Report on the predicted TFs in the Dicty genome
advertisement

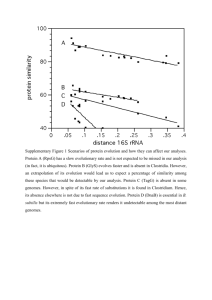
Report on the predicted TFs in the Dicty genome M. Madan Babu and Sarah. A. Teichmann Aim: To predict and analyse the transcription factors in the Dicty genome in terms of the DNA binding domain family, partner domains and compare their occurrence in other genomes. Materials: Martin M and Sarah K provided the Pfam and Superfamily assignments for the Dicty predicted proteins sequences (and for the other genomes). I identified 159 families (of the 5600 Pfam families) that can bind DNA and are seen in TFs. I also identified 47 Superfamilies (out of 1200 SCOP superfamilies) that are seen in DNA binding proteins. I then removed models of enzymes belonging to DNA binding domain superfamilies from subsequent analysis. Independently, Sarah Teichmann confirmed this list of models. Results: 1. From the Pfam assignments, there were 111 sequences, which were predicted to be TFs based on the occurrence of particular DNA binding domains. 2. From the Sfam assignments, there were 76 sequences that were predicted to be TFs based on the occurrence of particular DNA binding domains. The assignments were filtered so that models of enzymes belonging to DNA binding domain superfamilies were removed (For example, the superfamily winged helix DNA binding domain, has a family of enzymatic domains that do not bind DNA – the methionine amino peptidase insert domain, for instance). 3. Overlap between the two predictions: 55 sequences have been predicted as TFs by both Pfam and Sfam, and 51 and 21 sequences were uniquely predicted as TFs by Pfam and Sfam respectively. 4. The 111 sequences predicted as TFs using Pfam assignments belong to 15 different protein families. Their occurrence is as follows: # 1 1 DNA binding domain ARID DDT # 2 2 DNA binding domain Rcd1 YEATS 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 E2F_TDP HTH_3 NOT NmrA Not1 PAH Plus-3 SART-1 Ssrecog TBP WRKY YL1 zf-NF-X1 2 2 3 3 4 5 5 6 6 9 12 13 23 Zn_clus zf-MIZ HMG_box SRF-TF zf-C2H2 SAP SIR2 CBFD_NFYB_HMF homeobox PHD GATA bZIP myb_DNA-binding We clearly find that the myb_DNA-binding domain has expanded in Dicty. These belong to the SANT domain family that specifically recognize the sequence YAAC(G/T)G. The next popular DNA binding domain is the bZIP domain and the GATA domain. The GATA domain is a zinc finger domain that uses four Cys residues to coordinate the Zn ion and specifically recognise the sequences (A/T)GATA(A/G). 5. When we analyse the sequences that Sfam predicts to be TFs, we get the following statistics (The DBDs come from 13 different families): # 1 1 1 1 2 2 3 3 3 6 6 16 31 DNA binding domain 46774 – ARID like 47113 – Histone fold 47413 - lambda repressor-like DNA-binding domains 47954 - Cyclin-like 47454 - A DNA-binding domain in eukaryotic transcription factors 57701 - Zn2/Cys6 DNA-binding domain 47095 - HMG-box 55455 – SRF-like 57903 - FYVE/PHD zinc finger 46785 - "Winged helix" DNA-binding domain 57667 - C2H2 and C2HC zinc fingers 57716 - Glucocorticoid receptor-like (DNA-binding domain) 46689 - Homeodomain-like Here, we clearly find that the Homeodomain-like DBD has been expanded in the Dicty lineage. The next over-represented DBD is the Glucocorticoid receptor-like DNA binding domain, which has been expanded in C. elegans to a large extent. Table 1a and 1b compares the occurrences of DBDs in the other genomes. 6. If we look at the partner domains for the 111 Tfs, they come from 28 different families (+15 DNA binding domain families). These are: ARID, BRCT, CBFD_NFYB_HMF, DDT, DnaJ, E2F_TDP, GATA, HMG_box, HTH_3, NOT, NmrA, Not1, PAH, PHD, Plus-3, Rcd1, SAP, SART-1, SIR2, SRFTF, Ssrecog, SWIRM, TBP, WRKY, YEATS, YL1, ZZ, Zn_clus, ank, bZIP, bromodomain, histone, Homeobox, jmjC, jmjN, myb_DNA-binding, polyprenyl_synt, rrm, zf-C2H2, zf-MIZ, zf-NF-X1, zf-UBP, zf-UBR1 Domain content for the individual predicted TFs from Pfam assignments: http://www.mrc-lmb.cam.ac.uk/genomes/dtf/pf.tf.domain.content 7. Similarly for Sfam predicted TFs, they come from 12 families (+13 DNA binding domain families). These are: "Chaperone J-domain", "Homeodomain-like", "ARID-like", ""Winged helix" DNAbinding domain", "HMG-box", "Histone-fold", "lambda repressor-like DNA-binding domains", "A DNA-binding domain in eukaryotic transcription factors", "EF-hand", "Cyclin-like", "Ankyrin repeat", "Concanavalin A-like lectins/glucanases", "PH domain-like", "Rap30/74 interaction domains", "RNI-like", "BRCT domain", "P-loop containing nucleotide triphosphate hydrolases", "RNA-binding domain, RBD", "SRFlike", "Protein kinase-like (PK-like)", "C2H2 and C2HC zinc fingers", "Zn2/Cys6 DNA-binding domain", "Glucocorticoid receptor-like (DNA-binding domain)", "FYVE/PHD zinc finger", "Glycerol-3-phosphate (1)-acyltransferase" Domain content for the TFs predicted from Sfam assignments: http://www.mrc-lmb.cam.ac.uk/genomes/dtf/sf.tf.domain.content 8. Comparison of DBD occurrence in other genomes Occurrences of Sfam – DBDs in comparison to other genomes: Sfamily 46774 47113 47413 47954 47454 57701 47095 ec 0 0 29 0 0 0 0 sc 2 5 1 0 0 53 7 Ds 1 1 1 1 2 2 3 ce 8 2 9 2 17 0 27 mm 23 6 23 6 31 0 151 hs 19 5 24 3 30 0 77 at 10 15 4 1 1 0 22 55455 57903 46785 57667 57716 46689 0 1 115 0 0 43 4 13 19 30 10 21 3 3 6 6 16 31 3 42 93 125 361 222 6 88 151 1068 20 312 7 80 160 1039 19 319 113 61 44 58 32 283 9. Occurrences of Pfam – DBDs in comparison to other genomes: Pfamily ARID DDT E2F_TDP HTH_3 NOT NmrA Not1 PAH Plus-3 SART-1 SSrecog TBP WRKY YL1 zf-NF-X1 Rcd1 YEATS Zn_clus zf-MIZ HMG_box SRF-TF zf-C2H2 SAP SIR2 CBFD_NFYB_HMF homeobox PHD GATA BZIP myb_DNA-binding ec 0 0 0 12 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 Sc 2 1 0 1 0 0 1 1 1 0 1 1 0 1 1 1 3 51 2 7 4 37 5 4 4 0 14 10 8 0 ds 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 2 2 2 2 3 3 4 5 5 6 6 9 12 13 23 ce 9 8 6 1 0 0 1 2 1 2 2 3 0 3 2 2 2 0 8 32 3 160 11 6 7 0 47 29 24 0 mm 23 8 16 1 0 0 1 6 1 1 1 7 0 1 3 1 5 0 10 157 6 1104 31 10 8 0 100 16 50 0 hs 23 7 9 1 0 0 2 4 1 1 1 4 0 1 5 2 4 0 9 84 7 973 26 13 9 0 97 15 40 0 at 9 6 12 3 0 0 1 22 6 2 1 3 81 1 2 3 2 0 2 14 111 49 8 5 31 0 60 31 75 0 From these results we clearly see that different DBDs have been expanded in a lineage specific manner in the different genomes. For Dicty, Homeodomain (Myb_DNA-binding domain), GATA and BZIP domain containing proteins have expanded in a lineage specific manner. 10. Predicted TFs from other genomes Numbers of DNA-binding transcription factors in model organisms Organism E. coli S. cerevisiae Dicty C. elegans M. musculus H. sapiens A. thaliana Number of transcripts Number of proteins with DNA-binding domains Percentage of transcripts containing DNA-binding domains 4,280 6,357 12,730 31,677 32,911 32,036+ 28,787 267 245 132 1463 2460 2604 1667 6.2% 3.9% 1.0% 4.6% 7.4% 8.1% 5.7% DNA-binding domain assignments from Pfam and SUPERFAMILY were used to establish the repertoire of DNA-binding transcription factors in model organisms. Expectation value threshold of 0.002 was used in making the assignments. Coregulators that do not bind DNA directly are excluded. We find that the fraction of the genome coding TFs in the Dicty genome is remarkably small. This would mean that most of the transcriptional regulation could happen purely by chromatin remodelling as seen in some parasites like P. falciparum or that uncharacterised Dicty specific DBD exists. Supplementary information: http://www.mrc-lmb.cam.ac.uk/genomes/dtf/ Information on pfam and sfam assignments for the predicted TFs as tab delimited file: http://www.mrc-lmb.cam.ac.uk/genomes/dtf/tfs.domain.content Format: Identifier \t Pfam_assignment \t Sfam_assignment Pfam DBD occurrence profile: http://www.mrc-lmb.cam.ac.uk/genomes/dtf/pf.profile.ec.sc.ds.ce.mm.hs.at Format: Family \t ec \t sc \t ds \t ce \t mm \t hs \t at Sfam DBD occurrence profile: http://www.mrc-lmb.cam.ac.uk/genomes/dtf/sf.profile.ec.sc.ds.ce.mm.hs.at Format: Family \t ec \t sc \t ds \t ce \t mm \t hs \t at