EAST ASIA UNIT QUESTIONS
advertisement

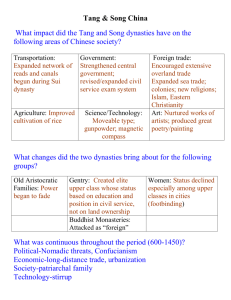
EAST ASIA UNIT QUESTIONS TANG AND SONG CHINA (CH. 12, SEC. 1) China? 1. What impact did improvements in transportation have on Tang and Song 2. “Gaining power depended on merit rather than birth.” Do you agree with this view of China under the Tang and the Song? Explain your answer. 3. Why was the reform of the civil service under the Tang so significant? 4. How did changes in agriculture support other developments during the Song Dynasty? 5. What were two key results (for each) from: a. the completion of the Grand canal under the Sui -- b. the use of the compass at sea -- 6. Review Tang and Song China: People and Technology, on pp. 328 & 329. Complete the Skillbuilder: Interpreting Charts questions in the spaces provided below. 1. 2. THE MONGOL CONQUESTS (CH. 12, SEC. 2) 1. Why was terror an important weapon for Genghis Khan? 2. What characteristics of their culture do you think contributed to the Mongols’ military success? Explain your answer. 3. What were the most important accomplishments of the Mongol Empire? THE MONGOL EMPIRE (CH. 12, SEC. 3) 1. Why did the Mongols employ foreigners rather than Chinese in high government offices? Do you think the Mongol policies towards the Chinese were effective? Explain your answer. 2. How did Europeans view Marco Polo’s account of is time in China? 3. What impact did the Mongol Peace (Pax Mongolia) have on interaction between east and west? 4. What happened to the Yuan Dynasty after Kublai Khan’s death? FEUDAL POWERS IN JAPAN (CH. 12, SEC. 4) 1. Why were Japanese missions to Tang China so important? 2. “The Japanese selectively borrowed from Chinese culture.” Use information form the text to support your answer. 3. Why do you think the shoguns chose to rule through puppet emperors rather than simply seizing the throne themselves? 4. Was the rise of the shogun beneficial for Japan overall? 5. What purpose did the samurai serve? KINGDOMS OF SOUTHEAST ASIA AND KOREA (CH. 12, SEC. 5) 1. On what was Khmer prosperity based? 2. What were two sources of prosperity for Southeast Asian empires? 3. How did geography influence the development and culture of Southeast Asia and Korea? Korea? 4. In what ways did the cultural development of Vietnam resemble that of 4. How did China influence Korea’s development? 5. How does the term “shrimp among whales” apply to modern Korea? (HINT: this term is not in the book,. Use geography to figure it out) CHINA LIMITS EUROPEAN CONTACTS (Ch. 19, sec. 2) 1. How did Beijing become the capital of China? 2. Why is Zheng He such a dramatic and influential figure in world history? How did his voyages relate to the theme of cultural diffusion? 3. Why do you suppose China lost interest in contacts abroad after 1433? 4. What factors, both within China and outside its borders, contributed to the downfall of the Ming Dynasty? 5. What did Christian missionaries bring to China? Do you think Lord George Macartney should have kowtowed to the Emperor Qian-long? Why or why not? 6. Why are Kangxi such a famous Chinese emperor? JAPAN RETURNS TO ISOLATION (Ch. 19, sec. 3) 1. Why was the time between 1467 and 1568 called the period of the “Warring States?” 2. Why do you think the emperor had less power than the shogun? 3. What was the difference between the Confucian ideal of society and the real society of Japan? 4. Why did the Japanese policy towards Christians change from acceptance to repression? 5. How did the Japanese express themselves culturally under the Tokugawa shoguns? 6. Do you think Japan’s closed-country policy effectively kept Western ideas and customs out of Japan?