Essential Questions - Thomas C. Cario Middle School
advertisement

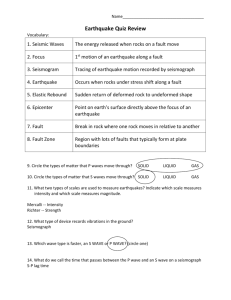
Essential Questions: Answer on a separate sheet of paper and attach to Unit Outline. 1. Explain the differences in finding the density of a block, marble and penny. Block: Find the mass with a triple-beam balance. Find the volume by multiplying the length x width x height. Divide mass by volume. Marble: Find the mass by placing the marble in a cup, subtract out the cups mass. Find the volume using the “volume by difference” method in a graduated cylinder. Divide mass by volume. Penny: Find the mass using a triple-beam balance. Find the volume using the “volume by difference” method in a graduated cylinder. Divide mass by volume. 2. Will a dry sponge have the same density as a wet one? Explain. No, the wet one will be more dense, because it will have more mass per volume. 3. How can you determine if something will sink or float in water? If the objects density is greater than 1, it will sink, if its density is less than 1, it will float. 4. Compare and Contrast p, s, and surface waves. (shape, speed, what they can travel through, etc) P-waves: Move back and forth parallel to the direction of the wave (slinky), fastest wave, and can travel through liquids and solids. S-waves: Move at right angles to the direction of the wave (rope), 2nd fastest wave, and cannot travel through liquid, only solid. Surface waves: Slowest wave and cause the most damage. Only travel on the surface of the Earth. 5. How do scientists know what the inside of the Earth is made of? Describe in detail. (hint: your answer should say something about the “shadow zone”) Scientists use the changes in speed and direction of seismic waves to determine the inside of the Earth. S-waves stop at the outer core (true liquid layer) and p-waves will slow down and bend. Both of these waves behavior end up creating the shadow zone on either side of the focus on the opposite side of the Earth, where no waves are detected by a seismograph. 6. What causes an earthquake to occur? An EQ occurs due to the breaking and/or shifting of rock beneath the Earth’s surface. 7. Can Earthquakes be predicted? Why or why not? No, there is no way to know exactly when the rock will break/shift, but scientists can use past data to identify high risk locations. 8. Where do most earthquakes occur in the US? West coast and where fault lines are present. 9. Describe how scientists measure earthquakes (Richter scale vs Mercalli Intensity Scale) The Richter scale is measured by magnitude (energy released) and the Mercalli scale is measured by damage/intensity. 10. Explain why a person who is standing outside in an open field is relatively safe during a strong earthquake. No heavy objects or glass could be projected to harm the person during the earthquake. 11. List 3 ways to make our classroom or home more earthquake-safe. Moorings, turn off water, electricity and gas, take heavy objects from high shelves and place them on lower shelves, and stay away from glass windows or doors. 12. Name 3 main ways earthquakes cause damage. Geologic damage, Building destruction, liquefaction, tsunamis, bridges and highways crack or get demolished. 13. How can you determine the epicenter of an earthquake/what information do you need? Find the time difference between the p and s waves for 3 stations, use the time travel graph to determine the distance to the epicenter from each station, draw circles around each station with the distance being the radius, and find where all circles intersect. 14. What is a tsunami and what causes it? A tsunami is caused by an earthquake occurring in the oceanic crust creating a large wave. 15. Robert says that our Earth is just one big rock. Do you agree or disagree? Explain your answer. No, the only true rock layers are the crust and upper mantle (lithosphere). Below that is the asthenosphere in the mantle which is made of “hot rock” and a more dense layer in the bottom of the mantle. The next layer is the Outer core, the only “true liquid” layer made of metal. The center of the earth is the most dense solid, the inner core, which is also a metal.