Animals, Habitats, and Food Chains Study Guide
advertisement
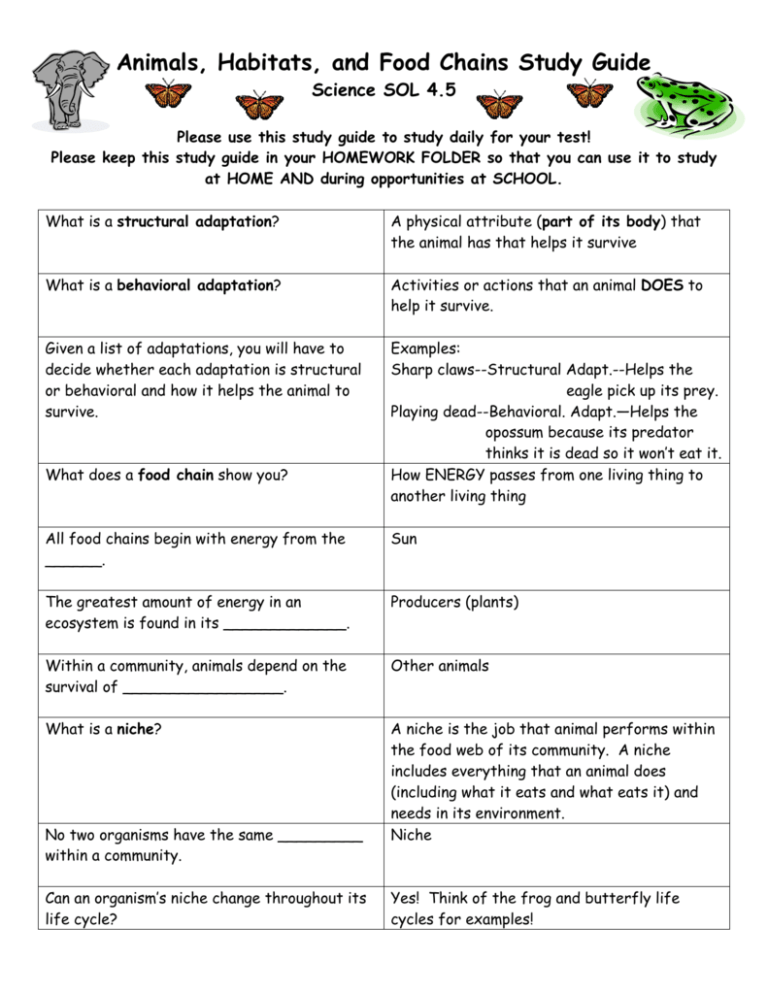
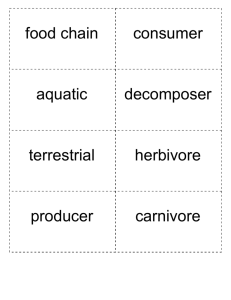
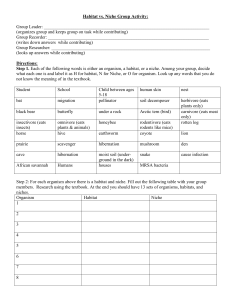
Animals, Habitats, and Food Chains Study Guide Science SOL 4.5 Please use this study guide to study daily for your test! Please keep this study guide in your HOMEWORK FOLDER so that you can use it to study at HOME AND during opportunities at SCHOOL. What is a structural adaptation? A physical attribute (part of its body) that the animal has that helps it survive What is a behavioral adaptation? Activities or actions that an animal DOES to help it survive. Given a list of adaptations, you will have to decide whether each adaptation is structural or behavioral and how it helps the animal to survive. Examples: Sharp claws--Structural Adapt.--Helps the eagle pick up its prey. Playing dead--Behavioral. Adapt.—Helps the opossum because its predator thinks it is dead so it won’t eat it. How ENERGY passes from one living thing to another living thing What does a food chain show you? All food chains begin with energy from the ______. Sun The greatest amount of energy in an ecosystem is found in its _____________. Producers (plants) Within a community, animals depend on the survival of _________________. Other animals What is a niche? A niche is the job that animal performs within the food web of its community. A niche includes everything that an animal does (including what it eats and what eats it) and needs in its environment. Niche No two organisms have the same _________ within a community. Can an organism’s niche change throughout its life cycle? Yes! Think of the frog and butterfly life cycles for examples! What is a producer? What is a consumer? Something that uses water, air, and sunlight to make its own food…PLANTS! Any living thing that eats other living things to get food energy (remember…plants are living things too!) What is a decomposer? A consumer that eats only dead plants and animals What do decomposers do? They break down dead plants and animals and return their food energy to the soil, which can later be used by new producers!! What are some examples of decomposers? Worms, mushrooms, bacteria Illustrate an example of a food web you could find in Virginia. Ex. What is a habitat? The place where an animal lives What does an animal’s habitat provide? Food, water, shelter, and space The size of an animal’s habitat is determined by _______________. The size of the animal Examples of habitats include _________. Oceans, streams, ponds, marshes, deserts, grasslands, and forests. Describe the life cycle of a frog. Eggs (in water)ÆEggs hatch into tiny tadpoles (in water)Ætadpoles slowly grow legs, lose their tail, and develop lungs (froglet) (water and land)Æ adult frog Describe the life cycle of a butterfly. Egg (on leaf)Æcaterpillar or “larva” (EATS A LOT!) Æpupa (cocoon or chrysalis) Æadult butterfly What are 2 ways that humans harm ecosystems? Clearing land (destroying habitats), pollution of water and air Why do people clear land (destroy habitats)? z To grow crops z To mine nonrenewable resources (coal, rocks, etc.) z To build homes and roads What are 4 ways that humans are beginning to help ecosystems? z Recycling (decreases trash and land needed for landfills) z Agreements to protect and preserve endangered animals and their habitats z Reclaiming and repairing land by turning it into parks z Farmers using more natural pest controllers instead of poisonous pesticides.