96292_BubbleGumLab12
advertisement

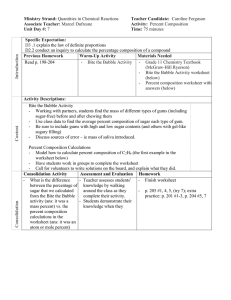
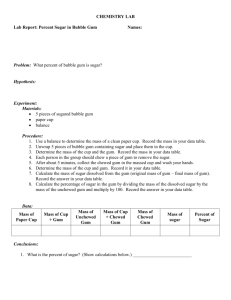
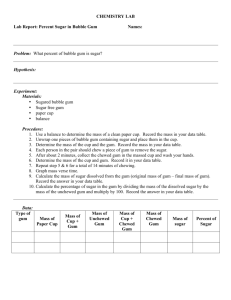
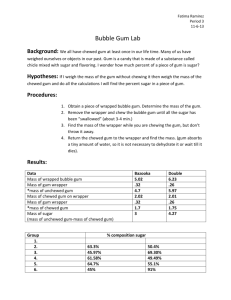
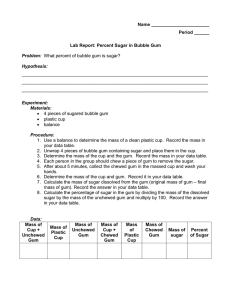
Integrated Science Name ______________________________ Bubble Gum Lab Purpose: To determine the mass of sugar in 2 pieces of gum. To determine the density of 2 pieces of gum. and calculate the % sugar content of each Materials: Ruler balance weigh paper or dish 2 pieces of different gums Procedure WORK IN PAIRS, but do your OWN paper! 1. Determine the mass of each piece of bubble gum in the wrapper. Record in Table, step 1. 2. Unwrap gum. Determine the volume of each piece of gum by measuring the length, width, and height in centimeters. a. Length: ______cm Width: ______cm Height: ______cm b. Volume = Length x Width x Height = ___________cm3 Record in Table, step 2 3. Calculate the density of each piece of bubble gum. a. Density = Mass Volume (step 1 step 2) Record in Table, step 3 4. Chew each piece of gum for five minutes. (You do one, your partner the other. If you do not have a partner, just do one piece, and copy a neighbor’s data for the other.) 5. After chewing, place your gum wad on its wrapper to dry. Re-measure the mass. Record in Table, Step 5. 6. Subtract the chewed mass from the whole mass (step 1) of each piece of gum. Record in Table, Difference in Mass, step 6. (Step 1 – Step 5) 7. Calculate the % sugar in each piece: divide the difference in mass (step 6 calculation) from the total mass for each piece of gum (step 1) and multiply x 100. % sugar = ( Difference in Mass Mass in step 1 ) x 100% Record in Table, step 7 Data Table Gum Type Double Bubble Step 1 Mass (g) Step 2 Step 3 Volume * Density (cm3) (g/cm3) Step 5 Chewed Mass (g) Step 6 Difference in Mass Step 7 % Sugar Questions 1. Which gum was more dense? ________________________ 2. Which gum has a greater % of sugar? _________________ 3. Are questions 1 and 2 related? That is, does the density have anything to do with the percentage of sugar present? Explain! Practice Problems 1. Two cans of soda, both having a volume of 355 mL, are put in a tank of water. One can floats and the other sinks. Can A has a mass of 360 grams, and Can B has a mass of 350 grams. a. Calculate the density of EACH can – SHOW YOUR SET-UP, INCLUDE UNITS! b. Which can, A or B, sank in the water tank? WHY? 2. Why does an ice cube float on water? i.e, WHY is it less dense? 3. Predict what will happen to the objects below when they are placed in the three solutions by writing “float” or “sink” in columns 2, 3 and 4. Object/Density In Water/D=1.0 g/mL Rock/D=3.5 g/mL Plastic/D=.9 g/mL Cork/D=.6 g/mL Egg/ D= 1.1 g/mL In Alcohol/D=.8 g/mL In Salt Water/D=1.2 g/mL