Curriculum Map for Modern Biology
advertisement

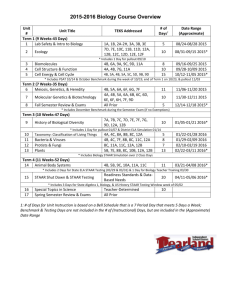
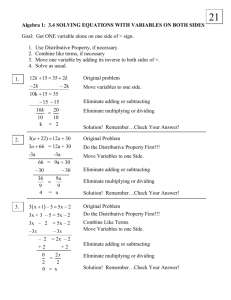
Modern Biology Stephen C. Wright Curriculum Map for Modern Biology Stephen C. Wright, Instructor 1st Quarter Unit Name - Introduction to Biology Objectives Students will know the following; What the word biology means and the meaning of different selected sciences, both physical and biological. A brief history of biology from primitive man to the present day, with some important contributions from specific scientists. (11B – Stage I – 1) The steps involved in the scientific method. (11A Stage H and I) The characteristics of life that all living things have. (12A – Stage I & J – 1) The physical conditions necessary for life. (12A – Stage I & J – 1) The 10 life actions that all living things have. (12A – Stage I & J – 1) The different kind of Heterotrophs. (12A – Stage I – 4) The difference between sexual and asexual reproduction (12A – Stage I – 4). The difference between biogenesis and abiogenesis and how abiogenesis was disproved. (11B – Stage I – 1) How life is classified into groups and what Binomial Nomenclature is. (12A – Stage I – 4) The five kingdoms of classification and at least one example of each kingdom. (12A – Stage I – 4) The difference between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. (12A – Stage I – 4) Safety procedures in order to conduct a laboratory. (13A – Stage I – 1) Students will be able to; Prepare a leaf collection using the instructions provided. (12A – Stage I – 4) Identify about 80 different kinds of trees by sight. (12A – Stage I – 4) Identify the different parts of a microscope. (11A – Stage H – 3, 12A Stage I - 2) Calculate the magnification of a microscope. (11A – Stage H – 3, 12A Stage I - 2) Focus a microscope and prepare a wet mount slide. (11A – Stage H – 3, 12A Stage I - 2) Identify an organism using a key. (12A – Stage I – 4) Construct a key that will identify another group of organism. (11B – Stage I – 2) Lesson Plan Overview Day 1 Day 2 Day 3 Day 4 Assign seats and pass out books. Go over class and lab rules. Begin lecture notes on how to prepare a leaf collection. Finish lecture on leaf collections. Lecture on objectives one and two. Assign vocabulary as homework. Collect vocabulary for a grade. Lecture on objectives three through eight Assign homework # 1. Check homework #1 and take a grade. Lecture on objectives nine through twelve. Modern Biology Day 5 Day 6 Day 7 Day 8 Day 9 Day 10 Stephen C. Wright Assign homework # 2. Check homework # 2 and take a grade. Assign homework # 3. Begin the exercise on classification of animals. Check homework # 3 and take a grade. Finish classification exercise. Lecture on microscopes. Assign microscope homework. Check microscope homework and take a grade. Begin microscope lab. Finish microscope lab. Review for test. Test on chapter Assign vocabulary from basic chemistry chapter. State Performance Descriptors 11A - Students who meet the standard know and apply the concepts, principles, and processes of scientific inquiry. (Stage H) 1. Formulate issue-specific hypothesis, generating inquiry questions for an issue investigational premise, or differentiating qualitative and quantitative data and their applicability, or using conceptual/mathematical/ physical models, or previewing associated research. 2. Design scientific issue investigation which addresses proposed hypothesis(es), proposing applicable survey instruments, or selecting associated research, analysis, and communication components. 3. Conduct issue investigation, using technologies for data collection and assimilation, or following established formats for random sampling, or following all procedural and safety precautions, materials and equipment handling directions. 4. Interpret and represent analysis of results, evaluating data sets to explore explanations of unexpected responses and data concurrence, or evaluating survey validity and reliability, or analyzing research and data for supporting or refuting the hypothesis. 11B - Students who meet the standard know and apply the concepts, principles, and processes of technological design. (Stage I) 1. Identify an historic engineering feat, innovation or model, researching historic dilemmas which necessitated new scientific or engineering solutions, or brainstorming the kinds of barriers or circumstances that existed, or identifying the simulation materials and procedural sequence which can simulate historic conditions, or determining success criteria, design constraints, and testing logistics encountered. 2. Construct innovation model, sketching progressive schematics of the design, or collecting appropriate materials, supplies, and safety equipment, or completing assembly of innovation or model. 12A - Students who meet the standard know and apply concepts that explain how living things function, adapt, and change. (Stage I) Modern Biology Stephen C. Wright 1. Apply scientific inquiries or technological designs to analyze the cellular organelles and functions, using different microscopic techniques, explaining functional processes chemically and structurally (e.g., osmotic, active and facilitated transport, enzyme action and protein/lipid/carbohydrate metabolism). 2. Apply scientific inquiries or technological designs to analyze the cellular organelles and functions, using different microscopic techniques, or explaining functional processes chemically and structurally (e.g., osmotic, active and facilitated transport, enzyme action and protein/lipid/carbohydrate metabolism). 4. Apply scientific inquiries or technological designs to compare taxonomic criteria among organisms, examining unicellular, colonial, and multi-cellular organisms for common and differing characteristics. 12A - Students who meet the standard know and apply concepts that explain how living things function, adapt, and change. (Stage J) 1. Apply scientific inquiries or technological designs to explain biochemical reactions, diagramming metabolic, hormonal, regulatory, feedback or transport molecular models in and between organ systems, explaining homeostasis, or tracing the balance of cellular ATP. 13A - Students who meet the standard know and apply accepted practices of science. (Stage I) 1. Apply appropriate principles of safety, following established procedures to maintain both personal & environmental safety when handling & disposing of chemicals, estimating risks/benefits to alternative procedures, mapping classroom laboratory facilities for safe egress & distances/times to access safety treatment features, manipulating, reading and troubleshooting scientific equipment safely, communicating school science storage and disposal policies for classroom investigations, demonstrating safety practices and emergency procedures pertaining to laboratory and field work, researching community disposal procedures (e.g., mercury thermometers or lead batteries), or participating in household waste and hazardous waste pickup programs in Illinois. 2. Apply scientific habits of mind to curricular investigations in life, environmental, physical, earth, and space sciences, identifying instances of how scientific reasoning, insight, creativity, skill, intellectual honesty, tolerance of ambiguity, skepticism, persistence, openness to new ideas, and sheer luck have been integral to discoveries, identifying specific studies which demonstrate how scientific conclusions are open to modification as new data are collected, or researching classroom and real-world standards for peer review. Unit Name – Basic Chemistry Objectives Students will know the following; What matter is and what it is composed of. (12C – Stage H – 3) What an atom is and the three main parts it is composed of. (12C – Stage H – 3) What an element is and how many occur naturally. (12C – Stage H – 3) The difference between an ion and an isotope. (12C – Stage H – 3) What compounds and molecules are. (12C – Stage I – 4) What a chemical symbol and chemical formula are. (12C – Stage H – 3) What the subscript number and coefficient numbers of a chemical formula mean. (12C – Stage H – 3) Modern Biology Stephen C. Wright What a mixture is, be able to describe the three different kinds of mixture, and give an example of each. (12C – Stage I – 4) The four different types of organic compounds. (12C – Stage I – 4) The components that comprise carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids. (12C – Stage I – 4) Students will be able to; Use a periodic table to figure the number of protons, neutrons, and electrons an atom has. (12C – Stage H – 3) Draw a model of different kinds of atoms. (12C – Stage H – 3) List the common elements found in the body. (12C – Stage H – 3) Explain the difference between an acid and a base. ( 12A – Stage I – 1) Use a pH scale to measure acids and bases. (11A – Stage I – 3 & 4) Test unknown samples of carbohydrates to determine if they are monosaccharides, disaccharides, or polysaccharide. (11A – Stage I – 3 & 4) Determine is an unknown substances contains a fat or protein when tested. (11A – Stage I – 3 & 4) Tell the difference between a monosaccharides, disaccharide, and polysaccharide, and give an example of each one. (12C – Stage I – 4) Lesson Plan Overview Day 1 Day 2 Day 3 Day 4 Day 5 Day 6 Day 7 Day 8 Day 9 Collect vocabulary Go over test in class Lecture on objectives one, two, and three Show students how to do a Bohr model of an atom. Assign atom drawings as homework. Go over atom drawings in class on the chalkboard. Assign quiz for day three. Lecture on objectives three through six. Assign problem solving worksheet. Take quiz Check problem solving worksheet Lecture on objectives seven through nine. Assign chapter checkup worksheet, and skills worksheet Check the chapter checkup worksheet and skills worksheet in class. Do pH lab. Start Carbohydrate lab Finish Carbohydrate lab Start Fat and Protein lab Finish Fat and Protein lab Review for test Test on Chapter Assign vocabulary on cell unit State Performance Descriptors Modern Biology Stephen C. Wright 11A - Students who meet the standard know and apply the concepts, principles, and processes of scientific inquiry. (Stage I) 3. Conduct inquiry investigation, using technologies for observing and measuring directly, indirectly, or remotely, completing multiple, statistically-valid trials, or accurately and precisely recording all data. 4. Interpret and represent analysis of results to produce findings that support or refute inquiry hypothesis, evaluating data sets to explore explanations of outliers or sources of error and trends, or applying statistical methods to compare mode, mean, percent error and frequency functions. 11B - Students who meet the standard know and apply the concepts, principles, and processes of technological design. (Stage H) 1. Collect and record data accurately, using consistent metric measuring and recording techniques with necessary precision, or recording data accurately in appropriate format, or graphing data appropriately according to the tested variables. 2. Represent results of analysis to produce findings, comparing data sets according to the design criteria, or evaluating multiple prototype solutions to the overall design success criteria, or proposing explanations for sources of error in the data set with regards to product design flaws, or model limitations. 12A - Students who meet the standard know and apply concepts that explain how living things function, adapt, and change. (Stage I) 1. Apply scientific inquiries or technological designs to explain metabolic processes within cells and between organisms and their environment, explaining gas exchange, food processing, transport, excretion, locomotion, body regulation, and nervous control, investigating enzyme actions in various reactions, or describing the applications of the polar nature of water and the pH index in biochemical reactions. 12C - Students who meet the standard know and apply concepts that describe properties of matter and energy and the interactions between them. (Stage H) 3. Apply scientific inquiries or technological designs to examine the chemical and physical characteristics of matter, constructing and discussing models and charts that explain these properties, or investigating the relationships among atoms, molecules, elements, and compounds, or classifying objects and mixtures based on these properties, or explaining the organization of elements in the Periodic Table, or investigating the properties of gases at varying temperatures and pressures. 12C - Students who meet the standard know and apply concepts that describe properties of matter and energy and the interactions between them. (Stage I) 4. Apply scientific inquiries or technological designs to explain how physical and chemical structures of matter affect its properties, relating bonding types and shapes of molecules to organic and inorganic compounds, or examining the colligative properties of solutes on the properties of solutions/mixtures. 13A - Students who meet the standard know and apply accepted practices of science. (Stage H) 1. Apply appropriate principles of safety within and beyond the science classroom, communicating and following clear instructions, or mapping classrooms for safe egress Modern Biology Stephen C. Wright and distances/times to access safety treatment features, or demonstrating safety practices and emergency procedures pertaining to laboratory and field work, or explaining the basis of safety practices and procedures. 2. Apply scientific habits of mind to curricular investigations in life, environmental, physical, earth, and space sciences, evaluating evidence, or inferring statements based on data, or questioning sources of information, or explaining necessity of manipulating only one variable at a time, or retrieving mathematical data accurately for scientific analysis. Unit Name - Cell Objectives Students will know the following; What the cell theory is. (12A – Stage I – 2) The scientists who made important discoveries about the cell. The difference between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. (12A – Stage I – 2) The common parts of a cell and be able to give their function. (12A – Stage I – 2) The difference between a chemical and physical change. (12C – Stage H – 3) The difference between a semipermeable, permeable, and impermeable membrane. (12A – Stage I – 2) The three things that affect the rate of diffusion. (12A – Stage I – 2) The difference between an isotonic, hypotonic and hypertonic solution. (12A – Stage I – 2) Students will be able to; Identify the common parts of the cell by labeling different drawings and illustrations. (12A – Stage I – 2) Be able to tell how plant and animal cells are different. (12A – Stage I – 2) List and define the different methods of cellular transportation. (12A – Stage I – 2) Examine the different structures of a cell. (11A – Stage I – 3 & 4, 12A – Stage I – 2) Make a model of a cell with dialysis tubing. (11A – Stage I – 3 & 4, 12A – Stage I – 2) Find out if iodine solution will pass through dialysis tubing. (11A – Stage I – 3 & 4, 12A – Stage I – 2) State how dialysis tubing might be like a cell membrane. (11A – Stage I – 3 & 4, 12A – Stage I – 2) Lesson Plan Overview Day 1 Collect vocabulary Go over test in class Lecture on objectives one through five. Have students fill out handout on structures of the cell as the lecture goes on. Assign Vocab. Review and cell drawing as homework. Day 2 Check homework on vocab. review and take a grade. Lecture on objectives six through eight. Assign chapter checkup as homework. Assign students to bring a pencil for class on days three through five. Assign Test for day seven. Assign quiz on cell parts. Day 3 Take quiz Do Cell lab. Day 4 Modern Biology Day 5 Day 6 Day 7 Stephen C. Wright Finish Cell lab Do Cell Permeability lab Check homework Review for test Test on Chapter Assign vocabulary on cellular chemistry unit State Performance Descriptors 11A - Students who meet the standard know and apply the concepts, principles, and processes of scientific inquiry. (Stage I) 3. Conduct inquiry investigation, using technologies for observing and measuring directly, indirectly, or remotely, completing multiple, statistically-valid trials, or accurately and precisely recording all data. 4. Interpret and represent analysis of results to produce findings that support or refute inquiry hypothesis, evaluating data sets to explore explanations of outliers or sources of error and trends, or applying statistical methods to compare mode, mean, percent error and frequency functions. 11B - Students who meet the standard know and apply the concepts, principles, and processes of technological design. (Stage H) 5. Report the process and results of a design investigation, selecting graphs and charts that effectively report the design data, or making oral and/or written presentations, or proposing logical explanations of success or errors, or generating additional design modifications which can be tested later. 12A - Students who meet the standard know and apply concepts that explain how living things function, adapt, and change. (Stage I) 2. Apply scientific inquiries or technological designs to analyze the cellular organelles and functions, using different microscopic techniques, or explaining functional processes chemically and structurally (e.g., osmotic, active and facilitated transport, enzyme action and protein/lipid/carbohydrate metabolism). Unit Name – Cellular Chemistry Objectives Students will know the following; What the word metabolism means. (12A – Stage H – 1, 12A – Stage I – 1) The difference between a catabolic reaction and an anabolic reaction. (12A – Stage H – 1, 12A – Stage I – 1) The difference between an endergonic and exergonic reaction. (12A – Stage H – 1, 12A – Stage I – 1) Three factors that affect enzyme action. (12A – Stage H – 1 & 2) The difference between aerobic and anaerobic respiration. (12A – Stage H – 1) The three main parts of cell respiration – glycolysis, krebs cycle, and electron Modern Biology Stephen C. Wright transport chain, and be able to describe what happens in each. (12A – Stage H – 1) Students will be able to; Explain how enzyme work by using two different models – lock and key model and induced fit model. (12A – Stage H – 1 & 2) Use iodine test for the presence of starch. (12A – Stage H – 1) Use Benedict’s solution to test for the presence of glucose. (12A – Stage H – 1) Look for evidence of enzyme action by testing a starch solution to which salivary amylase (an enzyme) has been added. (12A – Stage H – 1 & 2) Demonstrate the activity of an enzyme in living tissues. (12A – Stage H – 1 & 2) Learn how changes in temperature and pH affect the activity of catalase. (12A – Stage H – 1 & 2, 11A – Stage H – 1-5) Experimentally test for the presence of catalase in living tissues. (12A – Stage H – 1 & 2, 11A – Stage H – 1-5) Analyze three factors affecting enzyme action. (12A – Stage H – 1 & 2, 11A – Stage H – 1-5) Lesson Plan Overview Day 1 Day 2 Day 3 Day 4 Day 5 Day 6 Day 7 Day 8 Go over test in class Collect vocabulary Lecture on objectives one through three and all notes on enzymes. Assign HW # 1 Check homework #1 Lecture on Cell Respiration. Assign HW # 2 Check HW #2 Finish notes of Krebs Cycle and Electron Transport Chain. Assign HW #3 Do Amylase Lab Start Catalase Lab Finish Catalase Lab Check HW #3 Review for Test Test on Chapter Assign vocabulary on DNA/RNA State Performance Descriptors 11A - Students who meet the standard know and apply the concepts, principles, and processes of scientific inquiry. (Stage H) 1. Formulate issue-specific hypothesis, generating inquiry questions for an issue investigational premise, or differentiating qualitative and quantitative data and their applicability, or using conceptual/mathematical/ physical models, or previewing associated research. 2. Design scientific issue investigation which addresses proposed hypothesis(es), proposing applicable survey instruments, or selecting associated research, analysis, and communication components. 3. Conduct issue investigation, using technologies for data collection and assimilation, or Modern Biology Stephen C. Wright following established formats for random sampling, or following all procedural and safety precautions, materials and equipment handling directions. 4. Interpret and represent analysis of results, evaluating data sets to explore explanations of unexpected responses and data concurrence, or evaluating survey validity and reliability, or analyzing research and data for supporting or refuting the hypothesis. 5. Report the process and results of a design investigation, selecting graphs and charts that effectively report the design data, or making oral and/or written presentations, or proposing logical explanations of success or errors, or generating additional design modifications which can be tested later. 12A - Students who meet the standard know and apply concepts that explain how living things function, adapt, and change. (Stage H) 1. Apply scientific inquiries or technological designs to explain the chemical nature of biological processes, describing photosynthesis in terms of basic requirements and products, correlating respiration, or diagramming the nitrogen, water, oxygen, and carbon cycles with reference to ecosystem-to-molecular levels. 2. Apply scientific inquiries or technological designs to analyze the cellular organelles and functions, using different microscopic techniques, or explaining functional processes chemically and structurally (e.g., osmotic, active and facilitated transport, enzyme action and protein/lipid/carbohydrate metabolism). 12A - Students who meet the standard know and apply concepts that explain how living things function, adapt, and change. (Stage I) 1. Apply scientific inquiries or technological designs to explain metabolic processes within cells and between organisms and their environment, explaining gas exchange, food processing, transport, excretion, locomotion, body regulation, and nervous control, investigating enzyme actions in various reactions, or describing the applications of the polar nature of water and the pH index in biochemical reactions. Unit Name – DNA and RNA Objectives Students will know the following; The importance of chromosomes. (12A – Stage I – 3) The name of the structure of DNA and also the two scientists who discovered it. (12A – Stage I – 3) Students will be able to; Describe the parts that compose a DNA molecule and explain how a DNA molecule is put together. (12A – Stage I – 3) Describe the replication of DNA. (12A – Stage I – 3) Describe the transcription of DNA molecule into a near double molecule of mRNA. (12A – Stage I – 3) Describe the translation of mRNA into a protein chain. (12A – Stage I – 3) Build a model of a DNA molecule. (12A – Stage I – 3) Extract DNA from wheat germ. (11A – Stage I – 3 & 4) Lesson Plan Overview Day 1 Go over test in class Collect vocabulary Lecture on DNA Objectives. Modern Biology Day 2 Day 3 Day 4 Day 5 Day 6 Day 7 Stephen C. Wright Assign HW # 1 and #2 Build DNA model. Check HW # 1 and # 2 Lecture on DNA replication and RNA transcription. Assign HW # 3. Go over HW # 3 Lecture on Protein Synthesis. Assign HW # 4 DNA Extraction Lab Go over HW # 4 Review for Test. Test on Chapter Assign vocabulary on Cell Division. State Performance Descriptors 11A - Students who meet the standard know and apply the concepts, principles, and processes of scientific inquiry. (Stage I) 3. 4. Collect and record data accurately, using consistent metric measuring and recording techniques with necessary precision, or recording data accurately in appropriate format, or graphing data appropriately according to the tested variables. Represent results of analysis to produce findings, comparing data sets according to the design criteria, or evaluating multiple prototype solutions to the overall design success criteria, or proposing explanations for sources of error in the data set with regards to product design flaws, or model limitations. 12A - Students who meet the standard know and apply concepts that explain how living things function, adapt, and change. (Stage I) 3. Apply scientific inquiries or technological designs to explain the molecular nature of the genetic code, explaining the function, chemical reactions, and schematic diagrams of the molecular components of DNA, RNA and simple proteins, exploring the processes of recombinant DNA research, describing the role of chromosomes in the normal and aberrant display of hereditary traits, mutations and disease. Modern Biology Stephen C. Wright Second Quarter Unit Name – Cell Division Objectives Students will know the following; The difference between meiosis and mitosis. The difference between haploid and diploid. The two kinds of meiosis (spermatogenesis and oogenesis). What gametes are and be able to give two examples. Students will be able to; Describe what events happen in each phase of mitosis. Draw a picture of each phase of mitosis. Describe what goes on during the process of oogenesis and spermatogenesis. Recognize the different phases of mitosis under a microscope. Find the different phases of mitosis using an allium root tip slide or a whitefish blastula slide. Lesson Plan Overview Day 1 Day 2 Day 3 Day 4 Day 5 Day 6 Day 7 Go over test in class Collect vocabulary Lecture on Mitosis Watch video clip of actual cells in mitosis Assign HW on mitosis Check homework on mitosis. Assign second mitosis homework. Start lab on Onion Root Tip Slides and Whitefish Blastula Check 2nd mitosis homework. Finish lab. Start notes on meiosis. Give examples of haploid and diploid on the chalk board. Go over notes on oogenesis and draw diagrams of it. Assign homework on meiosis and oogenesis. Check HW on meiosis and oogenesis. Lecture on spermatogenesis and draw diagrams of it. Assign HW on spermatogenesis. Check HW on spermatogenesis. Review for Test Test on Chapter Assign vocabulary on Basic Genetics. State Performance Descriptors