PERIODIC TABLE 4 SQUARE QUESTIONS 1. What is the atomic
advertisement
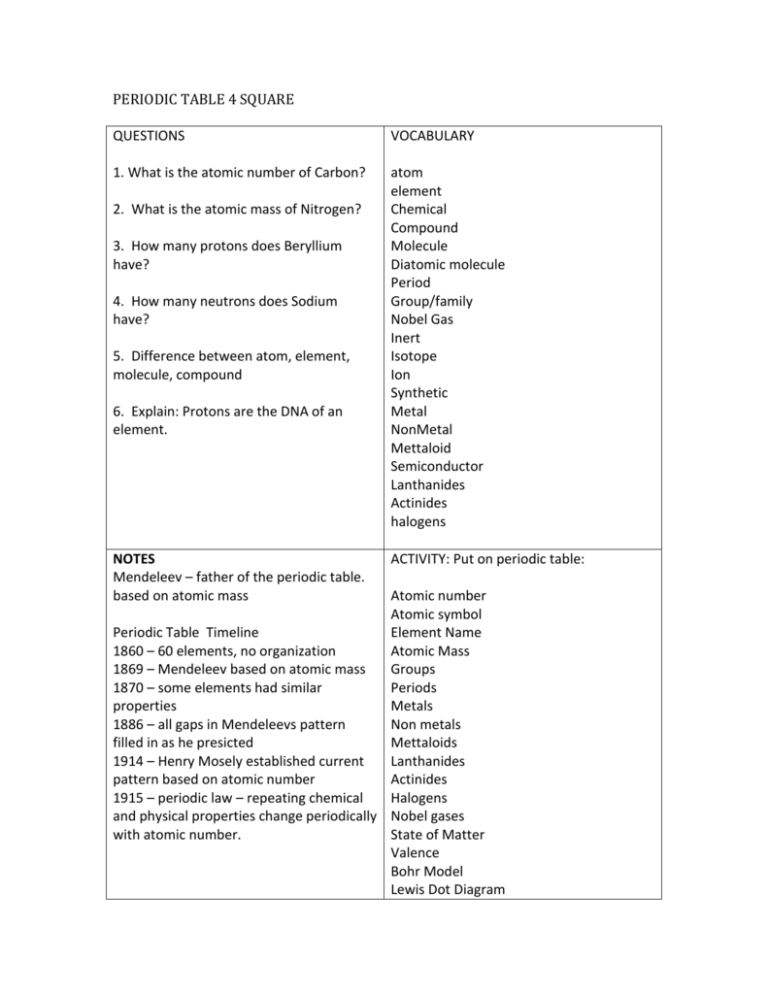
PERIODIC TABLE 4 SQUARE QUESTIONS VOCABULARY 1. What is the atomic number of Carbon? atom element Chemical Compound Molecule Diatomic molecule Period Group/family Nobel Gas Inert Isotope Ion Synthetic Metal NonMetal Mettaloid Semiconductor Lanthanides Actinides halogens 2. What is the atomic mass of Nitrogen? 3. How many protons does Beryllium have? 4. How many neutrons does Sodium have? 5. Difference between atom, element, molecule, compound 6. Explain: Protons are the DNA of an element. NOTES Mendeleev – father of the periodic table. based on atomic mass ACTIVITY: Put on periodic table: Atomic number Atomic symbol Periodic Table Timeline Element Name 1860 – 60 elements, no organization Atomic Mass 1869 – Mendeleev based on atomic mass Groups 1870 – some elements had similar Periods properties Metals 1886 – all gaps in Mendeleevs pattern Non metals filled in as he presicted Mettaloids 1914 – Henry Mosely established current Lanthanides pattern based on atomic number Actinides 1915 – periodic law – repeating chemical Halogens and physical properties change periodically Nobel gases with atomic number. State of Matter Valence Bohr Model Lewis Dot Diagram atom – smallest unit of an element that has all the properties of that element. element - pure substance that cannot be separated into simpler substances chemical – any substance with a defined composition compound – pure substance composed of 2 or more elements chemically combined molecule - smallest unit of a compound that has all the properties of that compound. Molecules are made up of atoms that are held together by chemical bonds. diatomic molecule – molecule made up of 2 atoms of the same element period – horizontal(left to right) row of elements group/family – vertical (top to bottom) column of elements nobel gases – un reactive non metals, group 18 on periodic table inert – cannot form chemical bonds beause they have full energy shells ions – charged particles that form when atoms gains or loose electrons isotope – atoms in a group that has the same number of protons as other atoms of that element but a different number of neutrons. synthetic – man made in a lab, not natural metal - shiny, conduct heat energy and electric current, malleable non-metals – dull, do not conduct heat or electricity, brittle mettaloids – properties of both metals and non-metals, called semiconductors semiconductor – properties of both metal and non-metal lanthanides – shiny reactive metals actinides – all radioactive or unstable halogens – very reactive nonmetals







