name period
advertisement

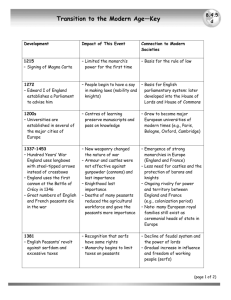
NAME _________________________________ PERIOD __________ OPEN-WEB TEST – MIDDLE AGES Use the following site: www.historylearningsite.co.uk *Castle Feature *Feudalism *The Domesday Book *Magna Carta *Black Death *Lifestyle of Medieval Peasants *Medieval Women *Medieval Monasteries PART II 21. What types of things were thrown from the murder holes? A. boiling water B. parts of dead bodies C. Both A and B D. Neither A nor B 22. Why were round towers considered to be a good defense structure? A. because no one could climb up them B. because if the enemy tried to dig under a castle to undermine a weak corner, they would not find a corner on a round tower C. because circles have no beginning and no end D. because round towers could have more windows 23. Where was the keep located in the castle? A. keep was built underground B. keep was built above any castle wall C. keep was built separate from the remainder of the castle 24. Who introduced feudalism to England? A. Alfred the Great B. William I (the Conqueror) C. Harold D. King John 25. Which of the following statements in NOT true concerning the introduction of feudalism to England? A. William was not popular with the people of England and needed to use force to maintain control B. It was physically impossible for William to rule every part of England himself C. William was looking to make extra money through taxes D. William needed to return periodically to France and was gone from England for weeks at a time, thus the need for control while he was away. 26. What method did William use to decide who was to “receive” land? A. they were noblemen who had fought bravely for him in battle B. they were the most wealthy men in the land C. they were noblemen who paid him extra money to have control of the peasants 27. What group was considered “lowest,” according to the feudal system? A. barons B. knights C. peasants/ conquered English D. duke 28. What was the purpose of The Domesday Book? A. to update the Bible’s book of “Revelation” B. to survey the population, providing information of who owned what throughout the country C. to determine what knights would be given a chance to go on Crusade 29. The Domesday Book provided an account for A. tax purposes C. religious purposes B. immigration purposes 30. What important city was left out of The Domesday Book? A. Sussex B. Hastings C. Stratford-upon-Avon D. London 31. When was the Magna Carta signed? A. 1066 B. 1215 C. 1486 D. 1607 32. The Magna Carta was an agreement between King John and the _______. A. barons B. earls C. knights D. peasants 33. King John angered the barons by A. refusing to let them farm extra land more money from taxes C. starting the Peasants’ Revolt B. demanding 34. Which of the following was NOT a clause of the Magna Carta? A. John will raise taxes only when necessary B. everyone will have access to courts C. costs and money should not be an issue if someone wanted to take a problem to the law courts D. no freeman will be imprisoned or punished without first going through the proper legal system 35. The Black Death killed ________ people between 1348 and 1350. A. 1.5 million B. 5 million C. 10 million D. 10,000 36. The Black Death was also known as _________ . A. Diptheria Plague D. Deadly Plague 37. What caused the Black Death? A. a virus fleas D. ticks from dogs B. Leprosy C. Bubonic B. infection from an exposed wound C. rats’ 38. What was NOT a reason that Black Death spread so quickly? A. people knew nothing about contagious diseases B. the disposal of bodies was very crude C. the filth that littered the streets was a perfect environment D. people refused to bathe. 39. One result of the Black Death was A. peasants made lower wages the price of food C. lords had an overload of help with farming 40. Many peasants worked as ______. A. farmers D. soldiers B. inflation, particularly B. teachers C. carpenters 41. The tax a peasant paid to the church was called a _______. A. catapult B. tithe C. levy 42. A cruck house was constructed from what materials? A. mud frame with straw plastered over B. stone frame with mud plastered over C. wooden frame with mud, straw, and manure plastered over D. mud frame with stone plastered over 43. Which of the following was NOT typical of a peasant’s home? A. curtain-covered doors B. straw lining for the floor C. glass windows D. little furniture 44. (True/False) Peasants left their animals to roam free at night. 45. (True/False) Peasants were routinely covered with dirt, fleas, and lice. 46. (True/False) Village water supplies were dirty and tainted. 47. (True/False) The rich were able to bathe frequently. 48. A peasant could expect to be fully bathed _____ in their life. A. once each year D. never B. twice C. once 49. What were London’s “stews” used for? king’s feast A.public baths B. feeding the peasants C. 50. Which of the following is NOT true of peasant children? A. many would have died before they were six months old B. they would not have attended school C. they were used at young ages to clear stones off the land D. they were sent out to hunt for small animals 51. (True/False) The majority of medieval women were involved in some type of farm work. 52. (True/False) Medieval law allowed women to divorce their husbands in cases of abuse or neglect. 53. (True/False) Girls from richer families tended to marry later than girls from poor families. 54. (True/False) Many women from poor families could, on average, expect to live until the age of sixty-five. 55. Medieval women could not…. A. join a guild B. marry without parents’ consent C. own property, unless they were widows D. all of the above 56. What was the most common cause of death among young women? A. disease B. Black Death C. childbirth D. starvation 57. (True/False) Medieval monasteries were wealthy. 58. People working on church land, …. A. were doing the work for free B. were doing the work to earn a small amount to purchase extra food C. were doing the work in exchange for the monks teaching them to read and write D. were doing the work to pay for the use of the church for ceremonies like marriages and deaths. 59. Monasteries were also sources for treatment A. financial advice B. religious training C. medical 60. (True/False) The medieval population had no concept of Heaven and Hell. 61. An army of peasants who marched on London did _________, something not done before or since. A. captured the King and held him for ransom B. assassinated the King C. captured the Tower of London 62. Who was the leader of the peasants? A. John Ball B. Wat Tyler C. Richard II 63. During the Peasants’ Revolt, one of the peasants’ demands was A. to be free of the burden of working on church land without pay B. to be able to purchase farms from the nobles C. to have a fresh water supply. 64. (True/False) Most people drank water as their “beverage.” 65. ________ was eaten by most people in Medieval England. (trout, etc.) 66. 67. 68. 69. A. bread B. chicken C. fish (True/False) Peasants frequently ate white bread. Pottage is a type of soup or stew made from oats. Peasants relied mainly on chickens for their meat. Peasants could be punished for hunting if permission was not granted from the lord. 70. What was the main drink in a medieval village? A. Milk B. Water C. Ale 71. Unusual dishes such as pigeon pie, woodcock and sturgeon would be served; wine available: This menu would be typical for A. a lord B. a peasant 72. “Ploughman’s lunch” with dark bread and cheese: This menu would be typical for lord B. a peasant 73. The Crusades were military actions against what group? Muslims A. a A. Christians B. Catholics C. 74. What city became the ultimate destination for the Crusaders? A. Constantinople B. London C. Jerusalem D. Cairo 75. The Crusades lasted nearly ________ years. A. 50 B. 100 C. 200 D. 1000 76. All of the following were gained from the Crusades EXCEPT carpets C. coffee D. algebra A. idea of democracy B. 77. As a result of the Crusades, the building of________ was improved. A. castles monasteries C. cathedrals B.