Chapter 2: Where in the World is Oklahoma
advertisement

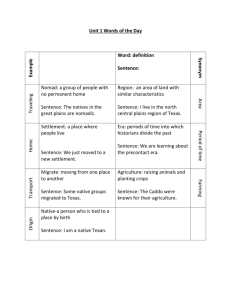
Chapter 2: Early Cultures in Our Land Section 1: The Earliest People prehistory: the time before writing was developed archaeologists: scientist who study the remains of ancient cultures - "middens" are prehistoric garbage dumps - Hiram Bingham, who discovered Machu Picchu, was the model for Indiana Jones I. Searching for Clues A. artifacts: any item made or used by people in the past 1. pottery, tools, bone, jewelry, paintings 2. petroglyphs: pictures or symbols that convey an idea B. fossils: the remains of living things 1. age measured by elements like carbon and fluorine 2. dendrochronology: counting the rings of a tree C. anthropology: the study of the cultural development of human beings II. Prehistoric Cultures / Paleo Indians A. land bridge between Siberia and Alaska called Beringia 1. nomads: people without permanent shelters a. followed herds of animals b. settled in temperate climates B. animal life was abundant / gigantic mammals C. Clovis People / New Mexico 1. short spears 2. skilled at flint knapping (shaping into weapons) 3. may have hunted some animals to extinction D. Folsom People / New Mexico and Great Plains 1. more advanced technology and hunting skills 2. primitive art 3. fire E. Archaic Foragers / Great Plains 1. with fewer large animals, they became dependent on crops 2. domesticated dogs 3. less nomadic 4. atlatl: hooked, wooden shaft for dart-throwing F. Woodland Culture 1. first true farmers; lived in fertile valleys 2. permanent shelters and villages 3. first to use bow and arrow G. Plains Village Farmers: similar to Woodlands, but on the prairie H. Mound Builders: constructed earthen temples, houses, and storage I. 1500 A.D. - climate change: many Indians abandon farming 1. protohistoric: between prehistoric and recorded history 2. nomadic way of life / buffalo hunters / tipis 3. travois: sled pulled by dogs Section 2: Historic Indian Cultures Viceroy Antonio de Mendoza authorizes exploration of southwestern parts of North America I. First Encounters A. Apache: "a gentle people"; lived a nomadic life; built wickiups B. Wichita: barterers, people who trade one item for another 1. traded maize (corn) for meat C. Caddo: farmers in Arkansas and Texas 1. wattle and daub: woven materials covered with mud D. Quapaw: farmers from the north II. Indian Culture A. different languages, religions, and customs B. Great Spirit and Mother Earth 1. afterlife of reward and punishment C. totems: animal or bird Spirit Guide D. shaman: wise medicine man 1. used herbs and prayers 2. oral histories E. all life is connected and equal F. polygamy: more than one wife G. gender roles: men were hunters, women were gatherers H. food eaten raw, roasted, boiled, or dried 1. fish, turtle, squirrel, duck 2. squash, pumpkin, corn 3. medicines: willow bark, mint, root of Black-eyed Susan