Cells
advertisement

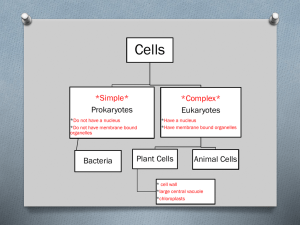
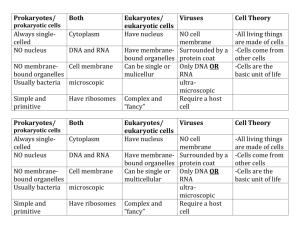
Cells -Cells discovered in ca.1660 by Antonie van Leeuwenhoek. -word Cell coined in 1665 by Robert Hooke (latin for small room). --Cell Theory: 1. All organisms composed of 1 or more cells. 2. Cells are the basic unit of organization in life. 3. All cells arise from pre-existing cells. Why Organize into Cells? -individual cells can be lost and replaced -organisms can outlive the cells that compose them. -Cells are always small (10-100 microns). --WHY? --Surface-to-Volume Ratio --as size increases, volume grows more rapidly than surface area. --Area increases as A2 --Volume increases as V3 --everything must enter/exit across the surface area. --a given surface area can only maintain a limited volume. Cell Classification: --2 Types of Cells: 1. Prokaryotic cells (bacteria) -lack (true) membrane bound organelles, and have no distinct nucleus. (No internal membranes). 2. Eukaryotic cells (all other organisms, plant, animal, etc.) -have true membrane bound organelles and a distinct nucleus. (Has internal membranes). Eukaryotic Cell Organelles: --Plasma Membrane -contains the cell -regulates transport -consists of a phospholipid bilayer --Cell Wall -Only present in Plants & Fungi -protects and supports cell -located outside of membrane -composed of= --Cytoplasm -fluid inside membrane - 50% cell volume --Nucleus -composes 5-10% of cell’s volume. -contains the cell’s DNA (chromatin). -nucleolus -nuclear envelope -nucleoid --Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER) -system of folded membranes. -surrounds the nucleus -composed of 2 parts: Rough ER = -ribosomes -functions in protein synthesis Smooth ER = no ribosomes -functions in lipid synthesis. --Golgi Complex -flattened stacks of folded membranes. -functions in the packaging & distribution -Cisternae= -Vesicles= -Lysosome= --Mitochondria - “Power house” of the cell -site of ATP synthesis in the cell. Chloroplasts=photosynthesize to produce sugars. -most abundant in leaf cells -appear green in color due to pigment chlorophyll. --Cytoskeleton -functions in anchoring organelles & maintaining cell shape. -3 components/ all protein fibers: 1. Actin filaments=longest -function in contraction of cell. -very abundant in muscle cells. 2. Microtubules=hollow tubes -provide shape to the cell. 3. Intermediate fibers=protein ropes (many woven strands). -connection of… --Centrioles = --function is unknown --animal cells only --Locomotion Structures -Flagella=long thread-like structures. -occur alone or in a pair. -Cillia=short thread-like structures -occur in mass number over large surface -both function in forward propulsion and in food gathering. -Pseudopodia= --Central Vacuole -large water storage structure of plant cells—NOT present in animals