certificate in counselling skills for medical practitioners
advertisement

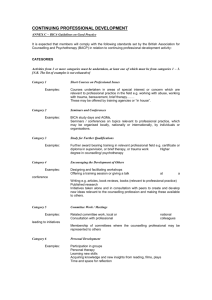
Jointly Organised and Presented by: CERTIFICATE IN COUNSELLING SKILLS FOR MEDICAL PRACTITIONERS (4TH INTAKE) An 8-week course, consisting of 6 topics and totaling ‘34’ contact hours 12 CME CORE POINTS IN FAMILY MEDICINE INTRODUCTION Counselling has become an integral part of an overall clinical management strategy. Empathic doctors achieve significantly better therapeutic outcome. Selecting the effective counselling approach can also facilitate the treatment process e.g. Cognitive Behavioural Therapy for Phobias and Addictions; Person-Centred Counselling for Bereavement and Stress; and Transactional Analysis Psychotherapy for Marital and Relationship Issues. This 8-week course offers medical practitioners an understanding of the counselling process and acquiring practical counselling skills, while developing the self. COURSE STRUCTURE Facilitator Week 1 (18 Aug 2007) Week 2 (25 Aug 2007) Week 3 (01 Sep 2007) Week 4 (08 Sep 2007) Week 5 (15 Sep 2007) Augustine Tan Augustine Tan Benny Bong Benny Bong A/Prof Cheong Pak Yean Prof Chee Kuan Tsee A/Prof Ong Thiew Chai Augustine Tan/Dr Tan Chue Tin Jessica Leong/Dr Tan Chue Tin : Micro-Skills in Counselling : Micro-Skills in Counselling : Counselling Intervention and Problem-Solving Process : Counselling Intervention and Problem-Solving Process : From Consultation to Counselling Overview of Psychological Disorders Week 6 (22 Sep 2007) : Counselling the Medically Ill Week 7 (29 Sep 2007) : Group Supervision / Case Conferencing Week 8 (06 Oct 2007) : Group Supervision / Case Conferencing LECTURE SCHEDULE / VENUE Classes will be held on Saturdays from 2.30pm to 5.30pm. Venue will be at the Administrative Conference Room/Doctors’ Dining Room, Level 2, Mount Elizabeth Medical Centre, 3 Mount Elizabeth, Singapore 228510. COURSE FEES S$985.00 inclusive of registration fee, group supervision, course notes, refreshments and GST. Participants may choose to go through an optional one hour of personal therapy with a counsellor accredited by the Academy at a subsidised rate of $75.00 per hour. TO APPLY Please contact Audrey at 9783 9219 (email: audrey@ecta.edu.sg) or visit our website at www.ecta.edu.sg FACULTY MEMBERS (The following lecturers are involved in the various courses run by ECTA) Dr Tan Chue Tin, Consultant Psychiatrist / Chairman & Medical Director, Executive Counselling & Training Academy Ms Jessica Leong, Psychotherapist / Clinical Director, Executive Counselling & Training Academy Dr Ang Yong Guan, Consultant Psychiatrist A/Prof Glen Bates, Professor of Psychology, Swinburne University of Technology, Melbourne Dr Irit Ben Ari, Cognitive-Behavioural Therapist, University of Haifa, Israel Mr Benny Bong, Psychotherapist Prof Chee Kuan Tsee, Emeritus Consultant Psychiatrist A/Prof Cheong Pak Yean, Consultant Physician Dr Amy Daniel, Psychotherapist A/Prof Calvin Fones, Consultant Psychiatrist Dr Daniel Fung, Consultant Child Psychiatrist Dr Lim Kok Kwang, Clinical Psychologist Ms Eva Lim, Psychotherapist A/Prof Ong Thiew Chai, Consultant Psychiatrist Dr Harold Robers, Clinical Psychologist Dr Cecilia Soong, Counsellor / Educator Mr Augustine Tan, Psychotherapist Mr Anthony Yeo, Family Psychotherapist Dr Brian Yeo, Consultant Psychiatrist COURSE COMPLETION A counselling certificate will be awarded by Mount Elizabeth Hospital and Executive Counselling and Training Academy upon acquiring 75% of attendance of the counselling course. * 40 doctors have graduated from this course. Some have gone on to other more in-depth counselling courses run by ECTA. CERTIFICATE IN COUNSELLING SKILLS FOR MEDICAL PRACTITIONERS (AWARDED 12 CME CORE POINTS IN FAMILY MEDICINE) This course is structured with the busy doctor in mind and integrates the special doctor-patient relationship into the counselling alliance and problem-solving interventions. In all there are eight weekly sessions covering five basic core modules: MODULE 1: MICRO-SKILLS IN COUNSELLING (18 & 25 August 2007) Synopsis: This competency-based module is designed to assist students in acquiring the basic micro-skills of counselling, as well as, an understanding of the change process and the counselling relationship. Primary emphasis is placed on the counselling interview and the development of the ‘self’ of the counsellor. Objectives: (i) to use micro-generic counselling skills (ii) to understand the ‘use of self’ in the counselling relationship MODULE 2: COUNSELLING INTERVENTION AND PROBLEM-SOLVING PROCESS (1 & 8 September 2007) Synopsis: Participants will learn to identify key counselling issues; to assess problem situation and strategise to problem-solve. Objectives: (i) to make an initial assessment of the presenting problem (ii) to use interviewing and problem-solving skills (iii) to develop a framework to intervene problems in a ‘patient-doctor’ relationship MODULE 3 (PART ONE): FROM CONSULTATION TO COUNSELLING (15 September 2007) Synopsis: An overview of the counselling theories in relation to medical practice. Participants will learn how to relate microskills in counselling to the clinical techniques used in medical consultation. They will also learn how to incorporate the formulation of counselling issues and intervention in clinical practice. Objectives: To integrate the theory and practice of counselling into the clinical situation. MODULE 3 (PART TWO): OVERVIEW OF PSYCHOLOGICAL DISORDERS (15 September 2007) Synopsis: Common psychiatric disorders like depression, anxiety, phobias, personality disorders and the psychoses have a wide range of clinical presentations. With the help of case histories, participants will learn how to recognise the essential diagnostic features of a particular psychiatric disorder and how they impact on the counselling relationship. Objectives: To be able to recognise the core symptoms of common psychiatric disorders. MODULE 4: COUNSELLING THE MEDICALLY ILL (22 September 2007) Synopsis: Medically ill patients are often anxious, depressed, guilt-ridden, angry and ambivalent. In many cases, they somatised their psychological problems. Such ‘fears’ will prevent effective communication and affect the doctor-patient relationship. Objectives: (i) to understand illness, the belief system and the fears relating to illnesses. The targets to be achieved in each from counselling (ii) to be aware of the common communication barriers in doctors and patients (iii) to recognise the characteristics of certain medical situations (iv) to be aware of the effects of positive and negative suggestions in communications MODULE 5: GROUP SUPERVISION / CASE CONFERENCING (29 September & 6 October 2007) Synopsis: The group supervision is designed for open conversation between the participants and a panelist comprising a psychiatrist, psychotherapist and family therapist. It will focus on counselling issues, therapeutic interventions, as well as ethical implications. Objectives: (i) to identify key counselling issues (ii) to raise supervisory issues (iii) to be aware of transference and counter-transference issues (iv) to be aware of ethical implications