Practice Problems Key Genetic Crosses
advertisement

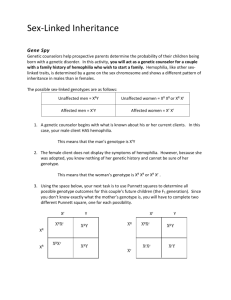
Name: KEY Hour: Date: (3 Points/Page) /21 Points For ALL practice problems in this packet, remember to: 1. list trait and alleles 2. create a key 3. list the parents being crossed (P1) 4. form the Punnett square 5. determine genotypic ratio 6. determine phenotypic ratio 1. In dogs, black hair is dominant to brown hair. Cross a heterozygous black colored dog with a brown dog. Determine the possible genotypes and phenotypes of the offspring. Trait: Key: Hair color HH = Hh = hh = Black Black Brown (H,h) P1: Hh H Hh Hh h h Genotype: 2 Hh : 2 hh Phenotype: 2 Black: 2 Brown x hh h hh hh 2. In birds, long beaks are dominant to short beaks. Cross two birds heterozygous for beak length. Determine the possible genotypes and phenotypes of the offspring. Be sure to follow the same format as the problem above. Trait: Key: Beak length BB = Long Bb = Long bb = Short Genotype: 1BB : 2 Bb : 1 bb Phenotype: 3 Long : 1 Short (B,b) P1: B b Bb B BB Bb LZHS Prentice Hall Biology – Genetics Practice Problems Key Biology I x Bb b Bb bb 1 Remember: With Incomplete Dominance- neither allele is dominant! There is an intermediate trait! - 3 completely different phenotypes are possible - the 3rd is intermediate to the other two (not blending) 1. In northeast Kansas there is a creature known as a wildcat. The fur color of this particular wildcat exhibits incomplete dominance. There are three possible fur colors: blue, red, and when alleles are mixed, purple. What would the possible genotypes and phenotypes of the offspring be if a blue wildcat were crossed with a red wildcat? Trait: Key: Fur Color RR Rr rr = = = (R,r) Blue Purple Red P1: Genotype: 4 Rr Phenotype: 4 Purple Wildcats RR x rr R Rr Rr r r R Rr Rr 2. The lubber grasshopper is a very large grasshopper, and is black in color with stripes. The color of the stripes exhibit incomplete dominance. Red stripes or Yellow stripes may be expressed; however, when alleles are mixed, orange stripes are expressed. What will be the genotypic and phenotypic ratios of the F1 generation be as a result of a cross between two grasshoppers, both with orange stripes? Trait: Key: Genotype: Stripe Color GG Gg gg = = = (G,g) Red Orange Yellow 1 GG : 2 Gg : 1 gg P1: Gg x G g Gg G GG Gg g Gg gg Phenotype: 1 Red: 2 Orange: 1 Yellow LZHS Prentice Hall Biology – Genetics Practice Problems Key Biology I 2 1. In fish, the alleles for scale color show co-dominance. Scale color may be orange or white in fish, however, when alleles are mixed scales will have orange and white stripes. If an orange fish is crossed with a white fish, the following genotypes and phenotypes may be determined regarding the possible offspring. Trait: Scale Color Key: RR Rr rr (R, r) = orange scales = orange & white spots = white scales P1: RR r r x rr R Rr Rr R Rr Rr Punnett Square: Genotype: (letters) 4 Rr Phenotype: (words) 4 (All) orange & white stripes 2. In fish, the alleles for scale color show co-dominance. Fish can have scales that are blue or yellow, however, when alleles are mixed a fish with both blue and yellow scales results. If two heterozygous fish are crossed, what are the genotypes and phenotypes of the possible offspring? Trait: Scale Color Key: BB Bb bb = = = (B, b) Blue Blue & yellow Yellow P1: Bb x LZHS Prentice Hall Biology – Genetics Practice Problems Key Biology I Bb 3 Punnett Square: B b B BB Bb b Bb bb Genotype: (letters) 1 BB : 2 Bb : 1 bb Phenotype: (words) 1 Blue : 2 Blue & Yellow : 1 Yellow LZHS Prentice Hall Biology – Genetics Practice Problems Key Biology I 4 Key: Phenotype Light brown rabbit Gray rabbit Albino rabbit with black spots Albino rabbit Genotype AA, AaB, Aab, Aa aBaB, aBab, aBa abab, aba aa 1. Cross a heterozygous Albino rabbit with black spots and a homozygous gray rabbit. What are the possible genotypes and phenotypes of the offspring? Key: See Above P1: aba x aBaB Genotype: 2 aB ab : 2 aBa Phenotype: 4 gray aB aB ab aB ab aB ab a aBa aBa 2. What are the possible genotypes and phenotypes of the offspring for a cross between an Albino rabbit with black spots that is homozygous with an Albino rabbit? Be sure to follow the same format as the previous problem. Key: See Above P1: abab x aa ab ab Genotype: 4 a ab Phenotype: 4 albino rabbits w/ black spots LZHS Prentice Hall Biology – Genetics Practice Problems Key Biology I a a ab a ab a a ab a ab 5 = female = male Use the following information for questions 1 & 2. In fruit flies, eye color is sex-linked. Normal eye color is red, and recessive eye color is white. Key: XRXR = female, normal, red XRY = male, normal, red XRXr = female, carrier, red XrXr = female, mutant, white XrY Xr Xr XR XRXr XRXr Y X rY X rY 1. Cross a white-eyed female fly with a normal male fly. Key: See Above P1: XrXr X Phenotype: 2. XRY 2 XRXr : 2 XrY Genotype: 2 carrier, females, red : 2 mutant, males, white Cross a carrier female with a white-eyed male. Key: See Above P1: XRXr Genotype: = male, mutant, white X XrY 1 XRXr : 1 XrXr : 1 XRY : 1 Xr Y XR Xr Xr XRXr Xr Xr Y XRY XrY Phenotype: 1carrier, female, red : 1mutant, female, white: 1normal, male, red : 1mutant, male, white Use the following information for question 3. In humans, colorblindness is sex-linked and recessive. (Remember, that means males only need one recessive to become colorblind.) Key: XRXR= female, normal vision XRY= male, normal vision XRXr= female, carrier, normal vision XrY= male, mutant, colorblind XrXr= female, mutant, colorblind 3. Cross a normal female with a colorblind male. Key: See Above P1: XRXR X XrY XR XR Xr XRXr XRXr Y XRY XRY Genotype: 2 XRXr : 2 XRY Phenotype: 2 carrier, normal vision, females : 2 normal vision, males LZHS Prentice Hall Biology – Genetics Practice Problems Key Biology I 6 1. In rabbits, long hair is dominant to short hair AND blue eyes are dominant to brown. Cross a short haired, heterozygous blue eyed rabbit, with a homozygous long haired, brown-eyed rabbit. Determine the possible genotypes and phenotypes of the offspring. Traits: Key: HH Hh hh EE Ee ee Hair Length Eye Color = Long = Long = Short = Blue = Blue = Brown (H,h) (E,e) P1: H H H H e e e e Genotype: 8 HhEe : 8 Hhee Phenotype: 8 Long Blue: 8 Long Brown hhEe h E HhEe HhEe HhEe HhEe x h e Hhee Hhee Hhee Hhee HHee h E HhEe HhEe HhEe HhEe h e Hhee Hhee Hhee Hhee 2. In dorks, thick glasses are dominant to thin glasses and pocket protectors are dominant to pencil cases. These two traits are being studied together. Cross a homozygous thick-glassed dork that has a pencil case with a dork that is heterozygous for both traits. Determine the possible genotypes and phenotypes of the offspring. Be sure to follow the same format as the previous problems. Traits: Glasses (G,g) P1: GGrr x GgRr Carriers (R,r) Key: GG = Thick Gg = Thick gg = Thin RR = Pocket Protector Rr = Pocket Protector rr = Pencil Case G r G R GGRr G r GGrr g R GgRr g r Ggrr G r GGRr GGrr GgRr Ggrr G r GGRr GGrr GgRr Ggrr Genotype: 4 GGRr : 4 GGrr : 4 GgRr : 4 Ggrr Phenotype: 8 Thick glasses, Pocket Protector : 8 Thick glasses, Pencil Case LZHS Prentice Hall Biology – Genetics Practice Problems Key Biology I G r GGRr GGrr GgRr Ggrr 7 You are now to create your own Di-hybrid cross. You must include two traits. However, the trait you select may be expressed in any of the ways learned in this chapter. For example, you may select one of your traits to exhibit complete dominance, while the other is incomplete or maybe even co-dominant. Once you have completed the creation of your problem, you must have a classmate attempt to solve the problem. You must then check the problem for errors and show your classmate how they did and teach them how to correct it if they made a mistake. Good luck and have fun! (Make sure to be school appropriate when selecting your traits!) Here are the lines for you to write the final draft of your problem. A great idea may be to make a rough draft on a separate sheet of paper, including you working out the problem to make sure it works first! Classmate’s Name: Traits: Key: ( , ) ( , ) = = = = = = P1: x Genotype: Phenotype: LZHS Prentice Hall Biology – Genetics Practice Problems Key Biology I 8