All information in this publication was received between 01 July
advertisement
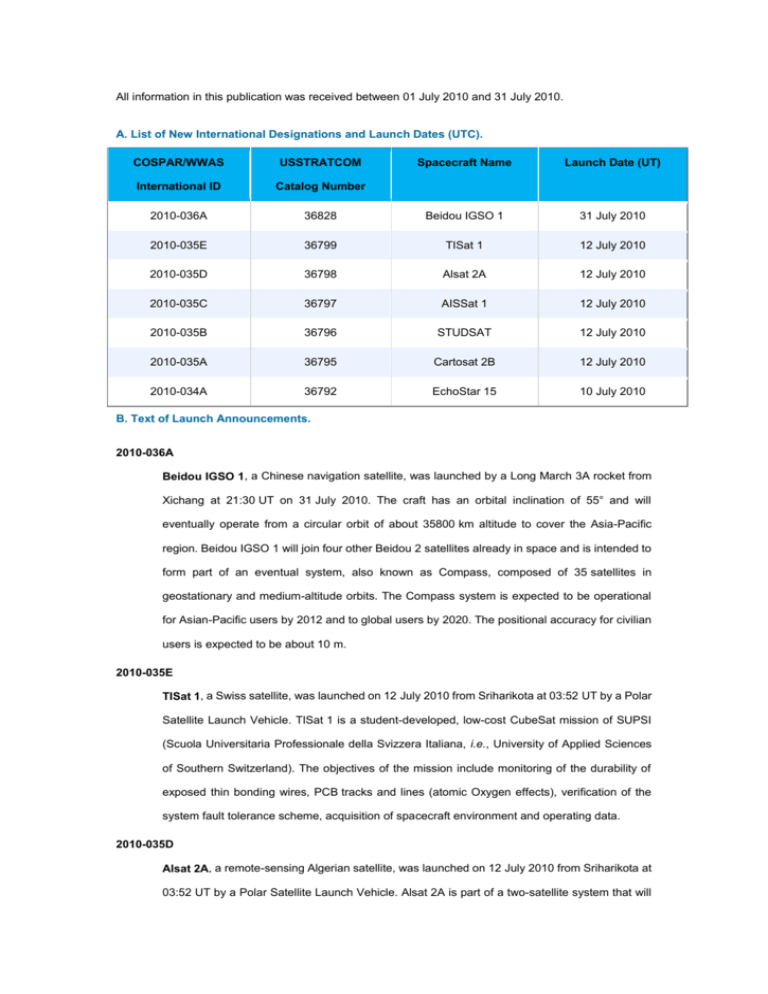
All information in this publication was received between 01 July 2010 and 31 July 2010. A. List of New International Designations and Launch Dates (UTC). COSPAR/WWAS USSTRATCOM Spacecraft Name Launch Date (UT) International ID Catalog Number 2010-036A 36828 Beidou IGSO 1 31 July 2010 2010-035E 36799 TISat 1 12 July 2010 2010-035D 36798 Alsat 2A 12 July 2010 2010-035C 36797 AISSat 1 12 July 2010 2010-035B 36796 STUDSAT 12 July 2010 2010-035A 36795 Cartosat 2B 12 July 2010 2010-034A 36792 EchoStar 15 10 July 2010 B. Text of Launch Announcements. 2010-036A Beidou IGSO 1, a Chinese navigation satellite, was launched by a Long March 3A rocket from Xichang at 21:30 UT on 31 July 2010. The craft has an orbital inclination of 55° and will eventually operate from a circular orbit of about 35800 km altitude to cover the Asia-Pacific region. Beidou IGSO 1 will join four other Beidou 2 satellites already in space and is intended to form part of an eventual system, also known as Compass, composed of 35 satellites in geostationary and medium-altitude orbits. The Compass system is expected to be operational for Asian-Pacific users by 2012 and to global users by 2020. The positional accuracy for civilian users is expected to be about 10 m. 2010-035E TISat 1, a Swiss satellite, was launched on 12 July 2010 from Sriharikota at 03:52 UT by a Polar Satellite Launch Vehicle. TISat 1 is a student-developed, low-cost CubeSat mission of SUPSI (Scuola Universitaria Professionale della Svizzera Italiana, i.e., University of Applied Sciences of Southern Switzerland). The objectives of the mission include monitoring of the durability of exposed thin bonding wires, PCB tracks and lines (atomic Oxygen effects), verification of the system fault tolerance scheme, acquisition of spacecraft environment and operating data. 2010-035D Alsat 2A, a remote-sensing Algerian satellite, was launched on 12 July 2010 from Sriharikota at 03:52 UT by a Polar Satellite Launch Vehicle. Alsat 2A is part of a two-satellite system that will enable Algeria to obtain very high-quality images for use in a wide variety of applications, including cartography, management of agriculture, forestry, water, mineral and oil resources, crop protection, management of natural disasters and land planning. Alsat 2B, the second part of the satellite system, will launch at a later date. 2010-035C AISSat 1, a Norwegian satellite, was launched on 12 July 2010 from Sriharikota at 03:52 UT by a Polar Satellite Launch Vehicle. AISSat 1 is equipped with an instrument that receives and forwards Automatic Identification System (AIS) signals, a radio communications network with transmitters on most large vessels. Using AIS the satellite will demonstrate maritime ship-tracking technologies. 2010-035B STUDSAT (STUDent SATellite), an Indian satellite, was launched on 12 July 2010 from Sriharikota at 03:52 UT by a Polar Satellite Launch Vehicle. The main objective of the satellite is to perform remote sensing and capture images of the surface of the Earth using its camera of resolution 90 m, which will be used for vegetation and terrain mapping. STUDSAT was designed and developed by a consortium of seven Engineering Colleges from Bangalore (4) and Hyderabad (3). The mission life is slated to be six months. 2010-035A Cartosat 2B, an Indian Earth observation satellite, was launched on 12 July 2010 at 03:52 UT from Sriharikota. The 694 kg satellite was launched by a Polar Satellite Launch Vehicle. The satellite carries a panchromatic, high spatial resolution, stereoscopic vision camera. The satellite's black and white camera has a resolution of 0.8 m and will observe Earth land and ocean surfaces from orbit. The imagery will have applications in resource mapping, urban planning, transportation studies, water monitoring, and crop inventories. 2010-034A EchoStar 15, a US communications satellite, was launched on a Proton-M rocket with a Breeze M upper stage from Baikonur on 10 July 2010 at 18:40 UT. The craft weighed 5521 kg. The satellite will broadcast direct-to-home programming service to the eastern half of the United States. In the coming weeks, ground controllers will command the satellite's own engine to circularize the orbit at about 35800 km altitude above the equator where the craft will match the Earth's rotation and appear parked at 61.5° W longitude. EchoStar 15 carries 32 Ku-band transponders and has a design life of 15 years. It will replace EchoStar 3.







