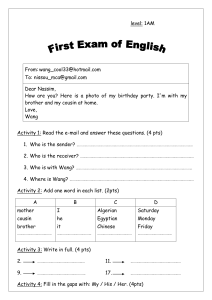
Resume of Ling Wang (L
advertisement

Resume of Dr. Ling WANG (L. WANG) AFFILIATION: Associate Professor, Dr. Ling WANG (王凌) Department of Automation, Tsinghua University, Beijing 100084, P. R. China Email: wangling@mail.tsinghua.edu.cn Tel: 86-10-62783125-272, 62785845-272 Fax: 86-10-62786911 EXPERIENCE & EDUCATION: [1] Associate Professor, Department of Automation, 2002~current [2] Assistant Professor, Department of Automation, 1999~2002 [3] Ph.D. student in Department of Automation, Tsinghua University, 1995~1999. (Supervised by Professor Da-Zhong ZHENG) [4] B.S. student in Department of Automation, Tsinghua University, 1990~1995 [5] Birth Date and Place: 1972-08-03, Wujin City of Jiangsu Province RESEARCH INTEREST: [1] Modeling, planning, scheduling and optimization of manufacturing systems [2] Optimization theory, algorithms and applications based on computational intelligence, including genetic algorithm, simulated annealing, tabu search, particle swarm optimization, differential evolution, neural networks, quantum computing, etc [3] Simulation optimization, ordinal optimization CURRICULUM: [1] [2] [3] [4] Intelligent optimization algorithms and applications. (for undergraduate students) Production scheduling and intelligent optimizations. (for graduate students) Neural networks. (for graduate students) Literatures retrieving and paper writing. (for graduate students) STUDENT: Ph.D. STUDENT: Ling-Lai LI (Vice Adviser) (’2001) Yi-Nan GUO (Co-Adviser) (’2001) Bo LIU (Vice Adviser) (’2001) Bin QIAN (Vice Adviser) (’2004) MS STUDENT: Liang ZHANG (’2002) Hui PAN (’2003) Bin-Bin LI (’2004) Qie HE (’2005) Fu-Zhuo HUANG (’2006) UNDERGRADUATE STUDENT: Wen-Feng LI, Ming YAN (’2000) Ling-Lai LI, Wei-Rong ZHU (’2001) Liang ZHANG, Wei ZHOU (’2002) Li-Jun JI, Xuan HUANG (’2003) Bin-Bin LI, Hao WU (’2004) Qie HE (’2005) Fu-Zhuo HUANG, Yu ZHOU (’2006) PROJECT: [1] NSFC Project (60204008): Computational intelligence based hybrid optimization theory and algorithms for complex systems. (200,000RMB, PI) (2003.1~2005.12) [2] NSFC Project (60374060): Study on intelligent simulation optimization theory and algorithms for complex manufacturing systems. (150,000RMB, PI) (2004.1~2006.12) [3] New Star of Science and Technology of Beijing City (2004A41). (70,000RMB, PI) (2004.7~2007.7) [4] NSFC Project (60574072): Study on optimization and scheduling theory and algorithms based on PSO for complex manufacturing process. (230,000RMB) (2006.1~2008.12) [5] 973 Project (2002CB312203): Study on real-time, intelligent operation and optimization theories and methods for complex manufacturing process. (340,000RMB, Investigator) (2002.12~2007.12) [6] 973 Project (G1998020310): Hybrid electrical systems. (20,000RMB, Investigator) (1998~2002) [7] 863 Project (863-511-930): Management mode and integration technology for process CIMS industries. (70,000RMB, Investigator) (2001.1~2001.12) [8] 863 Project: CIMS for Dalian petrochemical company. (20,000RMB, Investigator) (1999.10~2000.3) [9] 863 Project (2001AA411220): Overall plan and key technology for Chinese petrochemical automatic systems. (39,000RMB, Investigator) (2001.12~2002.11) [10] International Cooperation Project: Effective simulation and optimization for service network. (65,000RMB, Investigator) (2002.4~2004.4) [11] Key Member Program of Tsinghua University: Study on hybrid optimization algorithms. (60,000RMB, PI) (2000.6~2002.5) [12] Company Cooperation Project: Development of HIS. (18,000RMB, Co-PI) (2001.5~2001.12) [13] 985 Project: Theory, methods and technologies of system integration for 21 century oriented process industries. (10,000 RMB, Investigator) (2001~2002) [14] Teaching and Paper Foundation. (15,000+52,000RMB, PI) (2002~2004) AWARD: [1] National Natural Science Award (1st Place Prize) nominated by Ministry of Education of China, 2003. [2] Outstanding Ph.D. Dissertation Award of Tsinghua University (1st Place Prize). [3] Outstanding Paper Award of International Conference on Machine Learning and Cybernetics, ICMLC’02. [4] Excellent Paper of Chinese Control and Decision Conference, CDC'04. [5] New Star of Science and Technology of Beijing City, 2004. [6] Excellent Textbook of Tsinghua University (2nd Place Prize), 2004. [7] Excellent Class Advisor of Tsinghua University (1st Place Prize), 2005. DISSERTATION: [1] Ph. D. Dissertation: Study on some problems for hybrid optimization strategies and neural networks, 1999. [2] M.S. Dissertation: Stochastic optimization algorithms and their hybrid strategies, 1997. [3] B.S. Dissertation: Optimization problem on route of 1/N custom stream, 1995. PUBLICATIONS: BOOK: [1] Wang L. Intelligent optimization algorithms with applications. Beijing: Tsinghua University & Springer Press, 2001.10(First), 2003.03(Second), 2004.03(Third), 2004.11(Fourth). (SCI Times Cited 16) [2] Wang L. Shop scheduling with genetic algorithms. Beijing: Tsinghua University & Springer Press, 2003. (SCI Times Cited 5) [3] Wang L. Heuristic optimization method. In: Chinese Encyclopedia, 2nd ed. Beijing: Chinese Encyclopedia Press. INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL PAPER: Forthcoming [1] Liu B, Wang L, Jin YH. An effective PSO-based memetic algorithm for flow shop scheduling. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man and Cybernetics-B, 2006. (Accepted as regular paper). (SCI, EI) [2] He Q, Wang L. An effective co-evolutionary particle swarm optimization for constrained engineering design problems. Engineering Applications of Artificial Intelligence, 2006. (SCI, EI) [3] Li LL, Wang L, Liu LH. An effective hybrid PSOSA strategy for optimization and its application to parameter estimation. Applied Mathematics and Computation, 2006. (SCI, EI) [4] Pan H, Wang L, Liu B. Particle swarm optimization for function optimization in noisy environment. Applied Mathematics and Computation. (SCI, EI) [5] Pan H, Wang L, Liu B. Chaotic annealing with hypothesis test for function optimization in noisy environment. Chaos, Solitons and Fractals. (SCI, EI) [6] He Q, Wang L, Liu B. Parameter estimation for chaotic systems by particle swarm optimization. Chaos, Solitons and Fractals. (SCI, EI) [7] Liu B, Wang L, Jin YH, Tang F, Huang DX. Control and synchronization of chaotic systems by differential evolution algorithm. Chaos, Solitons and Fractals. (SCI, EI) [8] Liu B, Wang L, Jin YH. An effective hybrid particle swarm optimization for no-wait flow shop scheduling. International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology. (SCI, EI) [9] Wang L, Zhang L. Determining optimal combination of genetic operators for flow shop scheduling. International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology. (SCI, EI) [10] Wang L, Zhang L, Zheng DZ. An effective hybrid genetic algorithm for flow shop scheduling with limited buffers. Computers & Operations Research, 2006, 33(10): 2960-2971. (SCI, EI-06079696641) [11] Liu B, Wang L, Jin YH, Tang F. Directing orbits of chaotic systems by particle swarm optimization. Chaos, Solitons and Fractals, 2006, 29(2): 454-461. (SCI-028JV, EI-06059677656) [12] Wang L, Zhang L Stochastic optimization using simulated annealing with hypothesis test. Applied Mathematics and Computation, 2006, 174(2): 1329-1342. (SCI-027HY, EI-06109743893) [13] Zhang L, Wang L, Zheng DZ. An adaptive genetic algorithm with multiple operators for flow shop scheduling. International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology, 2006, 27(5-6): 580-587. (SCI-990EJ, EI-05509542884) 2005 [14] Wang L, Tang F, Wu H. Hybrid genetic algorithm based on quantum computing for numerical optimization and parameter estimation. Applied Mathematics and Computation, 2005, 171(2): 1141-1156. (SCI-015GM, EI-06059668761) [15] Wang L, Zhang L, Zheng DZ. Genetic ordinal optimisation for stochastic flow shop scheduling. International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology, 2005, 27(1-2): 166-173. (SCI-986QH, EI-05489516760) [16] Liu B, Wang L, Jin YH. Hybrid particle swarm optimization for flow shop scheduling with stochastic processing time. Lecture Notes in Artificial Intelligence, 2005, 3801: 630-637. (SCI-BDQ19, ISTP-BDQ19) [17] Wang L. A hybrid genetic algorithm-neural network strategy for simulation optimization. Applied Mathematics and Computation, 2005, 170(2): 1329-1343. (SCI-980YQ, EI-05449448565) [18] Tang F, Wang L. An adaptive active control for the modified Chua’s circuit. Physics Letters A, 2005, 346(5-60: 342-346. (SCI-979HD) [19] Wang L, Li LL, Tang F. Optimal reduction of models using a hybrid searching strategy. Applied Mathematics and Computation, 2005, 168(2): 1357-1369. (SCI-976UW, EI-05419411614, SCI Times Cited 1) [20] Liu B, Wang L, Jin YH, Tang F, Huang DX. Improved particle swarm optimization combined with chaos. Chaos, Solitons and Fractals, 2005, 25(5): 1261-1271 (SCI-929NL, EI-05219111132, SCI Times Cited 2) [21] Wang L, Wu H, Zheng DZ. A quantum-inspired genetic algorithm for scheduling problems. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, 2005, 3612: 417-423. (SCI-BDA32, EI-05439427037, ISTP-BDA32) [22] Wang L, Wu H, Tang F, Zheng DZ. A hybrid quantum-inspired genetic algorithm for flow shop scheduling. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, 2005, 3645: 636-644. (SCI-BDC10, EI-05449443744, ISTP-BDC10) [23] Tang F, Wang L. Synchronization of the modified Chua’s circuit with x|x| function. Communications in Theoretical Physics, 2005, 44(2): 303-306. (SCI-960TN) [24] Wang L, Zhang L, Zheng DZ. A class of hypothesis-test based genetic algorithm for flow shop scheduling with stochastic processing time. International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology, 2005, 25(11-12): 1157-1163. (SCI-928MA, EI-05229127233, SCI Times Cited 1) [25] Liu B, Wang L, Jin YH, Huang DX. Designing neural networks using hybrid particle swarm optimization. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, 2005, Vol. 3496: 391-397. (SCI-BCN38, EI-05399382245, ISTP-BCN38, SCI Times Cited 2) 2004 [26] Wang L, Tang F. NN-based GA for engineering optimization. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, 2004, Vol.3173: 448-453. (SCI-BAT64, ISTP-BAT64, INSPEC-8230178) [27] Wang L, Zhang L, Zheng DZ. The ordinal optimisation of genetic control parameters for flow shop scheduling. International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology, 2004, 23(11-12): 812-819. (SCI-829DZ, EI-04308280893, INSPEC-8175077, SCI Times Cited 1) [28] Wang L, Li LL, Tang F. Directing orbits of chaotic systems using a hybrid optimization strategy. Physics Letters A, 2004, 324(1): 22-25. (SCI-808CX, INSPEC-8211207, SCI Times Cited 4) 2003 [29] Wang L, Zhang L, Zheng DZ. A class of order-based genetic algorithm for flow shop scheduling. International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology, 2003, 22(11-12): 828-835. (SCI-752CH, EI-04037817728, INSPEC-8005335, SCI Times Cited 7) [30] Jiang YH, Wang L, Jin YH. Bottleneck analysis for network flow model. Advances in Engineering Software, 2003, 34(10): 641-651. (SCI-727WR, EI-03417667435, INSPEC-7969439) [31] Wang L, Zheng DZ. A modified evolutionary programming for flow shop scheduling. International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology, 2003, 22(7-8): 522-527. (SCI-741NA, EI-03507780860, INSPEC-7998582, SCI Times Cited 6) [32] Wang L, Zheng DZ. An effective hybrid heuristic for flow shop scheduling. International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology, 2003, 21(1): 38-44. (SCI-653WV, EI-03087368196, INSPEC-7649822, SCI Times Cited 17) 2002 [33] Wang L, Zheng DZ. Finite-time performance analysis for genetic algorithm. Progress in Natural Science, 2002, 12(12): 940-944. (SCI-620AV, EI-03047337279) [34] Zhou T, Wang L, Sun ZS. Closed-loop model set validation under a stochastic framework. Automatica, 2002, 38(9): 1449-1461. (SCI-586AC, EI-02307032983, INSPEC-7420690, SCI Times Cited 2) [35] Wang L, Zheng DZ. A modified genetic algorithm for job shop scheduling. International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology, 2002, 20(1): 72-76. (SCI-587DX, EI-02357058287, INSPEC-7409138, SCI Times Cited 3) 2001 [36] Wang L, Zheng DZ. An effective hybrid optimization strategy for job-shop scheduling problems. Computers & Operations Research, 2001, 28(6): 585-596. (SCI-413MP, EI-01015497525, INSPEC-6888306, SCI Times Cited 29) INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE PAPER: 2004 [1] Zhang L, Wang L. Genetic ordinal optimization for stochastic traveling salesman problem. The 5th World Congress on Intelligent Control and Robotics, Hangzhou, WCICA’2004, 2086-2090. (EI-04388368171) [2] Wang L, Zheng DZ. Hybrid strategy for parameter estimation and PID tuning. The 7th International Symposium on Advanced Control of Chemical Processes, Hongkong, ADCHEM’2003, 1011-1016. 2003 [3] Zhang L, Wang L. Optimal parameters selection for simulated annealing with limited computational effort. IEEE International Conference on Neural Networks & Signal Processing, Nanjing, ICNNSP'2003, 412-415. (ISTP-BY77R, INSPEC-8065044) [4] Li LL, Tang F, Wang L. Directing orbits of chaotic dynamical systems based on simplex-annealing strategy. IEEE International Conference on Neural Networks & Signal Processing, Nanjing, ICNNSP'2003, 748-750. (ISTP-BY77R, INSPEC-8046043) [5] Zhang L, Wang L, Tang F. Hypothesis-test based simulated annealing for stochastic flow shop scheduling. The Second International Conference on Machine Learning and Cybernetics, Xi'an, ICMLC’2003, 1607-1612. (EI-04128072128, ISTP-BY61C, INSPEC-7992938) 2002 [6] Zhang L, Wang L, Tang F. Order-based genetic algorithm for flow shop scheduling. The First International Conference on Machine Learning and Cybernetics, Beijing, ICMLC’2002, 139-144. (Outstanding Paper Award, ISTP-BW27J, EI-03127405529, INSPEC-7597628, SCI Times Cited 1) [7] Yang C, Ye H, Wang JC, Wang L. An artificial life and genetic algorithm based on optimization approach with new selecting methods. The First International Conference on Machine Learning and Cybernetics, Beijing, ICMLC’2002, 684-688. (ISTP-BW27J, EI-03127405646, INSPEC-7597916) [8] Wang L, Zheng DZ, Tang F. An improved evolutionary programming for optimization. The 4th World Congress on Intelligent Control and Robotics, Shanghai, WCICA’2002, Volume 3, 1769-1773. (ISTP-BV45G, EI-03047336817, INSPEC-7412463) 2001 [9] Wang L, Li WF, Zheng DZ. Design higher-order digital differentiator with simulated annealing. The 5th International Conference on Electronic Measurement & Instruments, Guilin, ICEMI’2001, 883-886. (ISTP-BU70Y) [10] Wang L, Li WF, Zheng DZ. A class of hybrid strategy for adaptive IIR filter design. The 8th International Conference on Neural Information Processing, Shanghai, ICONIP’2001, 85-89. (ISTP-BU46F) 2000 [11] Wang L, Zheng DZ. Global derivative-free training for feed-forward neural networks. The 3rd Asian Control Conference, Shanghai, ASCC’2000, 1570-1575. (SCI Times Cited 2) DOMESTIC JOURNAL PAPER: 2006 [1] Liu LH, Wang L, Liu B, Jin YH. Study on function optimization and model reduction based on a class of hybrid PSO algorithm. Control and Instruments in Chemical Industry, 2006, 33(2): 9-12. (in Chinese) 2005 [2] Liu B, Wang L, Jin YH, Huang DX. Advances in particle swarm optimization algorithm. Control and Instruments in Chemical Industry, 2005, 32(3): 1-7. (in Chinese). (EI-05279198140, SCI Times Cited 2) [3] Wang L, Zhang L. Genetic algorithm with multiple searching modes for flow-shop scheduling with limited buffers. Computer Integrated Manufacturing Systems— CIMS, 2005, 11(7): 1041-1046. (in Chinese). (EI-05359331186, INSPEC-8767726) [4] Wang L, Li BB, Zheng DZ. A fast genetic algorithm for model reduction and parameter estimation. Control and Decision, 2005, 20(4): 426-429,433. (in Chinese). (EI-05229136659, INSPEC-8519234) [5] Wang L, Wu H, Tang F, Zheng DZ, Jin YH. Hybrid quantum genetic algorithms and performance analysis. Control and Decision, 2005, 20(2): 156-160. (in Chinese). (EI-05149025694, INSPEC-8443907) 2004 [6] Zhang L, Wang L, Zheng DZ. Hypothesis-test based genetic algorithm for stochastic optimization problems. Control Theory and Applications, 2004, 21(6): 885-889. (in English). (EI-05108875003, INSPEC-8403801) [7] Li BB Wang L, Zheng DZ. Genetic algorithm with interpolation based evaluation and its application for parameter estimation. Control and Instruments in Chemical Industry, 2004, 31(6): 14-17. (in Chinese). (EI-05279198084) [8] Wang L, Huang X, Zheng DZ. A class of improved genetic algorithm with sifting strategy and performance analysis. Control and Decision, 2004, 19(11): 1290-1293, 1297. (in Chinese). (EI-05048803655, INSPEC-8409681) [9] Li LL, Wang L, Zheng DZ. Optimal reduction of models based on a class of SMSA strategy. Control and Decision, 2004, 19(8): 947-950, 953. (in Chinese). (EI-04468459062, INSPEC-8241286) [10] Wang L, Tong HH, Zheng DZ. Reference point based near insertion approach and two-stage approach for TSP. Control and Decision, 2004, 19(7): 831-833, 837. (in Chinese). (EI-04438424613, INSPEC-8197471) [11] Wang L, Ji LJ, Zheng DZ. Simulation optimization based on surrogate model and genetic algorithm. Control and Decision, 2004, 19(6): 626-630. (in Chinese). (EI-04378354978, INSPEC-8197457) [12] Wang L, Zheng DZ. A class of simulated annealing approach based on hypothesis test for stochastic optimization problems. Control and Decision, 2004, 19(2): 183-186. (in Chinese). (EI-04248214379, INSPEC-8053933) [13] Zhang L, Wang L, Zheng DZ. Parameter ordinal optimization for simulated annealing with limited computational efforts. Control and Decision, 2004, 19(2): 226-229. (in Chinese). (INSPEC-8053938) 2003 [14] Wang L, Li LL, Zheng DZ. A class of effective search strategies for parameter estimation of nonlinear systems. ACTA Automatica Sinica, 2003, 29(6): 953-958. (in Chinese). (INSPEC-8002292, SCI Times Cited 1) [15] Wang L, Zhang L, Tang F. On ordinal optimization of parameters and operators for genetic algorithm. Journal of Central South University of Technology, 2003, 34(4): 350-354. (in Chinese). (INSPEC-7894142) [16] Wang L, Zhang L, Zheng DZ. Advances in simulation optimization. Control and Decision, 2003, 18(3): 257-262, 271. (in Chinese). (INSPEC-7852060, SCI Times Cited 2) [17] Wang L, Wang X. CIMS architecture and manufacturing execution system for process industry. Computers Engineering and Applications. 2003, 39(10): 16-18. (in Chinese). [18] Wang L, Li WF, Zheng DZ. Optimal design of controllers for non-minimum phase systems. ACTA Automatica Sinica, 2003, 29(1): 135-141. (in Chinese). (INSPEC-7699080) [19] Li LL, Wang L. Chemical process optimization based on SMSA algorithm with multiple operators. Control and Instruments in Chemical Industry, 2003, 30(1): 25-28. (in Chinese). (EI-04328307443) 2002 [20] Wang L, Zhang L, Zheng DZ. A class of genetic ordinal optimization framework for stochastic simulation optimization. Control and Decision, 2002, 17(S): 699-702. (in Chinese). (EI-03087370158, INSPEC-7579635) [21] Tong HH, Wang L, He JR. Reference point-based near insertion approach and its improvement for traveling salesman problem. Computers Engineering and Applications, 2002, 38(20): 63-65. (in Chinese) [22] Lan H, Wang X, Wang L. Improved genetic annealing algorithm for global optimization of complex functions. Journal of Tsinghua University, 2002, 42(9): 1237-1240. (in Chinese). (EI-03027313247, INSPEC-7505243) [23] Li LL, Wang L, Zheng DZ, Zhou DH. Simplex-annealing hybrid approach for model parameters estimation. Journal of Tsinghua University, 2002, 42(9): 1207-1208, 1213. (in Chinese). (EI-03027313239, INSPEC-7505236) [24] Guo YN, Wang L, Tan DJ, Hao R. Coal blending control based on mixed optimization of genetic algorithm and neural network. Journal of China University of Mining & Technology, 2002, 31(5): 404-406. (in Chinese). (EI-02457195019) [25] Wang L, Li LL, Zheng DZ. Design adaptive IIR filters with a kind of simplex-annealing strategy. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2002, 24(7): 99-102. (in Chinese) [26] Wang L, Zheng DZ. An improved genetic algorithm to solve permutation scheduling problem. Systems Engineering—Theory and Practice, 2002, 22(6): 74-79. (in Chinese). (EI-02417136470) [27] Wang L, Tang F. Study on PID tuning based on genetic annealing strategy. Control and Instruments in Chemical Industry, 2002, 29(3): 21-24. (in Chinese) [28] Wang L, Wang X. Some key factors to design CIMS for process industry. Computers Engineering and Applications, 2002, 38(10): 50-52,108. (in Chinese) [29] Wang L, Zheng DZ. A class of simulated annealing for multi-objective optimization. Computers Engineering and Applications, 2002, 38(8): 4-5, 55. (in Chinese). [30] Tang F, Wang L. From local minimum to global optimum. Computers Engineering and Applications, 2002, 38(6): 56-58. (in Chinese). [31] Wang L, Zheng DZ. Stability analysis for several classes of dynamical feedback neural networks. Computing Technology and Automation, 2002, 21(1): 1-6. (in Chinese). [32] Wang L, Zheng DZ. Study on unified framework of hybrid optimization strategies. Control and Decision, 2002, 17(1): 33-36, 40. (in Chinese). (EI-02397107558, INSPEC-7385581) [33] Wang L, Zhang L, Zheng DZ. Generalized TSP-type traffic model and optimization. Computers Engineering and Applications, 2002, 38(2): 15-16, 42. (in Chinese). [34] Wang L, Zheng DZ. An improved evolutionary programming and its optimization performances analysis. Computers Engineering and Applications, 2002, 38(1): 8-10. (in Chinese). 2001 [35] Wang L, Li WF, Zheng DZ. Simulated annealing for designing higher-order digital differentiator. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2001, 23(12): 1-3. (in Chinese). [36] Wang L, Li LL, Zheng DZ, Zhou DH. SMSA approach for online joint estimation of time delay and parameters in nonlinear time-varying systems. Control and Instruments in Chemical Industry, 2001, 28(6): 5-9. (in Chinese). (SCI Times Cited 1) [37] Wang L, Zheng DZ. Advances in job shop scheduling based on genetic algorithm. Control and Decision, 2001, 16(S): 641-646. (in Chinese). (EI-02246976076) [38] Wang L, Li WF, Zheng DZ. Estimating model-parameter and tuning controller-parameter by a class of hybrid strategy. Control and Decision, 2001, 16(5): 530-534. (in Chinese). (EI-02236966472) [39] Wang L, Yan M, Li QS, Zheng DZ. A class of effective hybrid optimization strategy for complex functions with high dimension. Journal of Tsinghua University, 2001, 41(9): 118-121. (in Chinese). (EI-02116885825, SCI Times Cited 1) [40] Wang L, Zheng DZ. Optimization study on a class of flow shop scheduling with non-unique jobs. Computers Engineering and Application, 2001, 37(19): 76-78. (in Chinese). [41] Wang L, Zheng DZ. A kind of GASA hybrid optimization strategy. Control Theory and Applications, 2001, 18(4): 552-554. (in Chinese). (EI-01556802755, INSPEC-7057463) [42] Wang L, Wang X, Jin YH. MES---key element for the development of CIMS in process industry. Control and Instruments in Chemical Industry, 2001, 28(4): 1-5. (in Chinese). [43] Lan H, Wang X, Wang L. Analysis of a classic genetic-annealing algorithm towards global optimization for complex functions. Journal of Systems Simulation, 2001, 13(S): 111-113. (in Chinese). [44] Li QS, Wang L, Zheng DZ. Study on tuning controller for water turbine system. Basic Automation, 2001, 8(3): 10-12, 50. (in Chinese). [45] Wang L, Zheng DZ, Li QS. Survey on chaotic optimization methods. Computing Technology and Automation, 2001, 20(1): 1-5. (in Chinese). (SCI Times Cited 3) [46] Wang L, Wang X, Jin YH, Xiao DY. CIMS reference architecture based on life-cycle and integrated platform for process industry. Control and Instruments in Chemical Industry, 2001, 28(1): 1-4,8. (in Chinese). [47] Wang L, Li WF, Zheng DZ, Li QS. A Class of hybrid strategy to estimate model parameters. Basic Automation, 2001, 8(1): 5-7,38. (in Chinese). 2000 [48] Wang L, Wang X, Jin YH. Consider CIMS architecture for process industry. Automation Panorama, 2000, 17(S): 38-40, 50. (in Chinese). [49] Wang L, Zheng DZ. Simulated annealing with the state generator based on Cauchy and Gaussian distributions. Journal of Tsinghua University, 2000, 40(9): 109-112. (in Chinese). (EI-01436700268, INSPEC-6730349, SCI Times Cited 1) [50] Wang L, Zheng DZ. Unified framework for neighbor search algorithms and hybrid optimization strategies. Journal of Tsinghua University, 2000, 40(9): 125-128. (in Chinese). (EI-01436700272, INSPEC-6730353) [51] Wang L, Wang X. Survey on optimal design of batch chemical process. Journal of Tsinghua University, 2000, 40(S2): 265-269. (in Chinese). [52] Wang L, Zheng DZ. Meta-heuristic algorithms: a review. Control and Decision, 2000, 15(3): 257-262. (in Chinese). [53] Wang L, Zheng DZ. Training algorithm for FNN based on a class of nonlinear property. Control and Decision, 2000, 15(1): 19-22. (in Chinese). (CSA-0502030, EI-00095311003) [54] Wang L, Zheng DZ. A kind of chaotic neural network optimization algorithm based on annealing strategy. Control Theory and Applications, 2000, 17(1): 139-142. (in Chinese). (EI-00095313837, INSPEC-6553191) 1999 [55] Wang L, Zheng DZ. Study on TSP and optimization based on Hopfield neural network. Control and Decision, 1999, 14(6): 669-674. (in Chinese). (EI-00095310999) [56] Wang L, Zheng DZ. Hybrid optimization strategy for radial basis function neural network structure. Journal of Tsinghua University, 1999, 39(7): 50-53. (in Chinese). (CSA-0450084, EI-00045122367, INSPEC-6354635) Before 1999 [57] Wang L, Zheng DZ. Study on a class of GASA hybrid strategy and its convergence behavior. Control and Decision, 1998, 13(6): 699-672. (in Chinese). (SCI Times Cited 1) [58] Wang L, Zheng DZ. Two hybrid learning strategies of feedforward network. Journal of Tsinghua University, 1998, 38(9): 95-97, 101. (in Chinese). (EI-99094800492, INSPEC-6086762) [59] Zheng XZ, Wang L, Jin GF. Design binary optics elements for ICF uniform illumination with hybrid optimization method. Chinese Journal of Lasers A, 1998, 25(3): 265-269. (in Chinese). (EI-99084739370, INSPEC-5948174) [60] Wang L, Zheng DZ. The comparative research on several sub-optimization methods to solve TSP problem. Control and Decision, 1998, 13(1): 79-83. (in Chinese). [61] Song TY, Wang L. Statistics and simulation of forest spatial data. Journal of Beijing Forestry University, 1997, 19(3): 74-78. (in Chinese). [62] Wang L, Zheng DZ. The research on solving flowshop problem with simulated annealing algorithm. Journal of the Postgraduate of Tsinghua University, 1996, 26(1): 28-35. (in Chinese) DOMESTIC CONFERENCE PAPER: 2005 [1] Wang L, Wu H, Zheng DZ. Hybrid quantum genetic algorithm for model parameter estimation. Chinese Control and Decision Conference, Haerbin, 2005, 527-530. 2004 [2] Wang L, Zheng DZ. Integrated framework and key issues of simulation optimization. Chinese Control and Decision Conference, Huangshan, 2004, 799-802, 806. (Excellent paper of CDC'04, EI-04428413058) [3] Zhang L, Wang L. Zheng DZ. Hypothesis test based intelligent optimization algorithms and comparisons. Chinese Control and Decision Conference, Huangshan, 2004, 338-341. (Excellent paper of CDC'04, EI-04428413016) 2002 [4] Wang L, Zhang L, Zheng DZ. Fundamental study on genetic ordinal optimization algorithm. Chinese Process Control Conference, Macon, 2002, 98-102. 2001 [5] Wang L, Zheng DZ, Tang F. Chaos—a kind of new optimization technique. Chinese Control Conference, Dalian, 2001, 185-189. [6] Li QS, Wang L. Optimal design of binary optical instrument based hybrid algorithm. Chinese Control and Decision Conference, Xi’an, 2001, 346-349. [7] Li QS, Wang L. A kind of hybrid optimization algorithm for complex functions. Chinese Control and Decision Conference, Xi’an, 2001, 350-353. Before 2001 [8] Wang L, Zheng DZ. Study on performance of simulated annealing based on different neighbor generators. Chinese Control Conference, Hongkong, 2000, 430-434. [9] Wang L, Zheng DZ. Study on a class of variable-lot flow line scheduling problem. Chinese Control Conference, Ningbo, 1998, 491-494. [10] Wang L, Zheng DZ. Two kinds of training strategies for feed-forward networks. Chinese Control Conference, Lushan, 1997, 1059-1062. [11] Wang L, Zheng DZ. Study on simulated annealing for flow shop scheduling problems. Chinese Control and Decision Conference, Lushan, 1997, 390-394. [12] Wang L, Zheng DZ. Comparative study on several sub-optimal solutions for TSP. Chinese Control Conference, Qingdao, 1996, 604-607. REFEREE FOR ACADEMIC JOURNAL and SOCIETY: [1] NSFC [2] Fok Ying Tung Education Foundation [3] International Journal of Automation and Control (Editorial Board Member), (InderScience) [4] IEEE Transaction on Systems, Man and Cybernetics-B (IEEE) [5] IEEE Transaction on Evolutionary Computation (IEEE) [6] European Journal of Operational Research (Elsevier) [7] Computers & Operations Research (Elsevier) [8] Computers & Industrial Engineering (Elsevier) [9] International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology (Springer) [10] Journal of Global Optimization (Springer) [11] Information Sciences (Elsevier) [12] Journal of Systems Science and Systems Engineering (Springer) [13] Science in China [14] Chinese Science Bulletin [15] ACTA Automatica Sinica [16] Control Theory and Applications [17] Control and Decision [18] Information and Control [19] Journal of Software [20] Chinese Journal of Computers [21] Acta Electronica [22] CIMS [23] Systems Engineering: Theory and Practice [24] Journal of Tsinghua University [25] Journal of Zhejiang University [26] Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics [27] Journal of Wuhan University [28] Journal of Xi’an Jiaotong University [29] Journal of Beijing University of Science and Technology [30] Journal of Beijing Institute of Technology [31] Journal of North Jiaotong University [32] Journal of Shanghai Jiaotong University [33] Journal of Tianjin University [34] Journal of Northeast University [35] Journal of Central South University [36] Journal of Haerbin Industrial University [37] Journal of Qingdao University [38] Journal of University of Science and Technology of China [39] Journal of Dalian Institute of Technology [40] Journal South China Institute of Technology