File
advertisement

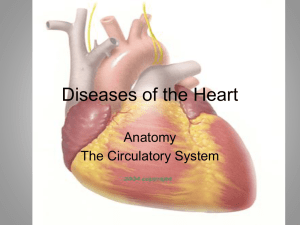
I can: Explain that plants require transport systems to move substances such as water from one place to another State that plants require water to transport materials and carry out photosynthesis State that water and minerals are transported through plants in xylem vessels State that xylem vessels are strengthened by lignin. Identify epidermal cells in leaves and state that they allow light to pass through to mesophyll cells. State that stomata are pores on the leaf epidermis that allow gas exchange State that the opening and closing of stomata is controlled by guard cells. Describe transpiration as water loss through the leaves of a plant State that water is lost by evaporation through the stomata. Describe the flow of water from the root hair cells, up xylem vessels and into the mesophyll cells of the leaf, finally leaving the plant by diffusing through the stomata. State that sugar is transported up and down the plant in living phloem cells. State that substances such as oxygen, nutrients and carbon dioxide are transported in the blood. State that red blood cells transport oxygen around the body. State that red blood cells contain a substance called haemoglobin that is involved in transporting oxygen. Describe how the biconcave shape of a red blood cell increases its surface area so oxygen can diffuse into it as quickly as possible. State that red blood cells do not have a nucleus so they can carry as much haemoglobin as possible. Describe the structure of arteries, including thick muscular walls to withstand blood travelling at high pressure and a narrow central channel. Describe the structure of veins, including thinner walls and a wider central channel than arteries. State that the blood in veins is at a much lower pressure than the blood in arteries, and they contain valves to prevent the backflow of blood. State that capillaries form networks at organs and tissues. Describe the features of capillaries such as thin walls and large surface area to allow the exchange of materials between the blood and body cells. Identify the top chambers of the heart as the left and right atria Identify the lower chambers of the heart as the left and right ventricles State that the pulmonary artery carries blood from the heart to the lungs, and the pulmonary vein carries blood from the lungs back to the heart State that the vena cava carry blood from the body to the heart and the aorta carries blood from the heart to the body. State that the coronary arteries supply the heart muscle with blood. Describe the flow of blood around the body, right atrium right ventricle pulmonary artery lungs pulmonary vein left atrium left ventricle aorta body vena cava right atrium. State that rings of cartilage hold the airways open at all times State that gas exchange in the lungs involves the movement of oxygen into the blood and carbon dioxide out of the blood State that gas exchange takes place in the alveoli Describe the features of the alveoli such as large surface area, thin walls, and good blood supply which allows efficient gas exchange. State that mucus in the airways traps dust and microorganisms State that cilia move the mucus up and out of the lungs. State that food is moved through the digestive system by peristalsis Describe the process of peristalsis as contraction of the muscles behind the food and relaxation of the muscles in front. State that villi contain a blood capillary to absorb glucose and amino acids, and a lacteal to absorb products of fat digestion. Describe features that allow villi to carry out absorption efficiently, including having a large surface area and thin walls.