More Notes on plates, earthquakes, and volcanoes
advertisement

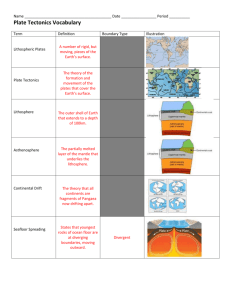
Effects of plate movement : Earthquakes, Volcanoes, Tsunamis Mountains, Sea-floor spreading, and Mid-ocean Ridges There are 3 types of plate boundaries : Convergent (plates move towards each other), Divergent (plates move away from each other), and Transform (plates slide past each other) All boundaries produce earthquakes Volcanoes form at divergent and convergent boundaries Seafloor spreading and Mid-Ocean ridges form at divergent boundaries There are 3 types of CONVERGENT boundaries: OceanicOceanic, Oceanic-Continental, Continental-Continental Subduction zones (where one plate subduct—slides under— another) occur at convergent boundaries involving one or more oceanic plates. Oceanic-Oceanic convergent boundaries produce underwater volcanoes, trenches, volcanic islands, and earthquakes. Oceanic-Continental convergent boundaries produce volcanoes/volcanic mountains, trenches, and earthquakes. Continental-Continental convergent boundaries produce folded mountains/mountain ranges, high plateaus, and earthquakes Transform boundaries produce earthquakes only. Each boundary type produces it’s own type of fault: Divergent produces a normal fault Convergent produces a reverse fault Transform produces a strike-slip fault The most famous transform boundary and strike slip fault is the San Andreas Fault, which runs through California and Mexico for about 800km (500mi) At each type of fault or boundary there is a different type of stress (a force that is applied to the plates or rock): There are 3 types of stress forces: Tension, Compression, and Shear Tension is when the rock is pulled apart or stretched Compression is when rock is squeezed or pushed together until it is folded or breaks Shear is when rock moves in opposite directions and breaks