Your IQ score is 135
advertisement

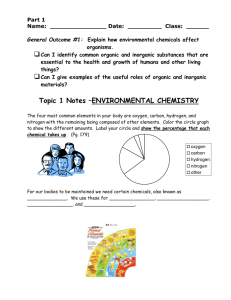
Science 9 Common Organic and Inorganic Chemicals Chemicals are a part of virtually everything … both outside and inside our bodies. Chemicals required to by plants and animals, and produced by them, can be classified as organic or inorganic substances or chemicals. Nutrients – organic and inorganic chemicals that are essential to our bodies, they circulate through out bodies to cells where they are used for energy, growth, body building, and cellular repair. Organic Chemicals organic chemicals contain carbon → they come mainly from green plants, and may be modified by animals they are essential to our health! they are classed as: o carbohydrates – energy source for metabolism (sources: rice, grains, potatoes, fruits) o proteins – basic building block for our bodies and help with chemical reactions (sources: meat, eggs, dairy, legumes, nuts) o lipids – essentially fats that store unused chemical energy (sources: vegetable & nut oils, some dairy) o vitamins – large organic molecules that help enzymes function (enzymes are special protein molecules that regulate chemical reactions in living organisms) Inorganic Chemicals inorganic substances that are not destroyed by cooking or exposure to air are called minerals inorganic chemicals are elements and their compounds and therefore can be found on the periodic table (e.g. Ca, N, O, C) plants need 18 different elements for proper growth and function; humans need 22 some important inorganic elements or minerals are: o Nitrogen (N) – a component of proteins which help animals build and repair body tissue and of chlorophyll which is essential for the growth of stems and leaves. o Calcium (Ca) – which is essential for cell division, makes up bones and teeth, and is important for blood clotting, and muscle and nerve function in our bodies. o Magnesium (Mg) – which is essential for photosynthesis in plants, and makes up bones and teeth in animals. o Potassium (K) – essential for early growth, chlorophyll production, resistance to disease, muscle contractions and nerve impulses. o Phosphorus (P) – a component of roots, flowers, bones, teeth and DNA; it is essential for cellular respiration, photosynthesis and other metabolic reactions. o Sulfur (S) – essential for the production of fruits and grains, protein synthesis, enzyme activation, and detoxification. inorganic chemicals are required by plants and animals in specific amounts – to little or to much can be harmful o macromineral – 100 mg/day or more needed o trace element – less than 100 mg/day needed most inorganic chemicals we need are found in the soil, and then taken up by plants (which are much better tasting!) o minerals get dissolved in water and then are absorbed into plants through the roots o without plants animals (including humans) would not be able to get the nutrients we need fertilizers are added to soil to improve nutrients for plant growth and uptake by humans and animals