NOTES – IONIC COMPOUNDS – CHAPTER 8
advertisement

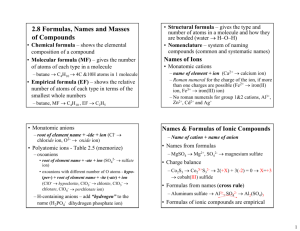
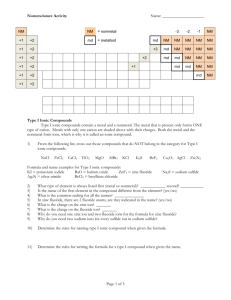
NOTES – IONIC COMPOUNDS – I. Chemical Bonds A. Definition 1. Why do atoms form bonds? 2. How do atoms form bonds? B. Formation of Cations (+ ions) 1. atoms lose one or more electrons a. 2. 3. examples of atoms that form cations a. b. c. C. Formation of Anions (- ions) 1. atoms that gain one or more electrons 2. 3. examples of atoms that form anions a. b. c. D. Ion Formation in Representative Elements Group Gain or Lose Charge of Ion _____________________________________________________________________________ 1 (1A) --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------2 (2A) --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------13 (3A) --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------14 (4A) --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------15 (5A) --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------16 (6A) --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------17 (7A) II. Formation and Nature of Ionic Bonds A. Formation (steps) 1. atom “M” loses electron(s) _________________________ 2. atom “N” gains electron(s) _________________________ 3. a. 4. electrostatic force that holds the oppositely charged ions together is the ________________ B. Ionic Compounds 1. 2. types of ionic compounds a. oxides b. salts c. binary compounds C. Properties of Ionic Compounds 1. for crystal lattices a. 2. high melting and boiling points a. 3. hard, rigid, brittle solids 4. nonconductors of electricity as solids a. III. Names and Formulas A. Formulas for Ionic Compounds 1. vocabulary a. formula unit b. monoatomic ion c. oxidation number d. polyatomic ion 2. composition of ionic compounds a. metal + nonmetal b. metal + polyatomic ion c. polyatomic ion + nonmetal d. polyatomic ion + polyatomic ion B. Formulas for Ionic Compounds 1. write formula for the _______________________first, then the ______________________ 2. Use_____________________________to indicate number of ions (criss-cross charges) a. sum of charges should be___________________ b. never change subscripts in __________________________________ c. put ____________________________________in parentheses when there is more than 1 C. Writing Names of Ionic Compounds 1. write the name of the ______________________first then the _______________________ a. IV. Metallic Bonds – Properties of Metals A. Metallic Bonds 1. valence electrons are __________________________________ a. 2. bond is formed by 3. “electron sea model” B. Properties of Metals 1. 2. 3. malleable a. 4. ductile a. 5. 6. 7. hardness and strength varies a. C. Alloys 1. mixture of two or more elements with metallic properties 2. types a. substitutional – b. interstitial