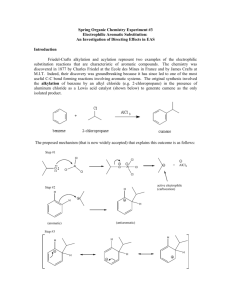
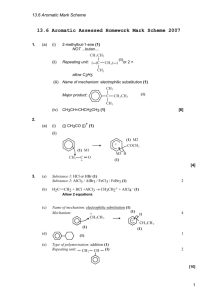
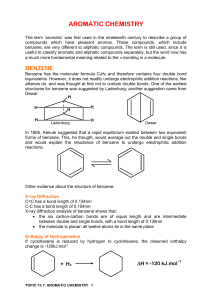
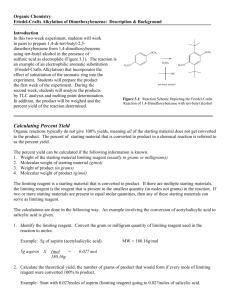
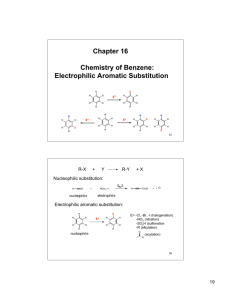
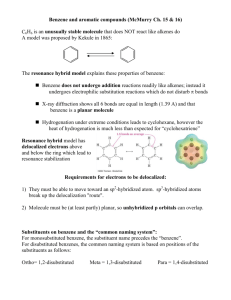
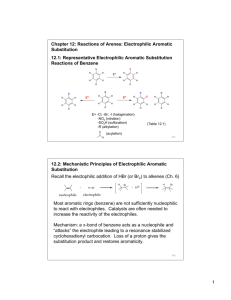
Reactions to functionalize benzene
advertisement
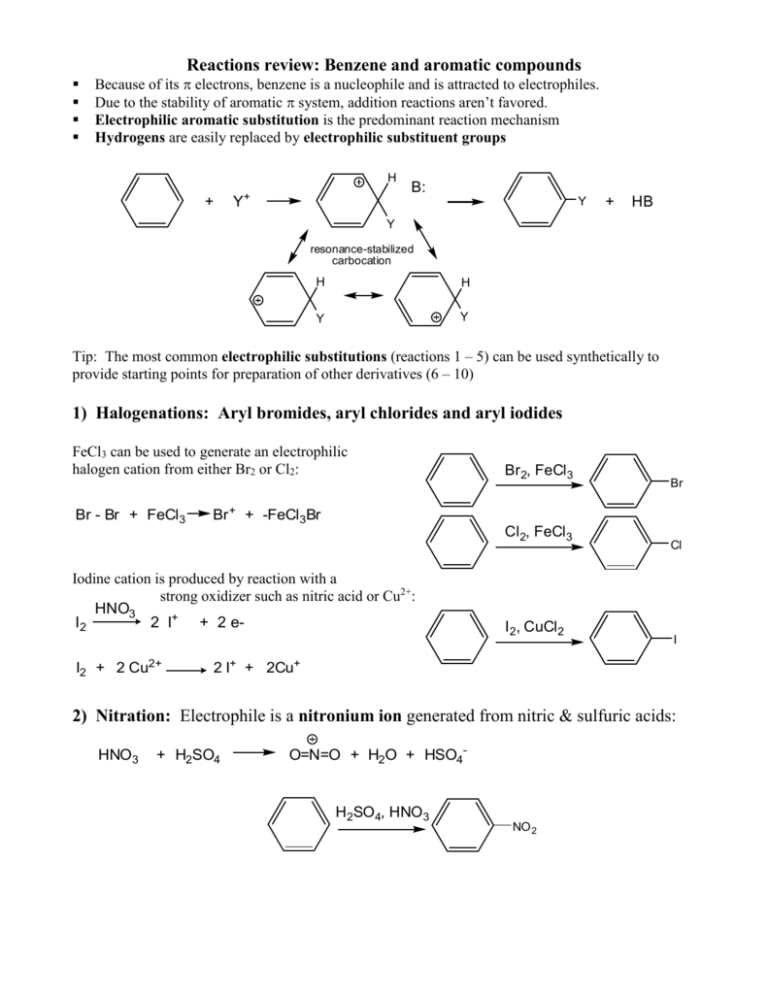
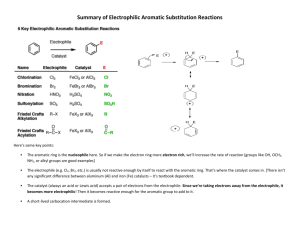
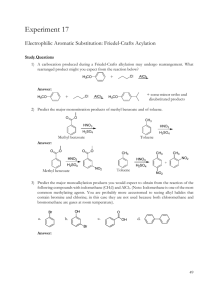
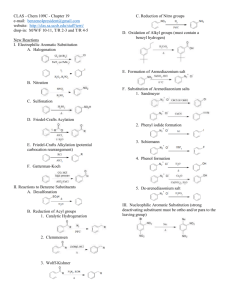
Reactions review: Benzene and aromatic compounds Because of its electrons, benzene is a nucleophile and is attracted to electrophiles. Due to the stability of aromatic system, addition reactions aren’t favored. Electrophilic aromatic substitution is the predominant reaction mechanism Hydrogens are easily replaced by electrophilic substituent groups H + Y+ B: Y + HB Y resonance-stabilized carbocation H H Y Y Tip: The most common electrophilic substitutions (reactions 1 – 5) can be used synthetically to provide starting points for preparation of other derivatives (6 – 10) 1) Halogenations: Aryl bromides, aryl chlorides and aryl iodides FeCl3 can be used to generate an electrophilic halogen cation from either Br2 or Cl2: Br - Br + FeCl3 Br 2, FeCl3 Br + + -FeCl3Br Cl2, FeCl3 Iodine cation is produced by reaction with a strong oxidizer such as nitric acid or Cu2+: HNO3 I2 2 I+ + 2 eI2 + 2 Cu2+ Br I 2, CuCl2 Cl I 2 I+ + 2Cu+ 2) Nitration: Electrophile is a nitronium ion generated from nitric & sulfuric acids: HNO3 + H2SO4 O=N=O + H2O + HSO4- H2SO4, HNO3 NO 2 3) Sulfonation/desulfonation: aryl sulfonates The electrophile (+SO3H) generated from fuming sulfuric acid reacts with benzene. The reverse, desulfonation occurs under conditions of heat and dilute acid H3O+ + SO3 O = S = O + H2O f uming H2 SO4 SO3H OH heat, dilute acid 3b) Alkali fusion: f uming H SO4 2 Treatment of sulfonates with base produces phenols SO3H 1) NaOH OH 2) H 3O+ heat, dilute acid (4) & (5) Friedel-Crafts acylations and alkylations Friedel-Crafts rxns are used to put an R group or an acyl group on benzene. Lewis acid AlCl3 used to generate an electrophilic “acylium ion” from an acyl or alkyl halide. Either of these electrophilic C species can undergo a substitution with benzene. acyl: alkyl: Cl R - C = O + AlCl3 [ R - C = O: R - Cl + AlCl3 R+ + -AlCl4 R - C = O: ] + -AlCl4 Alkylated aromatics: The Friedel-Crafts alkylation requires excess benzene, can’t take place with vinyl or aryl halides due to unstable carbocations and rearrangement of the carbocation possible: + H2 C H 2C AlCl3 H C Cl C H2 CH 3 + H2 C CH 3 C H2 CH 3 Aromatic ketones: The Friedel-Crafts acylation reaction requires excess AlCl3 due to tendency of complexation with carbonyl group and water to hydrolyze the Al salts O 1. AlCl3 + H3C C O C Cl 2. H2O CH 3 + Al(OH)3 + 3 HCl Aromatic aldehydes: Benzaldehydes can’t be made by F-C rxn; use Gattermann-Koch formylation: 1) NaOH 2) H 3O+ Reactions that transform substituents: Reactions (1) – (5) can be starting points for obtaining other substituents by transforming the product to another group 6) Grignard reactions with aryl halides: can prepare alcohols, benzoic acid Mg, ether OH RCHO Br Mg Br C H H 3O+ R O CO2 C OH H 3O+ 7) Phenols from aromatic halides: 1) NaOH, H 2O, o Cl 340 C, 2500 psi Elimination followed by addition: Alkali fusion of benzene sulfonates also produces phenols (see 3b) 2) OH H 3O+ 8) Reductions of nitro or carbonyl groups: Nitrobenzene to aniline: Wolff-Kishner reduction: O SnCl2, H+ NO 2 NH 2 OH- H2NN2H H2 C C CH3 NaOH 9) Oxidations of alkyl or amine groups: KMnO 4 CH 3 KMnO4 will oxidize any alkyl group having benzylic H to a COOH group COOH H3O+ Amino group can be oxidized back to nitro CF3CO 3H NH 2 NO 2 10) SN2 reactions at the benzylic carbon: Methyl group is brominated by NBS in a radical substitution, then the Br can be replaced by nucleophiles in SN2 reaction NBS CH 3 CH 2 Nu- Br NaOH CH2 Nu Gilman CN- CH 2 CH 2 OH CN C CH2 CH 3 H2 CH 3 Synthesizing polysubstituted benzene derivatives: Does the order of substituent placement matter? YES! When making polysubstituted benzenes, consider how the first substituent affects both the reactivity and orientation of the next substitution (consult Table 16.2) Ex: Friedel-Crafts reaction won’t proceed when the ring already has a deactivator Tips in planning synthesis: When ortho or para orientation is desired, put the activating group on first When meta orientation is desired, the deactivating group should go on first, provided that it doesn’t completely deactivate the ring (exception is Friedel-Crafts rxn) Take advantage of methods to convert activating to deactivating groups afterwards, for example CH3 to COOH or NH2 to NO2 Example: a multi-step synthesis of p-nitrobenzoic acid O2N CH 3 AlCl3 KMnO4 HNO3 CH 3Cl H 2SO 4 CH 3 H 3O+ O2N COOH