LECTURE ABOUT ATHENS
advertisement

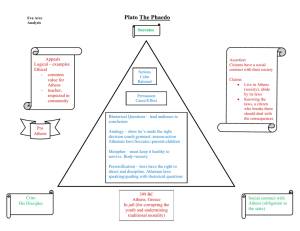
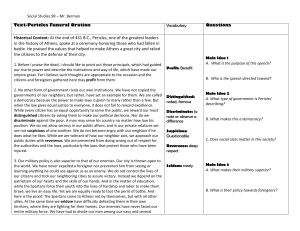
LECTURE ABOUT ATHENS Introduction -Athens’ power Where was Athens located? The Attica (lots of key words to locate Athens were studied): Attic, all the adjectives to locate a place The Delos league gave Athens a lot of power: The Delos league= the Delian league-FleetAllies- to make an alliance with. Athens’ enemies: Enemies-to wage war on/against- to declare war on Key question: What did it mean to be citizen in Athens? Citizenship I/ Athens was a specific political system A: The Athenian constitution study of an organised chart Ecclesia-Boule-Helié-to be drawn/to draw-To be sorted by lot – At random=randomlybalance of power-Isonomy- legislative executive judiciary power-to elect- magistratestrategist-Institution-Ostracism-To account for/to give an account on-a term-to vote- to enforce-to make a decision- Misthos- Dike ( justice in Greek) Types of political systems: democracy , republic, dictatorship, authoritarian regime, monarchy, constitutional monarchy, absolute monarchy, theocracy. B: How to comment on a text using personal knowledge: Pericles funeral oration A funeral oration- to praise ( vanter les mérites de, prôner)-to be biased-skill- to be skilled- a half-thruthII Citizens and non-citizens A/ Ctizens B/ Non citizens Metics- Xenoi - Citizen-slaves- foreigners- dowry- epheby- to be registered- right of blood- a demo-to depend on- to be taken into account- to be left aside. III/ Rights and duties: A/ Rights B/ Duties Rights- duties- to make decisions-to respect- religion- religious belief-to pay a tax-war tribute- Panathenaic festival-a frieze-clepsydra- Polytheist- a procession- a giftC: So was the Athenian democracy a perfect political system? Fair- unfair- equal-unequal- gapsConclusion