Diversity - Blyth-Biology11
advertisement

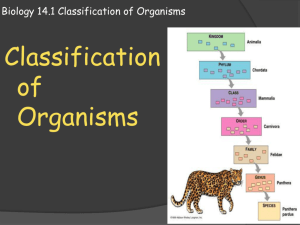
SBI3U Classification Name: _____________________ Taxonomy: Kingdom: Phylogeny: Organisms share common ancestry if they show similar stages of ____________________________ ________________________________________________________________________________. The Linnean System of Classification This system of naming and classifying organisms, or taxonomy, is known as ___________________________ ________________________________ and groups organisms according to their structural similarities. The first part of the name refers to the ___________ of the organism – a relatively small group of related species to which the species belongs. The second part of the name is the _______________ and usually describes an important characteristic of the organism. The ______________ is the smallest group where the organisms are most like each other. Organisms within a species ________ interbreed and produce viable offspring. What does that mean? ______________________________________________________________________________ The _______________ is the next grouping and are very similar to one another. Eg. Canis (dogs, wolves, etc.) Similar genera are grouped into a _____________. E.g. Hominidae (humans, chimps, and gorillas). Similar families are grouped into an ____________. Similar orders are grouped into a _____________. Similar classes are grouped into a ____________. There are 7 main taxon groups: K _________________ P*_________________ And similar phyla are grouped into a ______________. C _________________ 6 Kingdom Classification O _________________ *based on structure, function, evolutionary and biochemical relationships 1) _________________ 2) _________________ 3) _________________ 4) _________________ 5) _________________ 6) _________________ F _________________ G _________________ S _________________ *called “division” for plants and fungi Home Fun: Try your hand at classifying three life forms and learn about taxonomy. Launch the interactive program at: http://www.pbs.org/wgbh/nova/nature/classifying-life.html Write out the KPCOFGS for the 3 organisms given. SBI 3U Classifying Life The many ways to classify life! In biology, people study millions upon millions of different animals, plants, bacteria, etc., but how do they know how to classify them? Well, biology set up these different orders of classification. Life: All things that live, pretty simple. Domain: The broadest range of classification for life, under which falls kingdom, phylum, class, order, family, genus, species. There are currently three domains, and they are Archaea, Bacteria, and Eukarya. (Domain is the largest range of classification besides life.) Kingdom: Kingdoms are a very broad, but a smaller level of classification. Under this falls phylum, class, order, family, genus, species. There are currently six kingdoms (as of 2012, so this may be invalid whenever scientists decide to mess with the kingdoms again). Phylum: The next classification level, with a much greater number containing 35 different classification groups. Under this falls class, order, family, genus, and species. Phylum is the first real classification level where the organisms in it show similar evolutionary traits. Class: Now getting under class, organisms begin showing many similarities with others of its group. The rank of class also includes many terms people know, such as mammalia (or mammal). There are a great deal more classes then there are phyla, because the requirements becomes more refined and fewer organisms fit into each class. Below this is order, family, genus, and species. Order: The next step down after class. That’s it. Nothing more to really say. Stop reading about order. Family: Yet another step down after order. It refines organisms with particular, specific characteristics into similar groups. Organisms at this stage usually look similar. Genus: Second to last classification level. The scientific name of an organism group makes up part of its scientific name or binomial nomenclature (e.g. "Homo sapiens"). The part Homo is the genus of the organism. Below this falls species. Species: The last level of classification. The Species name makes up the second word in an organisms name/binomial nomenclature. For example, the lupus in canis lupus. Most likely scientists will make more changes to this several times every year for the rest of forever, but, for now, this is how you classify life.