Cell Theory and Structure Study Guide Answers 14 15
advertisement

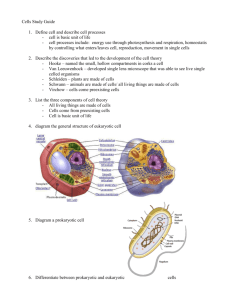
Cell Theory and Structure Study Guide 1. What does the cell theory say? (3 things) a) Cells are the basic unit of structure and function of all organisms. b) Cells come from pre-existing cells through cell division. c) All living organisms are composed of one or more cells. 2. What is the definition of a cell? The basic structural and functional unit of all organisms 3. What structures do all cells have regardless of type? Plasma Membrane, Ribosomes, Cytoplasm, Chromatin (DNA), RNA 4. Bacterial cells are examples of Prokaryotic cells. 5. The presence of a Nucleus is the determining factor in whether a cell is a prokaryote or eukaryote. 6. Cell walls are only found in certain prokaryotes (bacteria) and plant cells. Animals do not have them. 7. Which organelle is found only in animals? Lysosomes and centrioles 8. What organelles are found only in plants? Chloroplasts, Thyalkoids, Chromoplasts 9. What organelles are found only in bacteria? There aren’t any organelles unique to bacteria that we are studying at this time. 10. 11. 12. 13. Next to the following scientists names write their discovery that contributed towards the cell theory. a. Schwann – Studied animal tissue and said that it is made of animal cells. b. Schleiden – Studied plant tissue and said that it is made of plant cells. c. Virchow – first to propose that cells divide to form other cells d. Hooke – looked at cork underneath a microscope and saw the first cells – named cells e. Leeuwenhoek – first to see unicellular animal like organisms in milk and pond water using a microscope f. Hans and Zacharias Jansen – invented the first compound microscope 14. What are the 4 components of the plasma membrane? Phospholipid bilayer, transport protein, carbohydrate chain, cholesterol 15. Which part of the phospholipid bilayer is polar? The glycerol heads. Is it hydrophobic or hydrophilic? hydrophillic 16. Which part of the phospholipid bilayer is nonpolar? The fatty acid tails Is it hydrophobic or hydrophilic? hydrophobic 17. Which parts of the cell are hydrophilic? Inside the cell, Outside the cell, or Both? Both 18. What is the purpose of the transport protein? Move needed water and other substances through the plasma membrane. Contribute to its selective permeability. 19. 20. 21. What does “selectively permeable” mean? Only certain materials are allowed into or out of the membrane. Why is the plasma membrane considered to be a selectively permeable membrane? Because it controls what enters and leaves the cell through the transport proteins. 22. What does the fluid mosaic model of the plasma membrane say? Phospholipid bilayer creates a “sea” in which other molecules float. The phospholipids and other components can float/slide past one another. The different components have no set pattern and create a mosaic. 23. How does the plasma membrane help maintain a cell’s homeostasis? By controlling what enters and leaves the cell through selective permeability. 24. List evidence for the endosymbiont theory. Mitochondria/Chloroplasts share the following with prokaryotes: circular DNA, 70s ribosome size/density, binary fission cell division, electron transport chain found in plasma membrane, size of structure is 1-10 microns. The double lipid membrane surrounding mitochondria and chloroplasts could have been created when they were engulfed by a larger prokaryotic cell and part of its membrane enclosed the ancestor. Mitochondria and Chloroplast did not appear as individual organelles until eukaryotic cells first appeared on earth. 25. Summarize the Endosymbiont Theory: A larger prokaryotic cell engulfed the smaller mitochondrial ancestor, aerobic bacteria. Instead of eating it, the larger prokaryotic cell developed a symbiotic relationship with the aerobic bacteria because the aerobic bacteria provided energy for the larger prokaryote. Some prokaryotic cells also took in photosynthetic bacteria as well. The photosynthetic bacteria provided food in the form of sugar for its host cell. Over time, the photosynthetic bacteria evolved into chloroplasts and the aerobic bacteria evolved into mitochondria as they lost the ability to live on their own without the larger prokaryotic cell.