CIPD Assessment Activity
advertisement
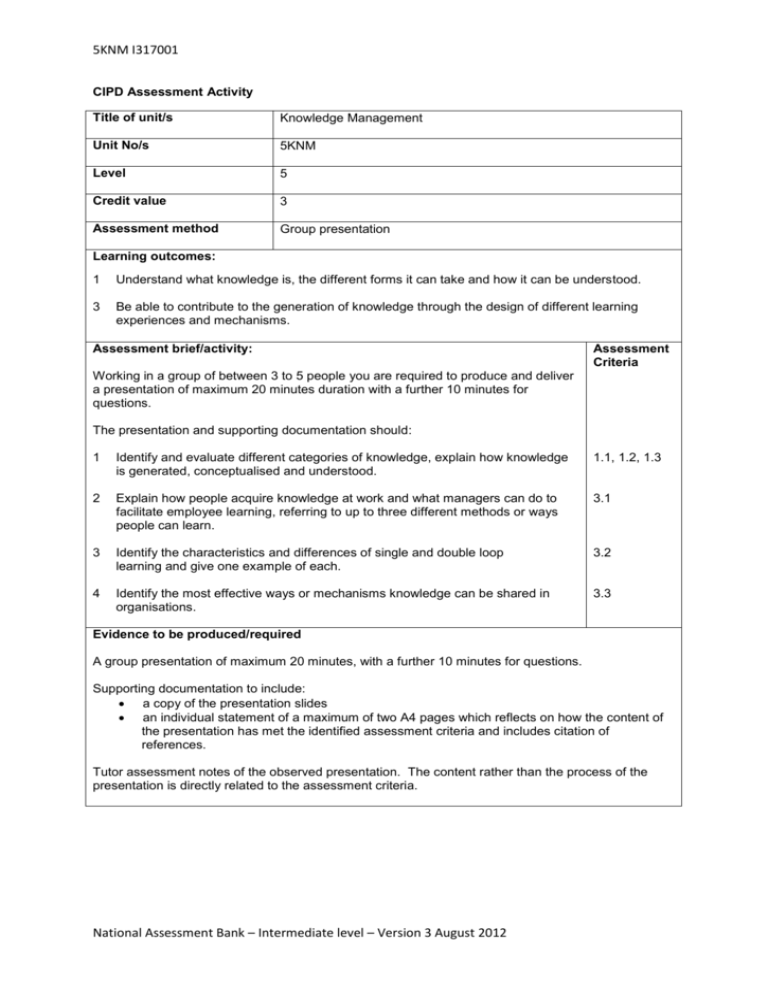
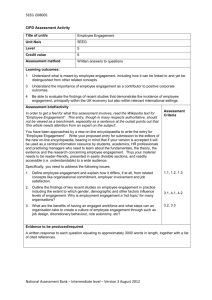
5KNM I317001 CIPD Assessment Activity Title of unit/s Knowledge Management Unit No/s 5KNM Level 5 Credit value 3 Assessment method Group presentation Learning outcomes: 1 Understand what knowledge is, the different forms it can take and how it can be understood. 3 Be able to contribute to the generation of knowledge through the design of different learning experiences and mechanisms. Assessment brief/activity: Assessment Criteria Working in a group of between 3 to 5 people you are required to produce and deliver a presentation of maximum 20 minutes duration with a further 10 minutes for questions. The presentation and supporting documentation should: 1 Identify and evaluate different categories of knowledge, explain how knowledge is generated, conceptualised and understood. 1.1, 1.2, 1.3 2 Explain how people acquire knowledge at work and what managers can do to facilitate employee learning, referring to up to three different methods or ways people can learn. 3.1 3 Identify the characteristics and differences of single and double loop learning and give one example of each. 3.2 4 Identify the most effective ways or mechanisms knowledge can be shared in organisations. 3.3 Evidence to be produced/required A group presentation of maximum 20 minutes, with a further 10 minutes for questions. Supporting documentation to include: a copy of the presentation slides an individual statement of a maximum of two A4 pages which reflects on how the content of the presentation has met the identified assessment criteria and includes citation of references. Tutor assessment notes of the observed presentation. The content rather than the process of the presentation is directly related to the assessment criteria. National Assessment Bank – Intermediate level – Version 3 August 2012 5KNM I317001 Guidance for Assessors for 5KNM (LO 1 & 3) This guidance is for assessors only and should not be handed out to candidates. Individual contribution should be assessed using the CIPD skills observation checklist (SOC) or similar, against the guidance below. Candidates should relate academic concepts and theories and professional practice to the way organisations operate, in a critical and informed way, and with reference to key texts, articles and other publications and by using organisational examples for illustration. All sources must be supported by citations presented in the format that the centre determines. Activity 1 Candidates should identify and evaluate the different categories of knowledge. Typically this should cover: AC 1.1, 1.2, 1.3 An understanding of tacit and explicit knowledge. Recognition that they are complimentary and that both types of knowledge are essential for knowledge creation. An awareness of how explicit knowledge is typically privileged and prioritised over tacit knowledge; explicit knowledge typically being characterised as objective with tacit knowledge by contrast being assumed to be personal, subjective and context specific. An understanding of the different levels of knowledge in organisations , individual , team and organisational An understanding of the role and importance of organisational knowledge. Candidates should be able to identify that knowledge is created through a dynamic process and is experiential, created in different contexts and across organisational boundaries. Candidates should be able to explain how knowledge is conceptualised and understood for example, knowledge as truth, as fact and as belief; the objectivist and practice-based perspectives. Question 2 Candidates should describe up to three key ways in which people learn at work namely : AC 3.1 Learning by formal training and education. Learning through the use of interventions in work processes. Learning that is embedded in and emerges from day to day work. Groups may make reference to the learning process and refer to key theories such as Honey & Mumford/Crossan & Zietsma. Candidates should also describe ways in which managers can facilitate employee learning. Typically this should include access to the following: Networking; mentoring; project work and post project reviews; access to inhouse learning and external learning events (workshops, courses conferences); coaching and action learning groups. A range of examples are possible. Well described and justified examples are what is required. Candidates should also be able to demonstrate an understanding of the theory of the “Learning organisation” and draw on references to key academic work in this area such as Peter Senge and (1990) and Mike Pedlar (et al 1997). National Assessment Bank – Intermediate level – Version 3 August 2012 5KNM I317001 Question 3 Candidates should describe the differing characteristics of single and double loop learning: AC 3.2 Single loop learning being concerned with finding the solution to a technical or a practical problem (“know – how”); whereas double loop learning is concerned with the underlying concepts, assumptions, values and policies that have lead to the problem in the first place (“know –why”) Candidates should give at least one example of each type of learning from their own experience or from an organisation they are familiar with. Question 4 Candidates should discuss two ways that knowledge is shared within organisations: AC 3.3 Typically these will include: Providing exchange forums such as face to face and electronic forums Developing a knowledge sharing culture by valuing and rewarding knowledge sharing Implementing mentoring systems Communities of practice Within team networks and interdepartmental networks; professional networks Candidates may make reference to the fact that technology is only one of many factors affecting the sharing of knowledge; creating an organisational culture of trust and recognition are equally as important. Groups may describe other examples from their own organisations or from an organisation they are familiar with. National Assessment Bank – Intermediate level – Version 3 August 2012