11_The Thin Lens Equation Problems Solutions v2
advertisement

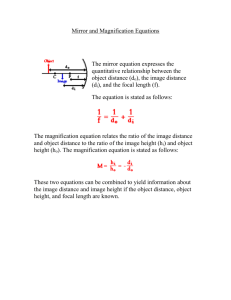
SNC2D The Thin Lens Equation Problems Solutions Thin Lens Equation: f - focal length, do - object distance, di - image distance; remember they must all be of the same units (all cm, all m, etc.) 1 1 1 f di do Magnification Equation: do - object distance, di - image distance; ho - object height, hi - image height; h d M = i or M = − i (the negative sign means that the image is inverted) do ho 1. An object 25 cm away from a lens produces a focused image on a film 15 cm away. What is the focal length of the converging lens? (9.4 cm) d i 15 cm, d o 25 cm, find f 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 , , 0.06667 0.04 0.10667 f di do f 15 25 f 1 f 9.375 cm so the focal length is 9.4 cm (rounded) 0.10667 2. If the focal length of the lens in your camera is 2 cm, at what distance must objects be placed so that a focused image is produced on a piece of film set 3 cm from the lens? (6 cm) d i 3 cm, f 2 cm, 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 , , 0.50 0.333 , 0.50 0.333 0.167 2 3 do do do f di do 1 do = 6 cm 0.167 3. (a) (b) (c) A tree 20 m high is located 40 m from the converging lens of focal length 8.0 cm. Calculate the distance from the lens to the image. (8.0 cm) Calculate the magnification. (0.0020) Calculate the height of the image of the tree. (4 cm, inverted) d o 40 m = 4000 cm, f 8.0 cm, ho = 20 m = 20000 cm 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 (a) , , 0.125 = 0.00025 , 0.125 – 0.00025 = 8 d i 4000 di di f di do 1 1 0.12475 = , di = 8.0 cm 0.12475 di (b) M = − (c) M = di do = 8 = -0.0020 (image is much smaller than object, and is inverted) 4000 hi hi , -0.0020 = , -0.0020 × 20000 = hi = -4 cm (negative means it is inverted) 20000 ho 4. A normal human eye has a focal length of about 2.3 cm. If you look at the tip of a pencil, 55.3 cm from your eye, how far is the image from the lens of your eye? (2.4 cm) d o 55.3 cm, f 2.3 cm 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 , , 0.435 = 0.018 , 0.435 – 0.018 = , 0.417 = , 2.3 d i 55.3 di di di f di do 1 di = , d i 2.40 cm 0.417 5. (a) (b) (c) A converging lens produces an image twice the size of the original. If the object is placed 40 cm from the lens, where is the image produced? (80 cm from the lens) What is the focal length of the lens? (26.7 cm) If the image is 6 cm tall, how tall is the original object? (3 cm) M = -2 (minus sign means inverted image, image will always be inverted for real images), d o = 40 cm, hi = 6 cm di di , 2×40 = d i , d i = 80 cm , -2 = 40 do 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 (b) , , = 26.6 cm 0.0125 +0.025 = 0.0375, f 0.0375 f di do f 80 40 f (a) M = − (c) M = hi 6 6 , 2 = , ho = = 3 cm 2 ho ho 6. The focal length of the lens in your eye is about 1.5 cm and the maximum size of an image that can be perceived on your retina is 5 cm (the retina is the part of your eye which acts as the screen). (a) If the object is 100 cm from your eye, where is the image produced? (1.52 cm) (b) If you want to see all of the object from this distance, what is its maximum size? (329 cm) f 1.5 cm, hi = 5 cm, d o = 100 cm 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 0.01 (a) , , 0.667 = di f d i d o 1.5 d i 100 1 1 0.667 – 0.01 = 0.657 = , d i = 1.52 cm 0.657 di hi d h d 5 1.52 and M = − i , so i = − i , = = - 0.0152 100 ho do do ho ho Re-arrange equation: 5 ho = -329 cm 0.0152 (b) M =