Distributive Property
advertisement

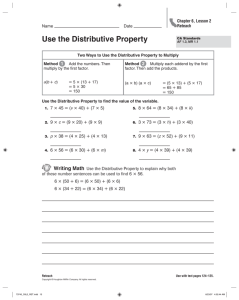
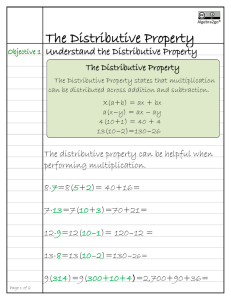
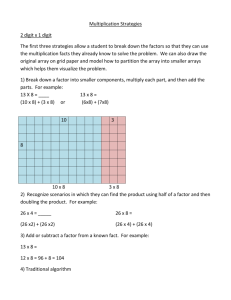
7.4 Distributive Property ALGEBRA ? Essential Question How can you use the Distributive Property to find products? Texas Essential Knowledge and Skills Number and Operations—3.4.E Represent multiplication facts by using a variety of approaches such as arrays, area models How can you use the Distributive Proper t y to f ind products? 3.4.K Solve one-step and two-step problems involving multiplication within 100 using strategies based on objects; pictorial models, including arrays, properties of operations Algebraic Reasoning—3.5.B Represent and solve one- and two-step multiplication problems within 100 using arrays, and equations Also 3.4.D, 3.5.D MATHEMATICAL PROCESSES 3.1.C Select tools, technology, and techniques 3.1.D Communicate mathematical ideas and reasoning 3.1.E Create and use representations Are You Ready? Lesson Opener Making Connections Invite students to tell you what they know about multiplying by 1, 5, and 6. What happens when you multiply any number by 1? (The answer is the same number.) What are different ways to multiply by 5? (Count by 5, add 5s) What are different ways to multiply by 6? (Count by 6, add 6s) Access Prior Knowledge Use the Are You Ready? 7.4 in the Assessment Guide to assess students’ understanding of the prerequisite skills for this lesson. Vocabulary Distributive Property Using the Digital Lesson Go to Multimedia eGlossary at thinkcentral.com You may wish to ask the students if they find it easier to multiply by 1 and 6 than to multiply by 7. Materials Learning Task What is the problem the students are trying to solve? Connect the story to the problem. • How far does Doc’s neighbor drive each day for work? (7 miles) • How many days per week does Doc’s neighbor drive to and from work? (5 days) • What operation could you use to find the total number of miles Doc’s neighbor drives for work per week? (Multiplication or addition) • What multiplication expression could you use to find the total number of miles Doc’s neighbor drives for work per week? (5 × 7) • What are different ways to solve 5 × 7? (Count by 7s, add 7 + 7 + 7 + 7 + 7, multiply 5 × 6 and add another 5) Literacy and Mathematics • Have students discuss the meaning of distribute in a larger context. Ask one student to distribute pieces of paper to each student to demonstrate the meaning of the word. • Have students write a short story about why Doc wants to know how many miles his neighbor drives. square tiles Resources For the student For the teacher Interactive Student Edition provides students with an interactive learning environment! Digital Management Center organizes program resources by TEKS! eTeacher Edition Math on the Spot Video Tutor Online Assessment System iTools Virtual Manipulatives Soar to Success Math Online Intervention Lesson 7.4 229A Name 7.4 Unlock the Problem ? Students should understand that they need to multiply the number of fish by the cost of each fish to find the total amount spent. ALGEBRA Number and Operations—3.4.E, 3.4.K Algebraic Reasoning— 3.5.B Also 3.4.D, 3.5.D MATHEMATICAL PROCESSES 3.1.C, 3.1.D, 3.1.E Distributive Property Essential Question How can you use the Distributive Property to find products? Unlock Unlock the the Problem Problem Mark bought 6 new fish for his aquarium. He paid $7 for each fish. How much did he spend in all? Have a volunteer read the definition of the Distributive Property. 6 groups of $7 • Circle the numbers you will use to solve the problem. Find 6 × $7. Activity • Describe the groups in this problem. You can use the Distributive Property to solve the problem. Work with students to make the array and break it apart. The Distributive Property states that multiplying a sum by a number is the same as multiplying each addend by the number and then adding the products. • How can you use the smaller arrays to find the total? Find the total for each smaller array and add them together. Activity • Does breaking apart a larger array into 2 smaller arrays make the problem easier to solve? Explain. Materials ■ square tiles Make an array with tiles to show 6 rows of 7. Yes; Possible explanation: I can use basic facts I already know to find the total for each smaller array and then add the totals to find the answer. Remember sum—the answer to an addition problem addends—the numbers being added Hands On Break apart the array to make two smaller arrays for facts you know. • Why do you think this is called the Distributive Property? Possible answer: because I am breaking apart the array so 6 multiplies both 2 and 5. 6×7= Mathematical Processes Use Math Talk to focus on students’ understanding of using a model to draw conclusions and explain reasons for their conclusions. Have several students draw their arrays on the board and write the multiplication problems they used to find 6 × 7. English Language Learners © Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company Math Talk ■ 6×5 Possible answers: 6 × (6 + 1); 6 × (4 + 3) 6×7=■ 6 × 7 = 6 × (5 + 2) Think: 7 = 5 + 2 Math Talk 6 × 7 = (6 × 5) + (6 × 2) Multiply each addend by 6. Mathematical Processes 30 + _ 12 6×7=_ Add the products. 42 6×7=_ ELL Language Support ELPS Beginning: Activity 36 2.E.3, 3.D.2, 3.F.2 Intermediate: Activity 22 1.A.1, 3.G.1, 4.C.1 Strategy: Identify Relationships Advanced: Activity 57 2.C.4, 3.D.2, 3.E Materials: square tiles Advanced High: Activity 30 1.F, 2.I.3, 3.H.3 229 Module 7 What other ways could you break apart the 6 × 7 array? 42 for his new fish. So, Mark spent $ _ Leveled Activities thinkcentral.com for the ELL Activity Guide containing these leveled activities. 6×2 Module 7 229 Kinesthetic / Auditory Small Group ELPS 2.C.4, 2.E.3, 3.D.2 • Students can understand the word distributive when they connect to the word distribute. • Put students in groups of 3. Give 1 student 7 tiles. • Distribute the 7 tiles among the other students. How did you distribute the tiles? I gave 4 to Sam and 3 to Nina. • Distribute sounds like distributive. What do you think the Distributive Property involves? distributing multiplication • Show students how the Distributive Property “distributes” multiplication by showing that 6 × (2 + 5) = (6 × 2) + (6 × 5). Share Share and and Show Show Draw a line to show how you could break apart this 6 × 8 array into two smaller arrays for facts you know. Possible answers given. 1. Share and Show The first problem connects to the learning model. Have students use the MathBoard to explain their thinking. 6 and _ 4 • What numbers do you multiply? _ 6 and _ 4 _ • 24 + _ 24 What numbers do you add? _ Use the checked exercises for Quick Check. Students should show their answers for the Quick Check on the MathBoard. Math Talk 4 +_ 4 ) 6 × 8 = 6 × (_ Mathematical Processes 6 ×_ 4 ) + (_ 6 ×_ 4 ) 6 × 8 = (_ Why do you have to add to find the total product when you use the Distributive Property? 24 + _ 24 6×8=_ 48 6×8=_ 3 2 Possible answer: I broke the larger array into two smaller arrays, so I have to add their products to find the total product. Write one way to break apart the array. Then find the product. Possible answers given. 2. Quick Check 1 a student misses the checked exercises IF 3. THEN 5 × (4 + 4) or (2 + 3) × 8 4 × (4 + 3) or (2 + 2) × 7 or (2 × 8) + (3 × 8); 40 or (2 × 7) + (2 × 7); 28 Problem Problem Solving Solving COMMON ERRORS C E Error When using the Distributive Property, students may break a number into its factors instead of its addends. Check students’ arrays and answers. Shade tiles to make an array that shows a fact with 7, 8, or 9 as a factor. Write the fact. Explain how you found the product. Possible explanation: I shaded 9 rows of 7 tiles. I can think 7 = 4 + 3. I can write 9 × 7 = 9 × (4 + 3); 9 × 7 = (9 × 4) + (9 × 3); 9 × 7 = 36 + 27 = 63 230 © Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company 4. Differentiate Instruction with RtI Tier 1 Lesson 34 Example 6 × 9 = (6 × 3) + (6 × 3) The student broke apart 9 into two factors, 3 and 3, instead of two addends, such as 3 and 6. Springboard to Learning Encourage students to write out their addition sentences before writing their multiplication sentences. For example: 6 × 9 = 6 × (6 + 3) = (6 × 6) + (6 × 3). Also have students use square tiles to reinforce the concept of breaking apart a larger array into two smaller arrays. If students complete the checked exercises correctly, they may continue with Problem 4. Enrich Logical / Mathematical Individual • Write the following problem on the board. 9×6=? • Challenge students to apply the Distributive Property, breaking apart one factor into 3 addends. Have them show each step of the process. Possible answers: (2 × 6) + (3 × 6) + (4 × 6) = 12 + 18 + 24 = 54 (3 × 6) + (3 × 6) + (3 × 6) = 18 + 18 + 18 = 54 • Then have students write another fact and repeat the process. Go to Go to thinkcentral.com for additional enrichment activities in the Enrich Activity Guide. Lesson 7.4 230 Name Problem Problem Solving Solving Problem Solving 5. Problems Problem 5 requires students to analyze a statement to find an error and justify their reasoning. No; possible answer: Robin can find 8 × 7 by multiplying 4 × 7 and doubling it. If she finds 3 × 7 and doubles it, she is finding 6 × 7. Go Deeper 6. To extend their thinking, in Problem 5 students must first recognize that there is an error through their understanding of the Distributive Property. Then they should explain why Robin’s way isn’t correct. Their explanation should include the correct answer. 8 × $9 = ■ 8 × 9 = (4 × 9) + (5 × 9) 8 × 9 = 36 + 45 8 × 9 = 81 Possible explanation: Brandon broke apart the If students have trouble finding the error that was made by Brandon, have students solve the problem and then compare their answer to his to find the error. factor 9 and multiplied by 9. He should have broken apart the factor 8 or multiplied by 8. Some students might realize that Brandon could have used the Distributive Property to solve (4 × 8) + (5 × 8) to get the correct answer of 72. Have students share any possible strategies they found to solve the problem. Through the Math on the Spot Video Tutor, students will be guided through an interactive solving of this type of H.O.T. problem. Use this video to also help students solve the H.O.T. problem in the Interactive Student Edition. With these videos and the H.O.T. problems, students will build skills needed in the TEXAS assessment. Multi-Step Brandon needs 8 boxes of spinners for his fishing club. The cost of each box is $9. How much will Brandon pay? Look at how Brandon solved the problem. Find and describe his error. For Problem 6, have students read the problem and discuss what they need to find. This problem requires higher order thinking skills and multiple steps to find and describe an error. Then they need to find the correct answer, showing each step. Use the array to help solve the problem and correct Brandon’s error. 8 × 9 = (4 + 4) × 9 4 ×_ 9 ) + (_ 4 ×_ 9 ) 8 × 9 = (_ © Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company M Math on the Spot Video Tutor V Sense or Nonsense? Robin says, “I can find 8 × 7 by multiplying 3 × 7 and doubling it.“ Does her statement make sense? Justify your answer. 36 + _ 36 8×9=_ 72 8×9=_ 72 for the spinners. So, Brandon will pay $ _ 3 RtI Tier 1 Lesson 34 2 1 Enrich 35 Name Name Math on the Spot videos are in the Interactive Student Edition and at thinkcentral.com. Module 7 • Lesson 4 231 LESSON 34 3.4.E, 3.4.K United Arrays Draw an array for each clue. Then use the arrays to solve each problem. A garden has 4 rows of 7 corn stalks. How many corn stalks in all are in the garden? You can use the Distributive Property to break an array into smaller arrays to help you find the answer. 1. Craig spent $27 to buy 3 calendars. The next day, he spent another $18 for more calendars. Each calendar cost the same amount. How many calendars did Craig buy? 2. On Monday, Mrs. Jones spent $32 on 4 books. On Tuesday, she spent $16 on more books. Each book cost the same amount. How many books did Mrs. Jones buy? 3. Hailey spent $12 to buy 2 fish. Her cousin spent double the amount on fish. Each fish cost the same amount. How many fish do Hailey and her cousin have altogether? Find 4 × 7. Step 1 Make an array to show 4 rows of 7. © Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company 4 4 4 4 231 Module 7 × × × × 7 7 7 7 4×4 16 + 4×3 + 12 = 28 6 books = 4 × (4 + 3) = (4 × 4) + (4 × 3) = 16 + 12 = 28 So, there are 28 corn stalks in all in the garden. Write one way to break apart the array. Then find the product. Possible answers are given. 1. 6 fish 2. 4. (3 × 4) + (3 × 5) or (2 × 5) + (1 × 5) or (1 × 9) + (2 × 9); 27 (3 × 3) + (3 × 2); Number and Operations Check students’ arrays. 5 calendars 4 rows of 7, or 4 × 7 Step 2 Break apart the array to make two smaller arrays for facts you know. Step 3 Write the multiplication for the new arrays. Multiply and then add the products to find the answer. Enrich 35 1 Algebra • Distributive Property OBJECTIVE Use the Distributive Property to find products by breaking apart arrays. Explain how you used the arrays to solve each problem. Possible answer: I drew two arrays for each problem then added the number of rows to find the number of items. 67 Enrich © Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company E35 Mathematical Processes Model ¥ Reason ¥ Communicate Daily Daily Assessment Assessment Task Task 3 Daily Assessment Task Fill in the bubble for the correct answer choice. You may use models or strategies to solve. 7. 8. 9. 36 C 48 B 42 D 64 (5 + 4) × 6 B (3 + 3) × 6 C (5 + 5) × 6 D (5 + 3) × 6 THEN IF NO • Soar to Success Math Warm-Up 12.22, 12.23 At a grocery store, the cans of nuts are arranged in 9 rows. There are 6 cans in each row. Which shows one way to find the total number of cans of nuts? A 1 Can students use the Distributive Property to find products? Use Diagrams Maurice planted 8 rows of popcorn plants. There are 6 plants in each row. The array shows Maurice’s garden. How many popcorn plants does Maurice have? A 2 YES • • Enrich 35 Homework and Practice Lesson 7.4 TEXAS Test Prep Coach Multi-Step Jillian bought 6 books for $7 each. She paid with $50. How much change should Jillian receive? A $37 C $43 B $18 D $8 Test Prep Coach helps teachers to identify common errors that students can make. In the Test Prep exercise, if students selected: A They broke the product into addends instead of the factors TEXAS Test Prep B They chose an example of the Associative Property Representation Which number sentence below is an example of the Distributive Property? A 6 × 8 = 40 + 8 B (8 × 2) × 3 = 8 × (2 × 3) C 6×8=8×6 D 6 × 8 = (6 × 2) + (6 × 6) 232 C The chose an example of the Commutative Property. © Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company 10. ? Essential Question Write Math How can you use the Distributive Property to find products? Possible answer: I can break apart one of the factors and multiply each addend by the other factor. Then I can add the products to find the answer. Differentiated Centers Kit Literature Collections Times Four Students read the book and determine how to use multiplication to find the total number of objects in each collection. Activities Factor Spin Students complete purple Activity Card 7 by using randomly generated factors to practice multiplication facts for 1, 2, 4, and 5. Activities Hurray for Arrays! Students complete blue Activity Card 15 by using arrays to model multiplication facts. Lesson 7.4 232 5 7.4 ALGEBRA Number and Operations—3.4.E, 3.4.K Algebraic Reasoning—3.5.B Also 3.4.D, 3.5.D MATHEMATICAL PROCESSES 3.1.C, 3.1.D, 3.1.E Name Fill in the bubble completely to show your answer. 5. Distributive Property Write one way to break apart the array. Then find the product. Possible answers are given for 1–2. 1. 3. TEXAS Test Prep Lesson Lesson Check Check 2. 4 × (4 + 4) or (1 + 3) × 8 or 5 × (4 + 2) or (2 + 3) × 6 or (2 × 8) + (2 × 8); 32 (2 × 6) + (3 × 6); 30 7. Shade tiles to make an array that shows a fact with 5, 6, or 7 as a factor. Explain how you found the product. Possible explanation: I shaded 7 rows There are 8 tables in the art class. Five students sit at each table. How many students are in the art class? 13 A 67 B 40 B 40 C 45 C 42 D 85 D 13 Jonas buys 6 packages of corn. Each package has 8 ears of corn. Which way can Jonas use to show how many ears of corn he buys? 8. (4 + 2) × 8 B (3 + 2) × 8 A (4 × 9) + (5 × 9) (6 + 6) × 8 B (3 × 5) + (6 × 5) (4 + 4) × 6 C (4 × 5) + (5 × 9) D (3 × 5) + (9 × 5) D Check students’ arrays and answers. 9. Problem Problem Solving Solving © Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company 4. Shawn makes a tile design by using 7 rows of 8 tiles. Explain how Shawn can break apart his design to find how many tiles he used. Possible explanation: Shawn can break apart the 7 to show 3 + 4. Then he can multiply and add: (8 × 3) + (8 × 4) = 24 + 32 = 56 Module 7 • Lesson 4 Homework and Practice Use the Homework and Practice pages to provide students with more practice on the concepts and skills of this lesson. 233-234 Module 7 A store sells bags of 9 apples. Mr. Hyon buys 5 bags of apples to make pies. Which way can Mr. Hyon use to show how many apples he buys? A 7 × 5 = 7 × (2 + 3); 7 × 5 = (7 × 2) + (7 × 3); 7 × 5 = 14 + 21 or 35. Seven large trucks are in a parking lot. Each truck has 6 wheels. How many wheels are there in all? A C of 5 tiles. I can think 5 = 2 + 3. I can write 6. 233 234 Multi-Step Minka buys 8 CDs for $6 each. She pays with three $20 bills. How much change should Minka receive? 10. Multi-Step Kent buys 5 bags of potatoes that cost $7 each. He gives the clerk $40. How much change should Kent receive? A $48 A $35 B $12 B $12 C $34 C $5 D $68 D $52 © Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company Ho mewo rk and Practice Module 7 Assessment Formative Assessment Vocabulary Vocabulary Vocabulary of Multiplication Distributive Property multiple 1. A ___ of 4 is any product that has 4 as one of its factors. 2. Use the Module Assessment to assess students’ learning and progress. The formative assessment provides the opportunity to adjust teaching methods for individual or whole class instruction. Commutative Property Choose the best term from the box to complete the sentence. multiple (p. 217) Distributive This is an example of the ___ Property. 3 × 8 = (3 × 6) + (3 × 2) This property states that multiplying a sum by a number is the same as multiplying each addend by the number and then adding the products. (p. 229) Concepts Concepts and and Skills Skills Write one way to break apart the array. Then find the product. q TEKS 3.4.E, 3.4.K Possible answers are given. 3. 4. 5 × (3 + 4) or (2 + 3) × 7 4 × (5 + 4) or (2 + 2) × 9 or (2 × 7) + (3 × 7); 35 or (2 × 9) + (2 × 9); 36 © Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company Find the product. 5. 3 3×1=_ 9. 2 × 1 _ q TEKS 3.4.E, 3.4.K 6. 10. 2 30 5×6=_ 6 × _6 36 11. 7. 6 × 7 _ 42 28 4×7=_ 12. 6 × 3 _ 18 8. 20 2 × 10 = _ 13. 3 × 8 _ 24 Module 7 235 Data-Driven Decision Making 3 2 1 Based on the results of the Module 7 Assessment, use the following i resources to strengthen individual or whole class instruction. Item Lesson TEKS* Common Error Intervene With RtI* Tier 1 Lessons Soar to Success Math 3, 4 7.4 3.4.E, 3.4.K May not understand how to find a product by breaking apart an array. 34 12.22, 12.23 5–13 7.1–7.2 3.4.E, 3.4.K May find an incorrect product when multiplying 31, 32 12.21, 12.22 12.23, 12.25 *TEKS—Texas Essential Knowledge and Skills; RtI—Response to Intervention Module 7 Assessment 235 Module 7 Assessment Name Module 7 Assessment Fill in the bubble for the correct answer choice. You may use models to solve. 14. TEXAS Test Prep Lori saw 6 lightning bugs. They each had 6 legs. How many legs did the lightning bugs have in all? q TEKS 3.4.E, 3.4.K 15. A 36 B 6 C 12 D 24 Zach gave his dog 1 dog biscuit each day, for 5 days. Then he gave his dog 2 dog biscuits a day for the next 5 days. How many biscuits did Zach give to his dog? q TEKS 3.4.E, 3.4.K 17. Items 1 3–13 2 14–17 B 30 C 15 D 7 Annette bought 4 boxes of pencils. If there are 8 pencils in each box, how many pencils did she buy? q TEKS 3.4.E, 3.4.K A 32 B 12 C 16 D 24 Shelly can paint 4 pictures in a day. How many pictures can she paint in 7 days? q TEKS 3.4.E, 3.4.K Record your answer and fill in the bubbles on the grid. Be sure to use the correct place value. Depth of Knowledge DOK Level 5 2 8 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 236 Data-Driven Decision Making © Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company 16. A 3 2 1 Item Lesson TEKS* Common Error Intervene With RtI* Tier 1 Lessons Soar to Success Math 14 7.3 3.4.E, 3.4.K May find an incorrect product when multiplying with 6 33 12.26, 12.28 15 7.2 3.4.E, 3.4.K May find an incorrect product when multiplying with 5 in a two-step problem 32 12.22, 12.23 16 7.1 3.4.E, 3.4.K May find an incorrect product when multiplying with 4 31 12.21, 12.25 17 7.1 3.4.E, 3.4.K May mark a gridded response item incorrectly when multiplying with 4 31 12.21, 12.25 *TEKS—Texas Essential Knowledge and Skills; RtI—Response to Intervention 236 Module 7 Assessment