Elements of Fiction elements_of_literature
advertisement

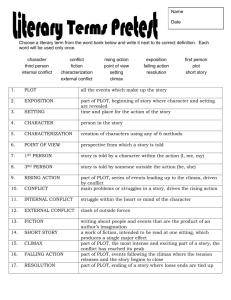
Elements of Fiction The word fiction means “anything made up or imagined.” Although events in a work of fiction may be based on real experiences, the story itself is created in the imagination of the writer. The two major types of fiction are novels and short stories. A novel is a long work of fiction. The events of a novel are normally quite complex and leave the reader with many impressions about the characters, the actions, the places described. A short story, on the other hand, is a brief work of fiction that can usually be read in one sitting. Short stories generally focus on one or two main ideas. (A third, less used form is the novella. Longer than a short story but shorter than a novel) Despite these differences in length and complexity, short stories, novellas and novels share certain elements. Understanding Fiction Characters are the people who take part in the action of the story. You learn about characters through their actions, thoughts and words, from how other people respond to them, and from how the writer describes them. The events of the story center on the most important characters, or main characters. Less important characters are known as minor characters. The main idea or message that the author wishes to share with the reader is sometimes called the theme. A writer rarely states the theme directly: but after reading the selection, the reader should be able to infer (draw conclusions from the information given) the theme. The plot is the chain of related events that make up the story. The plot centers on at least one major problem, or conflict. There are essentially five parts to a plot. Exposition: The opening of a short story, novella, or novel which normally provides background information the reader needs to know. The exposition introduces that characters, describes the setting, and may recap important events that occurred before the action of the story. The story’s conflict is also introduced. Rising Action: As the story progresses, the chain of events becomes more complex. The actions and feelings of the characters intensify as their problems become more complicated. This part of the story, known as the rising action, creates a desire in the reader to find out what will happen next. Climax: When the intensity of the story reaches a peak, or climax, a turning point in the action occurs. The climax of the story usually involves an important event, decision, or discovery that affects the final outcome. Typically, the climax is that point in the story when one force or set of forces succeeds against an opposing force or set of forces. Falling Action: Following the climax, the intensity of the story subsides. This part describes the results of the major events as the action winds down. i.e. What are the results of one force winning and another losing? Resolution: the final part of a story, or the resolution, tells how the story ends. In this part any loose ends are tied up and remaining questions resolved. The diagram below shows the various elements of the plot in a short story or novel. Five Elements of Plot Climax Rising Action Exposition Falling Action Resolution