Premium
(B/s + F.I)
Premium of Buy back = Securities Premium
( B/s+F.I – 1st Formula)
+
Divisible Profit
Study Circle
Company Accounts
Journal Entries
A) If the shares are partly paid up.
(1) Making a final call
Final Call A/c
Dr
To equity Share capital A/c
(2) Receiving a final call.
Cash /Bank A/c
Dr
Calls in Arrears A/c
Dr
To Final call A/c
(3) Receiving a Call in Arrears
Cash /Bank
To Calls in arrears
Dr
(4) Forfeiture of shares.
Equity Share capital A/c
Dr
To shares forfeited A/c
To calls in Arrears A/c
(5) Re Issue of forfeiture shares
Cash/Bank
Dr.
Share forfeited A/c
Dr.
To Equity share Capital A/c
(6) Transfer to Capital Reserve
Share forfeited A/c
Dr.
To Capital Reserve A/c
B) If the shares are fully paid –up
(7) For sale of investment
Cash/ Bank A/c
Dr
To Investment A/c
(Any diff will be transferred to Profit and loss A/c)
(8) For Fresh Issue.
Cash/ Bank A/c
Dr
To Equity share capital A/c
To Securities Premium A/c
(9) Buy back of equity shares
Equity share capital A/c
Dr
Cs Executive Refresher Course
Study Circle
Company Accounts
Cs Executive Refresher Course
Premium on Buy Back A/c
Dr
To Equity share holders A/c
(10) Meeting the premium on Buy back
Securities premium A/c
Dr
Divisible profit A/c
Dr
To premium on Buy back A/c
(11) Transfer to CRR.
Securities Premium A/c
Dr
Divisible Profit A/c
Dr
To CRR A/c
(12) Pay off
Equity share holders A/c
To Cash/ Bank A/c
Dr.
Study Circle
Company Accounts
Cs Executive Refresher Course
Limits of Buy Back
(1) No. of shares to be bought back should not exceed
(25% of paid up Equity share capital) divide by face value
(2) No. Of shares to be bought back should not exceed
(25% of paid up share capital + Free Reserves) divide by Purchase Price
(3) After buy back the debt equity ratio should not exceeds 2:1
List of free Reserve
(1) General Reserve
(2) Revenue Reserve
(3) Dividend equalisation Reserve
(4) Reserve Fund
(5) Sinking Fund
(6) Profit and loss A/c
(7) Securities premium
(8) Subsidiary Reserve
(9) Investment Allowance (utilised) Reserve
(10) Export Profit ( utilised) Reserve
(11) Foreign Project ( utilised ) Reserve
Practical Problem
Infobyte Ltd. resolved to buy back 30,000 of its fully paid equity shares of Rs. 10 each at Rs. 12 per
share. For this purpose, it issued 1,000 10% preference shares of Rs. 100 each at par. The Total
amount was payable on application. The company has Rs. 85,000 balance to the credit of the
Securities Premium Account, which was to be used for buy-back. The company had sufficient
balance in the General Reserve to meet the legal requirements for buy-back. Pass the necessary
journal entries.
Study Circle
Company Accounts
Cs Executive Refresher Course
Issue & Redemption of Debentures
The summarised Balance Sheet of Convertible Limited, as on 30th June, 2006, stood as follows :
Liabilities
Rs.
Share Capital : 5,00,000 Equity shares of Rs. 10 each fully paid
50,00,000
General Reserve
75,00,000
Debentures Redemption Fund
50,00,000
13.5% Convertible Debentures 1,00,000
Debentures of Rs. 100 each
Other Loans
Current Liabilities and Provision
1,00,00,000
50,00,000
1,25,00,000
4,50,00,000
Assets
Fixed Assets (at cost less depreciation)
1,60,00,000
Debentures Redemption Fund Investments
40,00,000
Cash and Bank Balance
50,00,000
Other Current Assets
2,00,00,000
4,50,00,000
The debentures are due for redemption on 1st July, 2006. The terms of issue of debentures
provided that they were redeemable at a premium of 5% and also conferred option to the debentureholders to convert 20% of their holding into equity shares at a predetermined price of Rs. 15.75 per
share and the payment in cash.
Assuming that :
i)
except for 100 debenture-holder holding totalling 25,000 debentures, the rest of them
exercised the option for maximum conversion;
ii)
The investments realise Rs. 44 lakhs on sale; and
iii)
all the transactions are put through, without any lag, on 1st July, 2006.
Redraft the Balance Sheet of the Company as on 1st July, 2006 after giving effect to the
redemption. Show your calculation in respect of the number of equity shares to be allotted and the
cash payment necessary.
Study Circle
Company Accounts
Cs Executive Refresher Course
Company Final Accounts
1
2
3
4
5
6
Particulars
Overall Managerial remuneration
(Exclusive of fee for attending meetings)
If the company has one managing director or wholetime director
If the Company has more than one managing
Director or whole time director (for all of them)
Remuneration of part time director where the
company has one or more managing director (for all
of them)
Remuneration of part time director where the
company has one or more managing director (for all
of them)
Remuneration to the manager
Maximum Limit
11% of net profit
5% of net profit
10% of net profit
3% of net profit
1% of net profit
5% of net profit
Section 349 and 350 of the companies act contain the provision relating to the manner of
determination of net profits for the proposed of calculating the managerial remuneration.
The provisions of the above sections are require that in computing net profits of a company in any
financial year for the purpose of calculating managerial remuneration the following points should
be considered:
1. Credit shall be given forBounties and Subsidies received from any government or any public authority constituted
or authorized in this behalf by the government unless the central Government otherwise
directs.
2. Credit shall not be given for the following suma. Profit, by way of premium, on shares or debentures of the company which are issued or
sold by the company;
b. Profit on sale by company of forfeited shares
c. Profit from capital nature including profit from the sale of the undertaking or any of
the undertaking of the company, or of any part thereof;
d. Profit from sale of any immovable property or fixed assets of a capital nature
comprised in the undertaking or any of the undertaking of the company unless the
business of the company consist whether wholly or partly of buying and selling any
such property or assets
Provided that where the amount for which any fixed assets is sold exceeds the written
down value thereof referred to in section 350, credit shall be given so much of the
excess as is not higher than the difference between the original cost of that fixed assets
and it’s written down value.
3. The following sums shall be deducted:
a. All the usual working charges;
Study Circle
Company Accounts
Cs Executive Refresher Course
b. Director’s remuneration;
c. Bonus or commission paid or payable to any member of the company’s staff, or to any
engineer, technician or person employed or engaged by the company, whether on an
whole-time or on a pat time or a part time or on a part time basis;
d. Any tax notified by the central government as being in the nature of a tax on excess or
abnormal profit;
e. Any tax on business profit imposed for special reason or in special circumstances and
notified by the central in this behalf;
f. Interest on debenture issued by the company;
g. Interest on mortgages executed by the company and on loans and advances secured by a
charges on its fixed or floating assets;
h. Interest on unsecured loans and advances;
i. Expenses on repair, whether to immovable or to movable property, provided the repair
are not of a capital reserves
j. Outgoing, inclusive of contribution made under clause (e) of subsection (1) of section
293 which states as follows:
“The board of Directors of a public company or of a private company which is
subsidiary of a public company, shall not, except with the consent of such public
company or subsidiary in general meeting, contribute to charitable and other funds not
directly relating to the business of the welfare of its employees, any amounts the
aggregate of which will, in any financial year, exceed Rs. 50, 000 or 5% of its averages
net profits as determine in accordance with the provision of section 349 and 350 during
three financial years immediately proceeding, whichever is greater:”
k. Depreciation to the extend specified in section 350 whichever allows following
deductions:
i.
Normal depreciation including extra and multiple shift allowances calculated at
the rates specified in the schedule XIV
ii.
Excess of written down value over the sale proceed or scrap value of the assets if
it is sold, discarded, demolished or destroyed before the depreciation on such
assets has been provided in full.
But section 350 does not allow the following deductioni.
Special depreciation.
ii.
Initial depreciation.
iii.
Development rebate reserve or investment allowance reserve;
l. The excess of expenditure over income, which had been arisen in computing the net
profit in accordance with section 349 in any year which begins at or after the
commencement of this Act, in so far as such excess had not been deducted in any
subsequent year preceding the year in respect of which the net profit have to be
ascertain;
Study Circle
Company Accounts
Cs Executive Refresher Course
2. Any compensation or damage to be paid by virtue of any legal liability including a
liability arising from a breach of contract;
3. Any sum paid by way of insurance against the risk of meeting any liability such as is
referred to in clauses (m);
4. Debt considered bad and written off or adjusted during the year of account.
4.
The following sums shall not be deducted;
a. Income tax and super tax payable by the company under the income tax Act, 1961 or
any other tax on the income of the company not falling under clauses (d) and (e) of (3)
above;
b. Any compensation, damages or payments made voluntarily that is to say, otherwise than
in virtue of ability such as is referred to in clauses (m) of 3 above.
c. Loss of a capital nature including loss on sale of the undertaking or any of the
undertaking of the company or of any part thereof not including any excess referred to
in the company or of any section 350 of the written down value of any assets which is
sold, discarded, demolished or destroyed over, its sale proceed or its scrap value.
It is important to note here that the above provision do not apply to a private company,
unless it is subsidiary of a public company.
The following is the Profit and Loss account of S.S. Ltd for the year ended 31st March 2008.
PARTICULARS
RS
PARTICULARS
RS
To Salaries & wages
1,50,000 By Gross Profit
40,00,000
To Repairs to Fixed Assets
50,000 By Profit on sale of Machinery
4,50,000
(Cost Rs 8 lacs and WDV Rs 4
lacs)
To General Expenses
40,000 By Subsidy from the
1,00,000
government
To Compensation for breach of
25,000
Contract.
To Depreciation
2,40,000
To Loss on sale of investment
35,000
To expenditure on Scientific
2,50,000
Research ( Cost of Setting up a
new laboratory)
To debenture interest
75,000
To interest on unsecured loans
15,000
To Provision for tax
16,00,000
To Proposed dividends
10,00,000
To balance c/d
10,70,000
45,50,000
45,50,000
Calculate the overall managerial remuneration under section 198.
Study Circle
Company Accounts
Cs Executive Refresher Course
Given is the Trial Balance of Marathon Limited as on 31st March, 2012. You are require to
prepare the Profit and loss Account and Balance Sheet on 31st March, 2012
Authorised Share capital divided into 8,000,
6% preference shares of `100 each and 20,000
equity shares of `100 each
28,00,000
Subscribed Capital
5,000 6% preference shares of `100 each
5,00,000
Equity Share Capital
8,00,000
Capital Reserve
5,000
Purchases - Coco, Tea, Coffee
58,800
- Bakery products
36,200
Wages and Salary
15,300
Rent, Rates and Taxes
8,900
Laundry
750
Sales - Coco, Tea and Coffee
82,000
- Bakery products
44,000
Coal and Firewood
3,290
Carriage
810
Sundry Expenses
5,840
Advertising
8,360
Repair
4,250
Rent of Rooms
48,000
Study Circle
Company Accounts
Cs Executive Refresher Course
Receipt from Billiards
5,700
Miscellaneous Receipts
2,800
Discount Received
3,300
Transfer Fee
700
Freehold Land and Building
8,50,000
Furniture and Fittings
86,300
Stock on hand, 1st April, 2011
Coco, Tea, Coffee
12,800
Bakery products
5,260
Cash in Hand
2,200
Cash with Bank
76,380
Preliminary and Formation Expenses
8,000
2000, 8% debentures of `100 each
2,00,000
Profit and Loss Account
41,500
Sundry Creditors
42,000
Sundry Debtors
19,260
Investment
2,72,300
Goodwill at Cost
5,00,000
General Reserve
2,00,000
19,75,000
Additional Information:
— Wages and Salaries outstanding 4,280
— Stock as on 31st march, 2012
— Coco, Tea, Coffee 22,500
— Bakery Products 16,400
19,75,000
Study Circle
Company Accounts
Cs Executive Refresher Course
— Provide 5% depreciation on Furniture and Fittings and 2% on Land and Building.
The equity capital on 1st April, 2011 stood at Rs 7, 20,000, that is 6,000 shares fully paid and
2,000 shares of Rs 60 paid. The directors made a call of Rs 40 per share on 1st October, 2011.
A shareholder could not pay the call on 100 shares and his shares were then forfeited and
reissued at Rs 90 per share as fully paid. The director proposes a dividend of 8% on equity
shares, transferring any amount that may be required from general reserve. Ignore taxation
Study Circle
Company Accounts
Cs Executive Refresher Course
Consolidation of Accounts-AS 21
Following are the balance Sheets of H Ltd. and S Ltd. as at 31st March, 2008.
I .EQUITIES AND
LIABILITIES
H Ltd.
S Ltd.
Amount (Rs.)
Amount (Rs.)
1 Shareholder’s funds
(a)Share Capital
Authorised, Issued subscribed and
paid up capital
Equity shares of Rs.100 each, fully
5,00,000
2,00,000
called up and paid up
(b)Reserve & Surplus
General Reserve
1,00,000
Profit & Loss A/c
1,40,000
60,000
2,40,000
90,000
80,000
40,000
50,000
1,50,000
2 Current Liability
Bills payable
Trade payables
Total
II.ASSETS
8,20,000
90,000
4,40,000
1 Non-current assets
(a) Fixed Assets
Machinery
1,60,000
90,000
Land & Building
2,00,000
40,000
1,30,000
30,000
Goodwill
(b) Long term Investment
1,500 Shares in S Ltd.(at cost)
4,00,000
2,50,000
2,40,000
3. Current Asset
Trade Receivables
Stock
Cash at Bank
Total
20,000
1,00,000
60,000
75,000
1,80,000
8,20,000
90,000
25,000
1,90,000
4,40,000
Study Circle
Company Accounts
Cs Executive Refresher Course
The Profit and Loss Account of S Ltd. showed a credit balance of Rs. 50,000 on 1st April 2007. A
dividend of 15% was paid in December 2007 for the year 2006-07. This dividend was credited to
Profit and Loss Account by H Ltd.
H Ltd. acquired the shares in S Ltd. on 1st October, 2007.
The Bills Payable of S Ltd. were all issued in favour of H Ltd. which company got the bills
discounted.
Included in the Creditors of S Ltd. is Rs. 20,000 for goods supplied by H Ltd. Included in
the stock of S Ltd. are goods to the value of Rs. 8,000 which were supplied by H Ltd. at a profit of
331/2 on cost.
In arriving at the value of S Ltd. shares, the plant and machinery which then stood in the
books at Rs. 1,00,000 on 1.4.2007 was revalued at Rs. 1,50,000. The new value was not
incorporated in the books. No changes in these have been made since then.
Prepare the consolidated balance sheet as on that date.
Study Circle
Company Accounts
Cs Executive Refresher Course
ECONOMIC VALUE ADDED
A concept critical in evaluating the performance of any business is economic value added. It measures the
economic rather than accounting profit created by a business after the cost of all resources including both
debt and equity capital have been taken into account.
Economic value added (EVA) is a financial measures of what economists sometimes refer to as economic
profit or economic rent. The difference between economic profit and accounting profit is essentially the
cost of equity capital – an accountant does not subtract a cost of equity capital in the computation of
profit, so in fact an accountant’s measures of income or profit is in essence the residual return to that
equity capital since all other costs have been deducted from the revenue stream. In contrast, an economist
charges for all resources in his computation of profit – including an opportunity cost for the equity capital
invested in the business – so an economist’s definition and computation of the profit is net above the cost
of all resources.
HOW TO CALCULATE ECONOMIC VALUE ADDED (EVA)
The under given table gives a view for how to calculate “ Economic Value Added ”
Earnings before Interest and Taxes (EBIT)
XXX
Less: Interest
XXX
Net Income
XXX
Less : Cost of Equity Capital
XXX
Economic Value Added (EVA)
XXX
Expressed as a formula:
EVA = “Net Operating Profit after Taxes “ – (Equity Capital X % Cost Of Equity Capital).
Study Circle
Company Accounts
Cs Executive Refresher Course
ILLUSTRATION
Balance Sheet of ABC Limited
As at 31st March, 2012
I.EQUITY AND LIABILITIES
Rs.
1.Shareholder’s Funds
Equity
2. Non- Current Liabilities
Long Term Debt
3.Current Liabilities
(a) Account Payables
(b) Bank Overdraft
Total
II.ASSETS
1.Non-current assets
(a) Fixed Assets
2.Current Assets
(a) Inventories
(i) Raw Material
(ii)Finished Goods
(b) Account Receivable
(c) Cash
Total
40,00,000
60,00,000
2,08,000
4,84,000
1,06,92,000
1,00,00,000
86,400
1,71,360
4,29,300
4,940
1,06,92,000
STATEMENT OF PROFIT OF ABC LIMITED
Sales
Less: Operating Expenses
EBIT
Less: Tax Expenses
NOPAT
28,62,000
11,48,400
17,13,600
6,85,440
10,28,160
The average rate of return on similar types of companies is 20% while risk free is 12.5%. Rate of return as
charges by bank is 18% and the tax rate is 40%.
Calculate Economic Value Added.
Study Circle
Company Accounts
Cs Executive Refresher Course
VALUATION OF GOODWILL
ILLUSTRATION
A Ltd. Proposed to purchase the business carried on by M/s. X & co. Goodwill for this purpose is agreed to
be valued at 3 year’s purchase of weighted average profit of the past four year’s. The appropriate weights
to be used are:
2007-2008
2008-2009
1
2
2009-2010
2010-2011
3
4
The profit for these years are : 2007-2008- Rs.1,01,000; 2008-2009- Rs.1,24,000;
2009-2010- Rs. 1,00,000 and 2010-2011- Rs. 1,40,000
On a scrutiny of the accounts the following matters are revealed:
(i)
(ii)
(iii)
On 1st December, 2009 a major repair was mad in respect of the plan incurring Rs.30,000 which
was charged to revenue. The said sum is agreed to the Capitalised for goodwill calculation
subject to adjustment of depreciation of 10% p.a. on reducing balance method.
The closing stock for the year 2008-2009 was overvalued by Rs.12,000.
To cover management cost & annual charge of Rs.24,000 should be made for the purpose of
goodwill valuation.
Compute the value of goodwill of the firm.
Study Circle
Company Accounts
Cs Executive Refresher Course
LIQUIDATION OF COMPANIES
st
The following information is extracted from books of Mehsana Limited on 31 July, 2012 on
which date a winding up order was made.
Unsecured creditors
3,50,000
Salaries due for five months
20,000
Managing director’s remuneration
30,000
Bills payable
1,06,000
Debtors - good
4,30,000
Doubt full (estimated to produce Rs.62,000)
1,30,000
- Bad
88,000
Bill Receivable(good Rs.10,000)
16,000
Bank Overdraft
40,000
Land(Estimated to produce Rs.5,00,000)
3,60,000
Stock (Estimated to produce Rs.5,80,000)
8,20,000
Furniture & fixtures
80,000
Cash in hand
4,000
Estimated Liabilities for Bills discounted
60,000
Secured Creditors holding first mortgage on land
4,00,000
Partly Secured Creditors Holding Second Mortgage on land
2,00,000
Weekly wages unpaid
6,000
Liabilities under work men’s compensation act, 1925
2,000
Income Tax due
8000
th
5000 9% mortgage debentures of 100 each interest payable to 30 June &
5,00,000
st
th
31 December, Paid 30 June 2012
Share Capital:
2,00,000
20,000 10 % Preference share of Rs. 10 each
50,000 Equity shares of Rs. 10 each
5,00,000
st
General reserve since 31 December,2004
1,00,000
In 2009, the company earned profit of Rs.4,50,000 but thereafter it suffered trading losses
totaling Rs.5,84,000. The company also suffered a speculation loss of Rs. 50,000 during the year
2010. Excise authorities imposed a penalty of Rs. 3,50,000 in 2011 for evasion of tax which was
paid in 2012.
From the foregoing information, prepare the statement of Affairs and the Deficiency Account.
Study Circle
Company Accounts
CS Executive Refresher Course
CORPORATE RESTRUCTURING
st
Q.41)Under given is the balance sheet of Rajbhasha & co as on 31 march,2012
I .EQUITIES AND LIABILITIES
1 Shareholder’s funds
(a)Share Capital
Authorised,issued subscribed & paid-up capital
12,500 9% Preference shares of Rs.8 each
1,00,000
1,50,000 equity shares of Rs. 1 each
1,50,000
2,50,000
(b)Reserve & Surplus
Profit & Loss account
(98000)
2 Non-Current Liability
10% Debentures
60,000
3 Current Liability
Trade payables
50,000
Bank Overdraft (Secured by land & building)
20,000
Debenture Interest
4,200
Total
74,200
2,86,200
II.ASSETS
1. Non-current assets
(a) Fixed Assets
Free hold land & building
34,000
Plant
96,000
Tools & dies
27,300
1,57,300
(b)Other non-current expenses
Research & development Expenses
18,000
2.Current Assets
Stock
42,500
Trade receivable
53,400
Investment
15000
Total
Dr Jinesh Shah
2,86,200
Andheri/Dadar-28272829
Page 30
Study Circle
Company Accounts
CS Executive Refresher Course
The scheme of re-organisation detailed below has been agreed by the parties approved by the
Court. You are required to prepare:
(a) Journal entries recording the transaction in the books. Including cash;
st
(b) The balance sheet of the company as on 1 April,2012 after the completion of
the scheme.
(i)
The following assets are to be revalued as shown below: plant Rs. 59,000
tools and dies Rs. 15,000; stock Rs.30,000 and debtors Rs.48,700.
(ii)
The research and development expenditure and debit balance of Profit &
loss account are to be written off.
(iii)
Price of land recorded in the books at Rs. 6,000 is valued at Rs. 14,000 and is
to be taken over by the debenture holders in part repayment of principal. The
remaining freehold land and building are to be revalued at Rs.40,000.
(iv)
A creditor for Rs. 18000 has agreed to accept a second mortgage debenture of
11% per annum secured on plant for Rs. 15,500 in settlement of his debt. Other
creditors totaling Rs. 10,000 agreed to accept a payment of Rs.0.85 in the
rupee for immediate settlement.
The investment at a valuation of Rs.22,000 is to be taken over by the bank.
(v)
(vi)
The ascertained loss is to be met by writing down the equity shares to Rs. 1 each
and preference shares to Rs.8 each. The authorized share capital is to be
increased immediately to the original amount.
(vii)
The equity shareholders agree to subscribe for two new ordinary shares at par
for every shares held. This cash is all received.
(viii)
The costs of the scheme are Rs.3,500. These have been paid and are to be
written off. The debenture interest has also been paid.
Dr Jinesh Shah
Andheri/Dadar-28272829
Page 31
Study Circle
Company Accounts
CS Executive Refresher Course
th
The following are the balance sheet of A Co. Ltd. & B Co. Ltd as on 30 September,2012
A Co. Ltd
Amount(Rs.)
I .EQUITIES AND LIABILITIES
1. Shareholder’s funds
(a)Share Capital
Authorised issued subscribed & paid-up capital
50,000 Equity shares of Rs.10 each ,
5,00,000
Fully called up & Paid up
(b)Reserve & Surplus
1,70,000
General Reserve
Profit & Loss account
30,000
2. Non-Current Liability
12% Debentures
1,00,000
Employee Provident Fund
15,000
3 Current Liability
Trade payables
50,000
Total
8,65,000
II.ASSETS
1) Fixed Assets
Building
1,50,000
Machinery
5,50,000
7,00,000
2.Current Assets
Stock
80,000
Trade receivable
70,000
Cash
15,000
Total
Dr Jinesh Shah
1,65,000
8,65,000
Andheri/Dadar-28272829
Page 32
Study Circle
Company Accounts
CS Executive Refresher Course
B Co. Ltd
Amount(Rs.)
I .EQUITIES AND LIABILITIES
1.Shareholder’s funds
(a)Share Capital
Authorised issued subscribed & paid-up capital
30,000 Equity shares of Rs.10 each ,
3,00,000
Fully called up & Paid up
2. Current Liability
Trade payables
40,000
Total
3,40,000
II.ASSETS
1. Non-Current Assets
(a) Fixed Assets
Tangible assets
Machinery
2,50,000
2. Current Assets
Stock
40,000
Trade receivable
50,000
Less : Provision for Doubtful Debts
5,000
Cash & Cash equivalents
45,000
5000
3. Total
90,000
3,40,000
The Two Companies agree to amalgamate and from a new company called C Co.Ltd. Which
st
takes over all the assets and liabilities of both the companies on 1 October, 2012.
The Purchase consideration is agreed at Rs. 6,61,500 and Rs. 3,15,000 for A Co. Ltd. And B Co.
Ltd. Respectively.
The entire purchase price is to be paid by C Co. Ltd. In fully paid equity shares of Rs. 10 each.
The Debentures of A Co. Ltd. Will be converted into equivalent number of debentures of C CO.
Ltd.
Dr Jinesh Shah
Andheri/Dadar-28272829
Page 33
Study Circle
Company Accounts
CS Executive Refresher Course
Give journal entries to close the books of A Co. Ltd. And B Co. Ltd. And show the opening
entries in the books of C Co. Ltd. Also prepare the opening Balance Sheet in the books of C Co.
st
Ltd. As on 1 October, 2012. The authorised capital of C Co. Ltd. Is 2,00,000 equity shares of
Rs.10 each.
Dr Jinesh Shah
Andheri/Dadar-28272829
Page 34
Study Circle
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
Company Accounts
CS Executive Refresher Course
Amalgamation
Determination of Purchase
Consideration
Net Assets Method
All Assets (AV)
xx
(xx)
Less: All Liabilities (AV)
Purchase Consideration
xx
Net Payment Method
-By Equity Shares in New Co
By Preference Shares in New Co.
By Debentures in New Co
By Cash/ Bank
Lumpsum Method: One Single Amount will be given as
Purchase Consideration.
AMALGAMATION
STEPS IN THE BOOKS OF OLD CO.
•
STEP 1: TRANFER EACH & EVERY ITEM OF BALANCE SHEET OF OLD CO. AS
UNDER:
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
ASSETS SIDE
a) fictitious assets
b) Cash/Bank
-if taken over
-if not taken over
c) All other assets
(Whether taken over or
Not taken over)
Dr Jinesh Shah
TRANSFER TO
Equity shareholders A/c (Dr Side)
Realisation A/c ( Dr side)
Cash/Bank A/c ( Dr side)
Realisation A/c ( Dr side)
{ At Book Values}
Andheri/Dadar-28272829
Page 35
Study Circle
Company Accounts
CS Executive Refresher Course
Continued………………………………
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
Liabilities Side
a) Equity Share Capital
b) Reserves & Surplus
c) Preference Share Capital
d) All other Liabilities:
-if taken over
-if not taken over
•
Step : 2 Entry for PC
•
•
Step: 3 Discharge of PC
Equity Shares in New Co A/c Dr
Pref Shares in New Co A/c Dr
Debentures in New Co A/c Dr
Cash/Bank A/c Dr
To New Co A/c
•
Note: At the end of Step 3 New
Company Account Should Tally
Transfer to
Equity Shareholders A/c (Cr Side)
Equity Shareholders A/c (Cr side)
Pref Share holders A/c ( Cr side)
Realisation A/c ( Cr side)
Liabilities not taken over A/c (Cr side)
New Company A/c Dr
To Realisation A/c
•
Dr Jinesh Shah
Andheri/Dadar-28272829
Page 36
Study Circle
•
•
Step 4: Sale of Assets not Taken
over
Step: 5: Realisation Expenses
Company Accounts
•
CS Executive Refresher Course
Cash/Bank A/c Dr
To Realisation A/c
Realisation Expenses A/c Dr
To Cash/Bank A/c
( If reimbursed by new Co)
Cash/Bank A/c Dr
To Realisation A/c
Step 6: Payment to Liabilities not taken
over
Liabilities not taken over A/c Dr
To Eq/Pref Shares in New Co
To cash/ bank A/c
(if any difference trf to Realisation A/c)
Step : 7: Payment to Preference Share
holders
Preference Shareholders A/c Dr
To Eq/Pref Shares in New Co.
To Cash/ Bank A/c
(If any difference trf to Realisation A/c)
Step 8: Close Realisation A/c & Transfer the difference to Equity
Shareholders A/c
Step 9: Close All other Accounts and transfer the Difference to Equity
Shareholders A/c
Step 10: Equity Shareholders A/c Should TALLY
Dr Jinesh Shah
Andheri/Dadar-28272829
Page 37
Study Circle
Company Accounts
CS Executive Refresher Course
Journal Entries in the Books of New
Company
•
1) For issue of Shares
Cash/Bank A/c
Dr
To Equity share capital A/c
To Securities Premium A/c
2) For Preliminary Expenses
Preliminary Expenses A/c
To Cash/Bank A/c
Dr
3) For Business Purchase
Dr
Business Purchase A/c
To Liquidator of Old Co.
Continued……………………..
•
Step 4: For Take over Assets & Liabilities
All Assets taken over (At agreed Values)
Dr
Good will A/c
Dr
To All liabilities to taken over A/c
To Business Purchase A/c
To Capital Reserve A/c
Step 5: For Discharge of Liquidator
Liquidator of Old Co. A/c
Dr
Discount on issue on Shares A/c
Dr
To Equity Share Capital A/c
To Preference Share capital A/c
To Debentures A/c
To Securities Premium A/c
To Cash/Bank A/c
Dr Jinesh Shah
Andheri/Dadar-28272829
Page 38
Study Circle
Company Accounts
CS Executive Refresher Course
Continued……………………..
•
•
Step 6: For Payment of Realisation expenses of Old Co.
Goodwill/Capital Reserve A/c
Dr
To Cash/Bank A/c
Step 7: For Cancellation of Mutual Debts
Dr
Creditors A/c
To Debtors A/c
Step 8: For Cancellation of Bills
Dr
Bills Payable A/c
To Bills Receivable A/c
Continued………………………..
•
Step 9: For Elimination of Unrealised Profit in Stock
Good will/Capital Reserve A/c
Dr
To Stock A/c
Step 10: For Carry Forward of Statutory Reserve
Amalgamation Adjustment A/c
Dr
To Statutory Reserve A/c
Dr Jinesh Shah
Andheri/Dadar-28272829
Page 39
Study Circle
Company Accounts
CS Executive Refresher Course
PART I – Form of BALANCE SHEET
0
Balance Sheet as at
Particulars
1
I.
Note No.
2
31 March 2012
3
(in Rupees)
31 March 2011
4
EQUITY AND LIABILITIES
1 Shareholders’ funds
(a) Share capital
(b) Reserves and surplus
(c) Money received against share warrants
1
2
2 Share application money pending allotment
3 Non-current liabilities
(a) Long-term borrowings
(b) Deferred tax liabilities (Net)
(c) Other Long term liabilities
(d) Long-term provisions
3
4
5
4 Current liabilities
(a) Short-term borrowings
(b) Trade payables
(c) Other current liabilities
(d) Short-term provisions
6
7
8
TOTAL
II.
ASSETS
Non-current assets
1 (a) Fixed assets
(i)
Tangible assets
(ii)
Intangible assets
(iii)
Capital work-in-progress
(iv)
Intangible assets under development
(b) Non-current investments
(c) Deferred tax assets (net)
(d) Long-term loans and advances
(e) Other non-current assets
11
12
2 Current assets
(a) Current investments
(b) Inventories
(c) Trade receivables
(d) Cash and cash equivalents
(e) Short-term loans and advances
(f) Other current assets
14
15
16
17
18
TOTAL
Dr Jinesh Shah
Andheri/Dadar-28272829
Page 40
Study Circle
Company Accounts
CS Executive Refresher Course
PART II - Form of STATEMENT OF PROFIT AND LOSS
Profit and loss statement for the year ended 31.03.2012
( ` in Rupees)
Refer
Note No.
Particulars
I. Revenue from operations
19
II. Other income
20
31 March 2012
31 March 2011
III. Total Revenue (I + II)
IV. Expenses:
Cost of materials consumed
Purchases of Stock-in-Trade
Changes in inventories of finished goods work-in-progress
and Stock-in-Trade
Employee benefits expense
Finance costs
Depreciation and amortization expense
Other expenses
21
22
23
Total expenses
Profit before exceptional and extraordinary items and
V. tax (III-IV)
Dr Jinesh Shah
Andheri/Dadar-28272829
Page 41







