5.3 Notes
advertisement

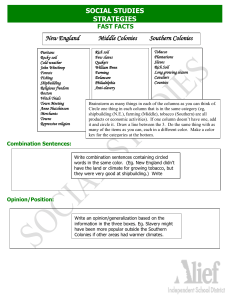
5.3 Notes The Colonial Economy The Southern Colonies Virginia, Georgia, Maryland, North Carolina, South Carolina The economies of the southern colonies depended on agriculture o Agriculture= farming They also exported materials for ship building, such as wood and tar There were both small farms and large plantations in the southern colonies Farms were successful because of a warm climate and a long growing season (Think about Ohioans going to Myrtle Beach for vacation) Cash Crops – crops that are sold for a profit o Tobacco, rice, and indigo were the most important cash crops Crops like indigo and rice required many workers to grow and harvest Slaves in the South The success of tobacco also led to an increase in the demand for tobacco, which led to more slaves Slaves did most of the hard labor on large plantations When a job was finished, slaves were sometimes allowed to do their own work. Sometimes a slave would be able to earn enough money to buy their freedom Slave Codes- laws that controlled slaves o Prevented slaves from rebelling In SC, slaves could not hold meetings or_own weapons Some colonies did not let slaveholders free their slaves The New England Colonies Connecticut, Massachusetts, New Hampshire, Rhode Island Harsh Climate and poor soil led to fewer farms and cash crops 1 Some people owned slaves, but they were not as important to the economy as in the south Trade was extremely important to New England’s economy Businessmen traded goods locally, with other colonies and overseas Fishing and _shipbuilding_ were two of the region’s leading industries o _Whaling also became very popular Whale oil was used for lighting lanterns Whale meat was eaten o Shipbuilding was also very prosperous because of the following reasons Large # of _forests_ in the area Local _fishing_industries needed ships Ships were also needed for _trading_ other goods The New England economy allowed for skilled _craftspeople_ to flourish Families sent __younger sons__ to learn skilled trades like blacksmithing, weaving, shipbuilding, and printing. _Apprentices_- young boys who learned skilled _trades___ from a master craftsman The Middle Colonies Delaware, Pennsylvania, New Jersey, and New York Combined qualities of New England and southern colonies Had a _decent growing season and __rich__ land, which led to many __farms_ __Staple Crops__- crops that are always needed o Ex: _Wheat, barley, oats____ Slaves___ were also important to the middle colonies o They worked as ____skilled laborers____, such as blacksmiths and __carpenters__ o Some worked on farms, on ships, in dockyards, or _shipbuilding_ _Trade__ and ___Free enterprise___ were important to the middle colonies Merchants also exported ___local goods__ to Britain and the West Indies 2 Women and the Colonial Economy Women made many important _contributions_ to the local economies o __Ran farms____ o Ran businesses such as clothing stores, ____bakeris___, grocery stores, and ____drug stores__ o Some were _nurses__ or __midwives_ (help to deliver __children_) Laws and customs put ______restrictions____ on women’s freedoms o Needed husband’s permission to ___work outside the home________ o Husband has the right to wife’s ___income__. 3