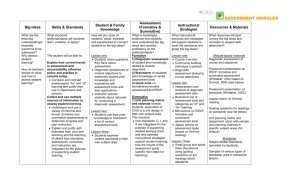
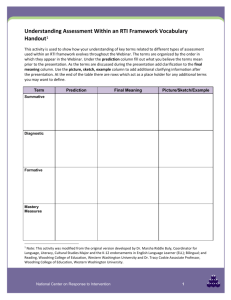
Example Unit Planning Matrix
advertisement
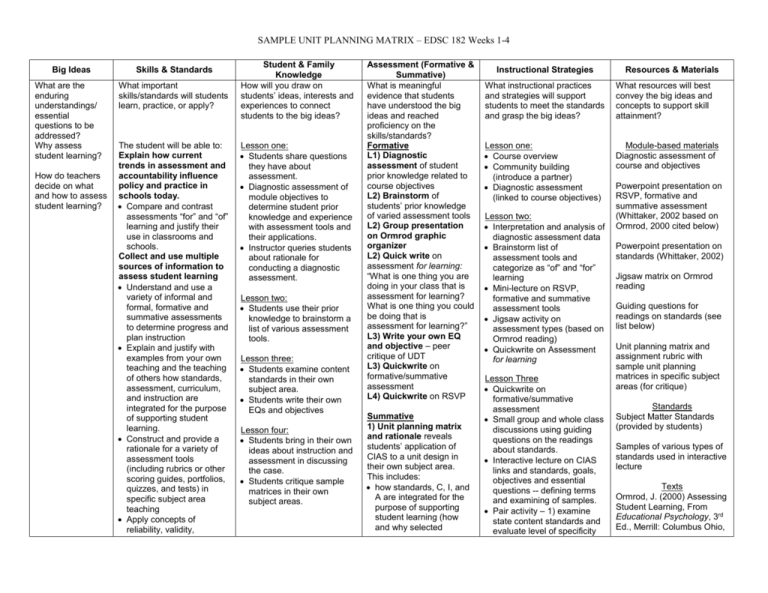
SAMPLE UNIT PLANNING MATRIX – EDSC 182 Weeks 1-4 Big Ideas What are the enduring understandings/ essential questions to be addressed? Why assess student learning? How do teachers decide on what and how to assess student learning? Skills & Standards What important skills/standards will students learn, practice, or apply? The student will be able to: Explain how current trends in assessment and accountability influence policy and practice in schools today. Compare and contrast assessments “for” and “of” learning and justify their use in classrooms and schools. Collect and use multiple sources of information to assess student learning Understand and use a variety of informal and formal, formative and summative assessments to determine progress and plan instruction Explain and justify with examples from your own teaching and the teaching of others how standards, assessment, curriculum, and instruction are integrated for the purpose of supporting student learning. Construct and provide a rationale for a variety of assessment tools (including rubrics or other scoring guides, portfolios, quizzes, and tests) in specific subject area teaching Apply concepts of reliability, validity, Student & Family Knowledge How will you draw on students’ ideas, interests and experiences to connect students to the big ideas? Lesson one: Students share questions they have about assessment. Diagnostic assessment of module objectives to determine student prior knowledge and experience with assessment tools and their applications. Instructor queries students about rationale for conducting a diagnostic assessment. Lesson two: Students use their prior knowledge to brainstorm a list of various assessment tools. Lesson three: Students examine content standards in their own subject area. Students write their own EQs and objectives Lesson four: Students bring in their own ideas about instruction and assessment in discussing the case. Students critique sample matrices in their own subject areas. Assessment (Formative & Summative) What is meaningful evidence that students have understood the big ideas and reached proficiency on the skills/standards? Formative L1) Diagnostic assessment of student prior knowledge related to course objectives L2) Brainstorm of students’ prior knowledge of varied assessment tools L2) Group presentation on Ormrod graphic organizer L2) Quick write on assessment for learning: “What is one thing you are doing in your class that is assessment for learning? What is one thing you could be doing that is assessment for learning?” L3) Write your own EQ and objective – peer critique of UDT L3) Quickwrite on formative/summative assessment L4) Quickwrite on RSVP Summative 1) Unit planning matrix and rationale reveals students’ application of CIAS to a unit design in their own subject area. This includes: how standards, C, I, and A are integrated for the purpose of supporting student learning (how and why selected Instructional Strategies Resources & Materials What instructional practices and strategies will support students to meet the standards and grasp the big ideas? What resources will best convey the big ideas and concepts to support skill attainment? Lesson one: Course overview Community building (introduce a partner) Diagnostic assessment (linked to course objectives) Module-based materials Diagnostic assessment of course and objectives Lesson two: Interpretation and analysis of diagnostic assessment data Brainstorm list of assessment tools and categorize as “of” and “for” learning Mini-lecture on RSVP, formative and summative assessment tools Jigsaw activity on assessment types (based on Ormrod reading) Quickwrite on Assessment for learning Lesson Three Quickwrite on formative/summative assessment Small group and whole class discussions using guiding questions on the readings about standards. Interactive lecture on CIAS links and standards, goals, objectives and essential questions -- defining terms and examining of samples. Pair activity – 1) examine state content standards and evaluate level of specificity Powerpoint presentation on RSVP, formative and summative assessment (Whittaker, 2002 based on Ormrod, 2000 cited below) Powerpoint presentation on standards (Whittaker, 2002) Jigsaw matrix on Ormrod reading Guiding questions for readings on standards (see list below) Unit planning matrix and assignment rubric with sample unit planning matrices in specific subject areas (for critique) Standards Subject Matter Standards (provided by students) Samples of various types of standards used in interactive lecture Texts Ormrod, J. (2000) Assessing Student Learning, From Educational Psychology, 3rd Ed., Merrill: Columbus Ohio, SAMPLE UNIT PLANNING MATRIX – EDSC 182 Weeks 1-4 practicality and standardization (RSVP) to the design of classroom assessment tools Establish and communicate learning goals for all students Explain and contrast the types and purposes of standards, goals and objectives and their corresponding roles in planning curriculum, instruction, and assessment Use grade level subject matter content standards to plan short and long term curriculum, instruction and ongoing assessment Use assessments to support, guide, and reflect on feedback related to student learning Use assessment tools that provide students with meaningful feedback about their progress Examine and use assessment results to inform planning of ongoing instruction. instructional strategies support student learning; how the results of the assessment guide specific next steps for teaching) the distinction between formative and summative assessment tools as assessments “of” and “for” learning, distinctions among and use of essential questions, content standards, and objectives in planning instruction and assessment (specifically the coherent links within and across columns in the matrix) ways to diagnose student prior knowledge early in the unit and for continuing to draw on student’s backgrounds and interests throughout. (EQ, S, or O); 2) Write your own EQ and objective and critique the UDT of both. Introduction to unit planning matrix assignment. Explanation for columns (as CIAS links) Lesson Four Quickwrite on RSVP Discussion of Schultz case to identify CIAS and RSVP issues and dilemmas; and provide a rationale for potential solutions. Critique unit matrix samples (from previous semesters) using assignment rubric and critiquing questions Group Activity – Share assessments and peer critique using discussion protocol (CIAS lens) Lesson Six Examine graded unit planning matrix and rationale Ch. 16 pp.632-683 Stiggins, R. (2002) Assessment Crisis: The absence of assessment FOR learning. Phi Delta Kappan, pp. 758-765. Thompson, S. (2001) The Authentic Standards Movement and its Evil Twin. Phi Delta Kappan, pp. 358362. Falk, B. (2002) Standards Based Reforms: Problems and Possibilities. Phi Delta Kappan, pp. 612-620. Wiggins, G. (1998) Essential Questions and Curriculum Template. Excerpts from Educative Assessment, Jossey-Bass, San Francisco, pp. 214-220. Schultz, S. (1998) Case 5: Exploring Alternative Assessment, Groupwork in Diverse Classrooms. A Casebook for Educators, Shulman, Lotan and Whitcomb (Eds.) Teachers College Press. Bond, D. (2000) Lecture notes and unit test guidelines. College of Education, San José State University, pg. 9-24.