CHAPTER 15 - WordPress.com
advertisement

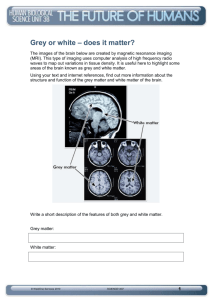
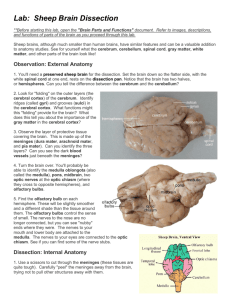
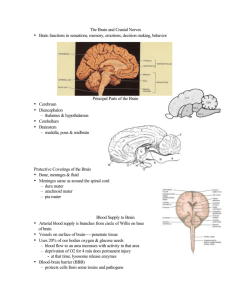
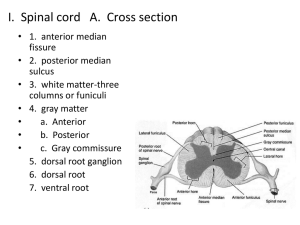
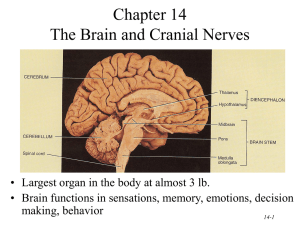
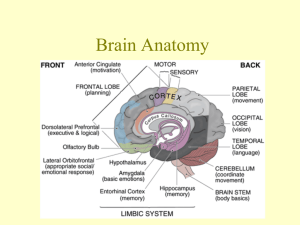
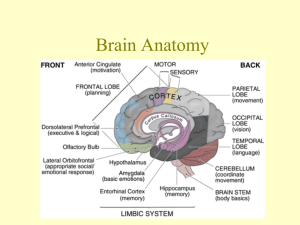
1 CHAPTER 15 THE BRAIN Six Major Divisions of the Adult Brain 1. Cerebrum 2. Diencephalon 3. Mesencephalon 4. Pons 5. Cerebellum 6. Medulla Oblongata Cerebrum Divided into large paired cerebral hemispheres separated by the longitudinal fissure Conscious thought process, intellectual functions, memory storage and retrieval Conscious and subconscious regulation of skeletal muscle contractions Diencephalon – the deep portion of the brain attached to the cerebrum 3 regions 1. epithalamus- roof of diencephalons- contains hormone secreting pineal gland 2. thalamus (rt & lft) from the walls of diencephalons- sensory information relay processing center 3. Hypothalmus- the floor of the diencephalons- visceral control center (pituitary gland) contains centers involved with emotions, autonomic function and hormone production. Link between nervous and endocrine system. Brain stem Consists of the Midbrain- mesencephalon – processes visual and auditory information Pons & Cerebellum –metencephalon – motor centers Medulla oblongata- myelencephalon- autonomic centers for cardiovascular, respiratory and digestive activities Gray and White matter organization Inner region of gray matter matter surrounded by tracts of white matter. Gray- surrounds ventricles and passageways form clusters of neuron cell bodies called nuclei. White- in cerebrum and cerebellum , covered by neural cortex- a superficial layer of gray matter. Ventricles- Fluid filled cavities within the brain 4 ventricles- 1 in each cerebral hemisphere 3rd in diencephalon 4th between pons and cerebellum extending into the medulla oblongata and continuous with spinal cord septum pellucidum separates the lateral ventricles of the cerebral hemisphere interventricular foramen- allowa communication with the ventricle of the diencephalons mesencephalon aqueduct- canal that connects the third ventricle with the fourth Cranial Meninges – surround the brain and act as shock absorbers Same 3 layers as SC meninges 1. dura mater a. falx cerebri- projects between the cerebral hemispheres b. tentorium cerebelli-between cerebellum and cerebrum c. falx cerebelli- divides 2 cerebellar hemispheres 2. Arachnoid- acts as roof over cranial blood vessels 3. Pia mater- anchored to the brain with astrocytes 2 CHAPTER 15 (contd.) Blood–brain barrier – special mechanism that prevents the passage of substances from the blood to the CSF and brain Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) Cushions neural structures Supports the brain Transports nutrients, chemical messengers and waste products Formed in the choroids plexus- combination of ependymal cells and permeable capillaries Originates in the roof of the 3rd ventricle CEREBRUM Largest region of the brain Conscious thought processes and all intellectual functions originate in the cerebral hemispheres Gyri- elevated ridges sulci- shallow depressions Fissures- deep grooves Lobes named after overlying bones Central sulcus separates the motor and sensory portions of the cortex Neurons of primary motor cortex are pyramidal cells Association areas- associated with sensory or motor regions of the cortex, interpret incoming data or coordinate a motor response. a.) Somatic motor association (premotor cortex) responsible for the coordination of learned motor activities b.) Somatic sensory association- integrates and interprets sensations concerning size and shapes of object Integration centers- receive and process information from many different association areas (split brain concept) Left- written lang. scientific skills, numerical Rt.-left hand, musical, artistic, space/pattrn Central white matter, covered by gray matter Contains fibers that form bundles from 1 region to another 1. association fibers- interconnections within the hemisphere 2. commissure fibers- connect the 2 hemispheres 3. projection fibers- link cerebrum with other regions of brain and spinal cord Basal nuclei- paired masses of gray matter within the cerebral hemisphere 1. basal nuclei 2. caudate nucleus 3. claustrium 4. amygdaloid body 5. globus pallidus Limbic system- A combination of the cerebrum, diencephalons and mesencephalon. Responsible for establishing emotional states and related behavior, and facilitating memory storage and retrieval. Fornix- tract of white matter that connects the hippocampus to the hypothalamus Mammillary bodies- prominent nuclei in the floor of the hypothalamus DIENCEPHALON – connects the cerebral hemispheres to the brain stem 1.Epithalamus- roof of 3rd ventricle, houses pineal gland 3 rd 2.Thalamus- lt. & rt. Separated by 3 ventricle Consists of paired of oval masses of mostly gray matter organized into nuclei. Acts as relay station for sensory and motor impulses a. intermediate mass- bridge of gray matter that crosses the 3rd ventricle to join the masses b. nuclei- all sensory impulses except smell; motor nuclei- voluntary motor actions and arousal 3. Hypothalamus- Contains centers involved with emotions and visceral processes; Connection between the nervous and endocrine system (mind over body phenomenon, associated with rage and aggression, feeding/satiety center) Infindibulum connects hypothalamus to pituitary gland MESENCEPHALON (midbrain) Contains cerebral aquaduct Cerebral peduncles- pair of fiber bundles (both motor and sensory) connects upper and lower brain Tectum- dorsal portion of midbrain- contains corpora quadrigemina (4 rounded elevations) 1. superior colliculi- 2 elevations- reflex centers for movement of eyeballs and head & neck in response to visual stimuli 2. inferior colliculi- 2 elevations- reflex centers for movement of head and trunk in response to auditory stimuli PONS Nuclei and white fibers in scattered tracts bridge connecting the SC with the brain and parts of brain with each other. Fibers run in two directions 1. middle cerebral peduncles- transverse fibers connect rt and lft sides 2. longitudinal fibers- belong to motor sensory tracts that connect SC with medulla or upper parts of brain stem. CEREBELLUM Second largest Tentorium cerebelli- extension of cranial dura mater to separate cerebrum from cerebellum Vermis- central constricted area Hemispheres- anterior, posterior and floccundular Falx cerebelli- extension of cranial dura mater between hemispheres Cortex- gray matter (surface) Cerebellar peduncles- attaches cerebellum to brain stem. Mostly efferent fibers 1. inferior cerebellar- connect cerebellum with medulla at base of brain stem and SC 2. middle cerebellar – cerebellum with pons 3. superior cerebellar- cerebellum with midbrain 4. Function: coordinates subconscious contraction of skeletal muscles. Maintain equilibrium and posture, predict future position of body while moving. MEDULLA OBLONGATA Contains all ascending and descending tracts between the SC and the brain Pyramids- ventral sides of medulla -2 Nucleus gracilis- rt and left, found on dorsal side of medulla Nucleus cuneatus- rt and left found on dorsal side of medulla- receive sensory fibers form ascending tracts of SC and relay info to opposite side of the medulla 3 cortex centers 1. cardiac center- regulates rate of heartbeat and force of the contraction 2. medullary rhythmicity area of respiratory center- adjusts basic rhythym of breathing 3.vasomotor (vasoconstrictor)- regulates the diameter of blood vessels. CRANIAL NERVES Numbered according to their position along the longitudinal axis of the brain. LEARN THEM!