Nutrition and Digestion Test
advertisement

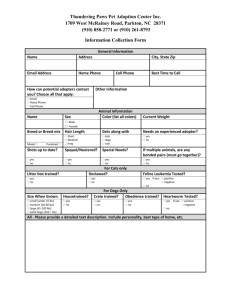
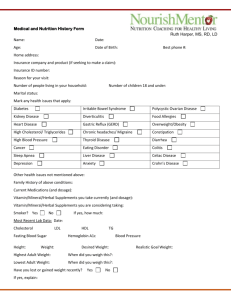
B105 Nutrition and Digestion Test Name __________________________________ Date _______________ Matching 1. ______ The cheapest and most abundant mineral in an animals body. Used in digestion, in lactation, in the blood supply and to regulate body temperature. A. Crude Protein 2. ______ Composed of amino acids it is used to build muscle, skin, bones and body tissues. C. Glucose 3. ______ Compounds made of carbon, hydrogen and oxygen and serve as the main source of energy for animals. 4. ______ The total amount of protein in a diet. B. Vitamins D. Water E. Monosaccharides F. Fats G. Carbohydrates 5. ______ Simple sugars H. Protein 6. ______ Complex sugars I. Roughage 7. ______ The simplest of all sugars, found in plants and in the blood. 8. ______ The sweetest of all sugars, found in fruit and honey. J. Minerals K. Cellulose L. Disaccharides 9. ______ The starchy substance that forms the cell walls of plants making it difficult to digest. 10. _____ Feed like grain that has a high concentration of carbohydrates and energy. 11. _____ Feeds high in fiber and protein but lower in energy. 12. _____ Organic compounds known as lipids which serve as concentrated storage places for excess energy. 13. _____ A inorganic nutrient that aids in the formation of muscle, bone, blood and enzymes. 14. ____ Vitally important in helping the animal fight stress and disease and maintain good health. M. Concentrate N. Fructose Multiple Choice (circle the correct answer) 15. Which stage of production are the nutritional requirements of the animal the highest? A. Calving to breeding B. Breeding to weaning C. Mid gestation D. Late gestation 16. Over 80 % percent of the animal’s body is made up of A. Muscle B. Bone C. Water D. Skin 17. The most expensive portion of a ration is A. Carbohydrates B. Protein C. Vitamins D. Minerals 18. _____ makes up ½ of all the mineral needs in an animals body. A. Sodium B. Phosphorous C. Iron D. Calcium 19. _____ makes up ¼ of all the mineral needs in an animals body. A. Sodium B. Phosphorous C. Iron D. Calcium 20. Animals generally need about ______ pounds of water for every pound of solid feed they consume. A. 1 B. 10 C. 6 D. 3 21. The first three body condition scores are considered … A. Too Thin B. Too Fat C. Border line D. Optimum 22. A body condition score of 4 is considered… A. Too Thin B. Too Fat C. Border line D. Optimum 23. A body condition score of _______ is considered optimum A. 3 or 4 B. 5 or 6 C. 7 D. 2 24. The last three body condition scores are considered… A. Too Thin B. Too Fat C. Border line D. Optimum 25. A cow with a body condition score of 3 looks… A. Smooth and square B. Sharp and angular C. Full and fleshy D. All of the above. 26. A cow with a body condition score of 8 appears… A. Smooth and square B. Sharp and angular C. Thin and emaciated D. All of the above. 27. What regions of the animal’s body will they deposit fat before an animal starts depositing external subcutaneous fat? A. Around the heart and internal organs B. Under the skin C. Between the muscle. D. In the muscle. 28. What region of the animal’s body is the last place they will deposit fat? A. Around the heart and internal organs B. Under the skin C. Between the muscles. D. In the muscle. 29. When is the most critical time to evaluate body condition scores? A. Before weaning B. At calving C. 100 days prior to calving D. During breeding 30. A change in one body condition degree or score is equal to _______ pounds on a small framed cow. A. 60 to 80 lbs B. 30 to 40 lbs C. 100 to 150 lbs D. 200 to 250 lbs 31. A change in one body condition degree or score is equal to _______ pounds on a large framed cow. A. 60 to 80 lbs B. 30 to 40 lbs C. 100 to 150 lbs D. 200 to 250 lbs 32. Mature cows of all breeds should be at a body condition score of _____ prior to calving. A. 4 B. 5 C. 6 D. 7 33. The recommended body condition score at calving for a two year old first calf heifer is… A. 4 B. 5 C. 6 D. 7 34. The best period of time during the cow’s production cycle to alter the body condition score is… A. Calving to breeding B. Breeding to weaning C. Mid gestation D. Late gestation 35. Is converted by the animal’s body from carotene found in green leafy forages. Can be stored in the liver for many months. A. Vitamin A B. Vitamin D C. Vitamin K D. Vitamin C 36. Referred to as the sunshine vitamin because animals use ultraviolet light to manufacture this vitamin. Animals in confinement often need this vitamin. A. Vitamin A B. Vitamin D C. Vitamin K D. Vitamin C 37. Vitamin needed to produce a enzyme that helps to form blood clots. A. Vitamin A B. Vitamin D C. Vitamin K D. Vitamin C True or False 38. ______ Young animals need diets high in carbohydrates for growth. 39. ______ A loss of 20% of the water in a animal will result in death. 40. ______ The average cow will consume about 12 gallons of water per day. 41. ______ Two different types of feeds may have the same amount of protein but different kinds of amino acids. 42. ______ Fat cows have difficulty calving while thin cows are prone to have difficulty rebreeding. 43. ______ A certain type amino acid is needed for growth while a different type is used for milk production. 44. ______ When energy intake is low external body fat is the first body tissue used to meet nutritional requirements. 45. ______ Thin cows after calving can improve their body condition score if they are fed a nutrient rich ration. 46. ______ Modern livestock operations balance rations based on the percent of protein in the feed ingredients. 47. ______ Fat contains 2.25 times more energy than carbohydrates. 48. ______ Fat in the diet is essential for the production of certain hormones. 49. ______ Cows with a moderate BCS tend to produce more colostrums and have healthier calves. 50. ______ Fat cows produce less milk because the deposit fat in the udder. 51. ______ In the mouth of ruminants there are upper and lower incisors which help break up the food for digestion. 52. ______ The saliva of monogastric animals contains enzymes that immediately start to break down sugars. 53. ______ Monogastric animals produce larger quantities of salvia than do ruminants. 54. ______ On young ruminants milk goes directly to the abomasum by means of an esophageal groove for digestion. Matching 55. ______ Single Stomached animals A. Villi 56. ______ Multicompartment stomached animals B. Omasum 57. ______ An enlargement found on a horse that enables it to utilize high fiber feeds by means of microbial fermentation. C. Mouth D. Papillae 58. ______ The first stomach the feed goes to. The walls are makeup of a network of sub compartments like a honeycomb. Serves as a storage place for hardware that does not float. Feed is sorted and regurgitated here. E. Colon F. Ruminant 59. ______ Giant storage vat where food is soaked, mixed and fermented by bacteria. Makes up 80% of the total stomach. G. Abomasum 60. ______ Grinds roughage using blunt muscular papillae that extend from many folds in the walls of the rumen. I. Reticulum 61. ______ The true stomach of a ruminant. It contains glands that excrete acids and produce enzymes which digest feed. H. Monogastric J. Small Intestine K. Cecum 62. ______ Found in the small intestine provide surface area and allow absorption into the blood stream. 63. ______ Tiny nipple like projections found in the rumen that aid in the absorption of nutrients. L. Rectum M. Rumen 64. ______ The organ that connects between the stomach and the Large intestine 65. ______ The first place the digestive process starts. 66. ______ The second part of the large intestine. It provides storage for waste material 67. ______ The final part of the large intestine. 68. Balance the protein in a ration for a 600 lb heifer being fed grass hay with a protein value of 8% and corn with a protein value of 9%. She is eating 3% of her body weight per day. She needs 11% protein in her diet. Corn ______ Grass Hay _____ Corn ________ Grass Hay ________ % of the diet in corn __________ % of the diet in grass hay _________ Total pounds of the diet fed __________ Lbs of corn in the diet ___________ Lbs of grass hay in the diet. _________ 69. Determine the nutritional needs of a 1500 lb cow in late gestation with a body condition score of 7. This cow is currently being fed 14 lbs of alfalfa hay and 10 lbs of corn each day. She should be consuming 2% of her body weight each day. How much feed should she be consuming? _______ How much is she being fed? _____ Is this amount... A. Deficient B. Adequate C. Excessive 70. Determine the energy content of the diet. Alfalfa hay has 58.0 % TDN and Corn has 89.0% TDN. The recommended amount of TDN for this cow is 52%. _____ lbs of Alfalfa X _____ % TDN = _____ lbs TDN from alfalfa. _____ lbs of corn X _____ % TDN = _____ lbs TDN from corn Total TDN _______ Total pound of feed in the diet ________ Divide the Total TDN by the total pounds of feed in the diet and convert it to a percentage. ______ % TDN in the diet. ______ Recommended TDN % in the diet. Is this amount... A. Deficient B. Adequate C. Excessive