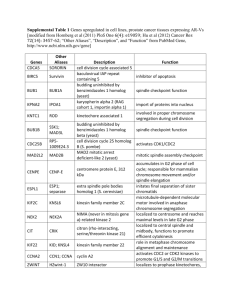
Supplementary Table 5 - Word file (525 KB )
advertisement

Supplementary Material Table 5- Drosophila protein kinases with cell cycle phenotypes and their putative orthologues. Name /Link Putative Orthologues Previously Known Functionsa (Human, Drosophila, C.elegans; S.pombe, S.cerevisae) to FlyBase Link to InParanoid database Nonreceptor tyrosine kinase – effector of cdc42 1; dorsal closure, expressed highly in mitotic Ack HS-Ack1 domains2 Regulates entry into mitosis; centrosome maturation and spindle formation; mutants display aurA HS-Aurora A defects in centrosome and spindle behaviour3 aurora B HS-AurB*; SC-Ipl1p* Chromosome alignment & spindle assembly checkpoint & cytokinesis; chromosome condensation & cytokinesis3 BubR1 HS-BubR1; SC-Bub1 Spindle assembly checkpoint4;spindle assembly checkpoint-similar role to S. cerevisiae mad3 ; contains KEN box5, mutants show lower MI and faster exit from mitosis6 cdc2 HS-CDK1; SC-cdc28; Regulates G2 to M-phase transition and entry to mitosis7; activation of the APC8; G2/M transition SP-cdc2 of mitotic cycle9 G1/S transition and S phase progression; G1/S transition and S phase cdc2c HS CDK2 G1/S transition; Cell growth10,11 Cdk4 HS-CDK6/4 Regulation of RNA polymerase 212 Cdk8 HS-CDK8 Interacts with pRb13. Regulation of RNA polymerase 214 Cdk9 HS-CDK9 Cytokinesis15; cytokinesis16 CG10522 HS-CIT HS-ULK2; CE-Unc- Axon morphogenesis and elongation, may signal through ras17 51 Cell spreading and motility - colocalises with ezrin in lamellipodia18 CG1344 HS-Pace-1;CSSCY1* CG14030/ HS-BUB1*; SC-Bub1 Spindle assembly checkpoint; Does not contain KEN box; functionally similar to HS Bub1 and SC BUB1 Bub15 CG15072 HS-KIAA0999/QSK AMPk-related kinase activated by LKB19 NTKL localises to the centrosomes during mitosis20 CG1951 HSKIAA1360;NTKL*;SC -SCY1 Activated by SRC21 CG2309 HS-ERK8 Chromatin assembly following DNA replication; DNA damage checkpoint target22; essential for CG2829 HS-TLK1/2 nuclear divisions, cell viability and chromatin assembly23. CG3216 HS-Atrial natriuretic G-protein coupled receptor protein signaling pathway- respond to cGMP24 ; may inhibit proliferation25 peptide receptor * CG10967 Cdc7-related kinase - DNA replication26 Similarity to leucine-rich repeat kinase (LRRK1) MAST2 localizes to spermatid manchette through other MAPS; activates NFKB (Mus musculus)27,28 CG7094 HS-CSNK1A1*; CE- Wnt signalling29 kin-19* Novel RSKL similar to JIL, S6K and S6KII CG7156 HS-RSK-LIKE PROTEIN Cdc2-related kinase 1; involved in gliosis30 CG7236 HS-CDKL1 CG7597 HS-CRK7/CDC2L5; Cdc2-related protein kinase 7; MPM-2 antigen-possibly involved in splicing and transcription31; CE-B0285.1 RNAi mutants show slow developmental growth32 CG7643 HS-TTK; SC-MPS1 Spindle assembly checkpoint33 and centrosome duplication34; duplication of spindle pole bodies & spindle assembly checkpoint4 Pre-mRNA splicing machinery; phosphorylate SR proteins; SPK-1, required for embryogenesis and germline CG8565 HS-SRPK2*; CESPK-1* development35 Extracellular matrix remodelling36,37 CG9488 HS-DDR2* CkIalpha HS-CSNK1A1 Interacts with Axin to inhibit JNK cascade; promotes armadilllo degradation38; induced after DNA damage39 CkIIalpha HS-CK2A1;SC-CKA1 Associated with APC - phosphorylates p53; multiple signalling pathways40; circadian clock Up-regulated in ovarian cancer41; Interacts genetically with drl dnt HS-RYK Lammer dual specificity kinase 2; meiotic progression42; septation and proliferation43 Doa HS-CLK2/3/4; SPLkh1 Receptor tyrosine kinase; axon pathfinding; Wnt receptor signalling pathway drl HS-RYK PFTAIRE (cdc2-related) protein kinase 1; Ecdysone-induced protein 63E required for embryonic Eip63E HS-PFTAIRE-1 and larval development NO/cGMP/cGK signaling - negative regulator of cell proliferation44;response to hypoxia; for HS-PRKG1 behaviour fray HS-OSR1 or SPAK Oxidative stress response- phosphorylates PAK1; MAP4K in JNK pathway45; Nerve ensheathment fs(1)h HS-BRD4/MCAP or BRD4 associates with chromosomes and injection of antibodies arrests cells in G2/M 46; RING3 is linked to human leukaemia; trans-activates genes dependent on E2F47 RING3* Gcn2 HS-GCN2; SC-GCN2 Phosphorylates eIF2alpha in amino acid deprivation, signalling the activation of NFKB 48; protein synthesis in stress response gek HSCDC42BP;CEAbnormal accumulation of F actin in oogenesis; RNAi gives dumpy & slow growing embryos K08B12.5. gish HS-CK1G3;CEGlial cell migration; Mitotic spindle orientation49; growth and division - cell morphogenesis and cytokinesis50. Y106G6E.6;SCYCK1 or 2 Replication and DNA damage G2 checkpoint51; cell cycle coordination in syncytial embryo; grp HS-Chk1 mutants show rapid entry into M, defects in chromosome condensation and degradation of cyclin A CG32742 CG5483 CG6498 HS-cdc7; SC-cdc7 HS-KIAA1790 HS-MAST1 or 2 1 gwl hippo hop htl ik2 Ilk inaC InR Candidate gene for autosomal dominant thrombocytopenia on human chromosome 1052; sporulation and meiosis53; cek1 is a suppressor of cut 8 (necessary for anaphase)54; mutants show chromosome condensation defects55 HS-STK4 or 3; SC- Induction of apoptosis56; apoptosis- mutants have higher levels of cyclinE and DIAP1;mitotic exit cdc15* network57 JAK-STAT signalling; haemocyte proliferation & cell fate determination- interacts with CDK458 HS-JAK2/3/1 Receptor tyrosine kinase for FGFs; interacts with ras; important for cell migration in several HS-FGR2/3/1/4 mesodermal lineages; pbl may act downstream of htl in regulating cell shape 59 NFK beta signalling; NFK beta signalling - defense response. HS- NAK/TBK1 HS-ILK1 or ILK2; CE- Phosphorylates GSK-3 - connects integrins to actin cytoskeleton; upregulated in several cancers60; focal adhesions of cytoskeleton ILK SC-PKC1 Mutants have behaviour defects; morphogenesis checkpoint61 Insulin-like growth factor I receptor-mediates cell proliferation; signals to MAPK/ras and to PI3K HS-IGF1R 62 ; mutants are long lived and have a smaller body HS-FLJ14813; SCrim15; SP-cek1* Activated by MAPK and SAPK/p38; phosphorylates CREB63; phosphorylation of Histone H364 ; activation of NF-kappaB65; histone H3 phosphorylation; transcriptional control, maintenance of chromatin structure66 Stress response-phosphorylates MAPK p3867; asymmetric development of the egg . lic HS-MAP2K3/6 Tumour suppressor - activates 13 kinases of the AMPK subfamily19; oocyte microtubule lkb1 HS-lkb1 organization. Activated in response to IFN in the p38 pathway68 MAPk-Ak2 HS-MAPKAPK2/3 Interacts with Cdc42 and Rac - promotes filopodium formation and cell migration69,70;cytoskeleton mbt HS-PAK7/5/4 & photoreceptor development JAK-STAT and JNK cascades -links response to stress to cell cycle progression71 Mkk4 HS-MAP2K4 mnb HS-DyrK1;CE-mbk1 Candidate target of Down’s Syndrome; mutants have small brains; spindle positioning and asymmetric cell or 2* division72 Negative regulator of CDK1; regulates mitotic entry Myt1 HS-Myt1 nmo HS-NemoLK; CEWnt signalling - polarization/rotation of cells - NFKB interactor; embryogenesis W06F12.1 Muscle specific tyrosine kinase receptor; interacts with ras in oocytes Nrk HS-MUSK Phosphorylates CDC25C regulating interaction with 14-3-373; regulator of oocyte cytoskeleton; par-1 HS-MARK3 interacts genetically with lkb1; regulator of wnt signalling Metabolism74; embryonic morphogenesis HS-PHKG PhK Activation of p70s6k75; upstream effector of S6k76;Mutant cells are smaller. Pk61C HS-PDK1 Pk92B HS-ASK1/MEKK5/1; Apoptosis77; stress & morphogenesis checkpoint 61 SC-Bck1* Pka-C2 HM-PKA-Cbeta*; SC- Regulates mitotic progression through cdc2078 PKA1 or 2* Mediates activation of NF-kappaB and MAPK pathways (JNK/p38)79; immunity pll HS-IRAK1 Multiple mitotic functions –cytokinesis80; multiple mitotic functions polo HS-plk1; SC-cdc5 Vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 1 precursor; regulation of proliferation and cell Pvr HS-VEGFR1/2/3 migration81; organisation of actin cytoskeleton in cell migration82 Cytokinesis83; tissue polarity Rok HS-ROCK Cell proliferation and growth84; interacts with Pk61C,Tor & Akt1 – Mutants cells are smaller85 S6k HS-RPS6KB1/2 Central nervous system development86; Phosphorylates tuberin inhibiting its ability to suppress S6kII HS-RSK3/2/1/46 mTor signalling87, Phosphorylation and inhibition of myt1 kinase 88-activates bub189 (Xenopus laevis) Required for mitosis (Mus musculus)90 SAK HS-SAK SNF1A HS-AMPK2;SC-SNF1 metabolic stress response; regulation of pol II and initiation of meiosis91 Src64B HS- FYN* regulation of actin polymerisation; contraction of actin/myosin during cellularization 92; cell proliferation93 TATA box binding protein associated – induces G1 progression through p5394; G2/M progression Taf1 HS-TafII250 through transcriptional activation of string/cdc2595 tkv HS-BMPR1B Type I TGF receptor; cell growth and division - anterior/posterior patterning JIL-1 HS-RPS6KA5/4 tor Tor HS-RET* HS-FRAP1 trbl wee wts Mutants show disruption in anterior/posterior axis; Activates ras and STAT 96 Target of rapamycin – regulates G1/S transition97; Mutant cells are smaller and arrest in G198; growth control SKIP3 is upregulated in human tumours99; Negative regulator of CDK1; Induces Proteolysis of HS-trb2/1/SKIP3 string and twine100 HS-Wee1; SP-wee1* Mitotic checkpoint phosphorylation of CDK1; Wee1p phosphorylates Cdc2p on Tyr15101; regulates mitotic entry Tumour suppressor; inhibits G2/M and promotes apoptosis102; mutants show overgrowth and HS-LATS1/2 abnormal morphogenesis; interacts genetically with CycA and cdc2 H. Sapiens (HS); C. elegans (CE); S. Cerevisiae (SC); S. Pombe (SP). We obtained orthologues from other organisms in the Inparanoid database103 (confidence value=0.05 or higher). We indicate the closest homologue after a BLAST104 search in NCBI, when the orthology is not clear (entries with *). a-Information on Drosophila phenotypes was taken from literature search and FlyBase (www.flybase.org). Information was also drawn from 2 WormBase(http://www.wormbase.org/), from the Budding Yeast Database (SGD) (http://www.yeastgenome.org/) and from OMIM (Online Mendelian Inheritance of Men@ NCBI). Entries are shown in alphabetic order and more detail is given than in Table 1. Due to limitations of space we regret that it is not possible to mention all published works relevant to this table. 3 References 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. 19. 20. Gu, Y., Lin, Q., Childress, C. & Yang, W. Identification of the region in Cdc42 that confers the binding specificity to ACK. J Biol Chem (2004). Sem, K. P. et al. ACK family tyrosine kinase activity is a component of Dcdc42 signaling during dorsal closure in Drosophila melanogaster. Mol Cell Biol 22, 3685-97 (2002). Carmena, M. & Earnshaw, W. C. The cellular geography of aurora kinases. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 4, 842-54 (2003). Lew, D. J. & Burke, D. J. The spindle assembly and spindle position checkpoints. Annu Rev Genet 37, 251-82 (2003). Logarinho, E. et al. Different spindle checkpoint proteins monitor microtubule attachment and tension at kinetochores in Drosophila cells. J Cell Sci 117, 1757-71 (2004). Basu, J. et al. Mutations in the essential spindle checkpoint gene bub1 cause chromosome missegregation and fail to block apoptosis in Drosophila. J Cell Biol 146, 13-28 (1999). Gould, K. in Protein Kinase Functions (ed. Woodgett, J.) 277-302 (Oxford University Press, Oxford, 2000). Kraft, C. et al. Mitotic regulation of the human anaphase-promoting complex by phosphorylation. Embo J 22, 6598-609 (2003). Stern, B., Ried, G., Clegg, N. J., Grigliatti, T. A. & Lehner, C. F. Genetic analysis of the Drosophila cdc2 homolog. Development 117, 219-32 (1993). Meyer, C. A. et al. Drosophila Cdk4 is required for normal growth and is dispensable for cell cycle progression. Embo J 19, 4533-42 (2000). Datar, S. A., Jacobs, H. W., de la Cruz, A. F., Lehner, C. F. & Edgar, B. A. The Drosophila cyclin D-Cdk4 complex promotes cellular growth. Embo J 19, 4543-54 (2000). Leclerc, V., Tassan, J. P., O'Farrell, P. H., Nigg, E. A. & Leopold, P. Drosophila Cdk8, a kinase partner of cyclin C that interacts with the large subunit of RNA polymerase II. Mol Biol Cell 7, 505-13 (1996). Simone, C., Bagella, L., Bellan, C. & Giordano, A. Physical interaction between pRb and cdk9/cyclinT2 complex. Oncogene 21, 4158-65 (2002). Peng, J., Marshall, N. F. & Price, D. H. Identification of a cyclin subunit required for the function of Drosophila P-TEFb. J Biol Chem 273, 13855-60 (1998). Madaule, P. et al. Role of citron kinase as a target of the small GTPase Rho in cytokinesis. Nature 394, 491-4 (1998). D'Avino, P., Savoian, M. & and Glover, D. Mutations in sticky lead to defective organization of the contractile ring during cytokinesis and are enhanced by Rho and suppressed by Rac. Journal of Cell Biology 5, 61-71 (2004). Tomoda, T., Kim, J. H., Zhan, C. & Hatten, M. E. Role of Unc51.1 and its binding partners in CNS axon outgrowth. Genes Dev 18, 541-58 (2004). Sullivan, A., Uff, C. R., Isacke, C. M. & Thorne, R. F. PACE-1, a novel protein that interacts with the C-terminal domain of ezrin. Exp Cell Res 284, 224-38 (2003). Lizcano, J. M. et al. LKB1 is a master kinase that activates 13 kinases of the AMPK subfamily, including MARK/PAR-1. Embo J 23, 833-43 (2004). Kato, M., Yano, K., Morotomi-Yano, K., Saito, H. & Miki, Y. Identification and characterization of the human protein kinase-like gene NTKL: mitosis-specific centrosomal localization of an alternatively spliced isoform. Genomics 79, 760-7 (2002). 4 21. 22. 23. 24. 25. 26. 27. 28. 29. 30. 31. 32. 33. 34. 35. 36. 37. 38. 39. 40. 41. Abe, M. K. et al. ERK8, a new member of the mitogen-activated protein kinase family. J Biol Chem 277, 16733-43 (2002). Groth, A. et al. Human Tousled like kinases are targeted by an ATM- and Chk1dependent DNA damage checkpoint. Embo J 22, 1676-87 (2003). Carrera, P. et al. Tousled-like kinase functions with the chromatin assembly pathway regulating nuclear divisions. Genes Dev 17, 2578-90 (2003). Hum, D. et al. Characterization of a cGMP-response element in the guanylyl cyclase/natriuretic peptide receptor A gene promoter. Hypertension 43, 1270-8 (2004). Pedram, A., Razandi, M. & Levin, E. R. Natriuretic peptides suppress vascular endothelial cell growth factor signaling to angiogenesis. Endocrinology 142, 1578-86 (2001). Johnston, L. H., Masai, H. & Sugino, A. A Cdc7p-Dbf4p protein kinase activity is conserved from yeast to humans. Prog Cell Cycle Res 4, 61-9 (2000). Zhou, H. et al. Microtubule-associated serine/threonine kinase-205 kDa and Fcgamma receptor control IL-12 p40 synthesis and NF-kappaB activation. J Immunol 172, 255968 (2004). Walden, P. D. & Millette, C. F. Increased activity associated with the MAST205 protein kinase complex during mammalian spermiogenesis. Biol Reprod 55, 1039-44 (1996). McKay, R. M., Peters, J. M. & Graff, J. M. The casein kinase I family in Wnt signaling. Dev Biol 235, 388-96 (2001). Yen, S. H., Kenessey, A., Lee, S. C. & Dickson, D. W. The distribution and biochemical properties of a Cdc2-related kinase, KKIALRE, in normal and Alzheimer brains. J Neurochem 65, 2577-84 (1995). Ko, T. K., Kelly, E. & Pines, J. CrkRS: a novel conserved Cdc2-related protein kinase that colocalises with SC35 speckles. J Cell Sci 114, 2591-603 (2001). Simmer, F. et al. Genome-Wide RNAi of C. elegans Using the Hypersensitive rrf-3 Strain Reveals Novel Gene Functions. PLoS Biol 1, E12 (2003). Liu, S. T. et al. Human MPS1 kinase is required for mitotic arrest induced by the loss of CENP-E from kinetochores. Mol Biol Cell 14, 1638-51 (2003). Fisk, H. A., Mattison, C. P. & Winey, M. Human Mps1 protein kinase is required for centrosome duplication and normal mitotic progression. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 100, 14875-80 (2003). Kuroyanagi, H. et al. SPK-1, a C. elegans SR protein kinase homologue, is essential for embryogenesis and required for germline development. Mech Dev 99, 51-64 (2000). Olaso, E. et al. DDR2 receptor promotes MMP-2-mediated proliferation and invasion by hepatic stellate cells. J Clin Invest 108, 1369-78 (2001). Ferri, N., Carragher, N. O. & Raines, E. W. Role of discoidin domain receptors 1 and 2 in human smooth muscle cell-mediated collagen remodeling: potential implications in atherosclerosis and lymphangioleiomyomatosis. Am J Pathol 164, 1575-85 (2004). Yanagawa, S. et al. Casein kinase I phosphorylates the Armadillo protein and induces its degradation in Drosophila. Embo J 21, 1733-42 (2002). Santos, J. A. et al. The casein kinase 1 alpha gene of Drosophila melanogaster is developmentally regulated and the kinase activity of the protein induced by DNA damage. J Cell Sci 109 ( Pt 7), 1847-56 (1996). Litchfield, D. W. Protein kinase CK2: structure, regulation and role in cellular decisions of life and death. Biochem J 369, 1-15 (2003). Katso, R. M. et al. Overexpression of H-Ryk in mouse fibroblasts confers transforming ability in vitro and in vivo: correlation with up-regulation in epithelial ovarian cancer. Cancer Res 59, 2265-70 (1999). 5 42. 43. 44. 45. 46. 47. 48. 49. 50. 51. 52. 53. 54. 55. 56. 57. 58. 59. 60. Morris, J. Z., Navarro, C. & Lehmann, R. Identification and analysis of mutations in bob, Doa and eight new genes required for oocyte specification and development in Drosophila melanogaster. Genetics 164, 1435-46 (2003). Kim, K. H. et al. Negative regulation of filamentous growth and flocculation by Lkh1, a fission yeast LAMMER kinase homolog. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 289, 1237-42 (2001). Fischer, T. A. et al. Activation of cGMP-dependent protein kinase Ibeta inhibits interleukin 2 release and proliferation of T cell receptor-stimulated human peripheral T cells. J Biol Chem 276, 5967-74 (2001). Chen, W., Yazicioglu, M. & Cobb, M. H. Characterization of OSR1, a member of the mammalian Ste20p/germinal center kinase subfamily. J Biol Chem 279, 11129-36 (2004). Dey, A. et al. A bromodomain protein, MCAP, associates with mitotic chromosomes and affects G(2)-to-M transition. Mol Cell Biol 20, 6537-49 (2000). Guo, N., Faller, D. V. & Denis, G. V. Activation-induced nuclear translocation of RING3. J Cell Sci 113 ( Pt 17), 3085-91 (2000). Jiang, H. Y. et al. Phosphorylation of the alpha subunit of eukaryotic initiation factor 2 is required for activation of NF-kappaB in response to diverse cellular stresses. Mol Cell Biol 23, 5651-63 (2003). Zipperlen, P., Fraser, A. G., Kamath, R. S., Martinez-Campos, M. & Ahringer, J. Roles for 147 embryonic lethal genes on C.elegans chromosome I identified by RNA interference and video microscopy. Embo J 20, 3984-92 (2001). Robinson, L. C. et al. The Yck2 yeast casein kinase 1 isoform shows cell cycle-specific localization to sites of polarized growth and is required for proper septin organization. Mol Biol Cell 10, 1077-92 (1999). Koniaras, K., Cuddihy, A. R., Christopoulos, H., Hogg, A. & O'Connell, M. J. Inhibition of Chk1-dependent G2 DNA damage checkpoint radiosensitizes p53 mutant human cells. Oncogene 20, 7453-63 (2001). Gandhi, M. J., Cummings, C. L. & Drachman, J. G. FLJ14813 missense mutation: a candidate for autosomal dominant thrombocytopenia on human chromosome 10. Hum Hered 55, 66-70 (2003). Thevelein, J. M. & de Winde, J. H. Novel sensing mechanisms and targets for the cAMP-protein kinase A pathway in the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Microbiol 33, 904-18 (1999). Samejima, I. & Yanagida, M. Identification of cut8+ and cek1+, a novel protein kinase gene, which complement a fission yeast mutation that blocks anaphase. Mol Cell Biol 14, 6361-71 (1994). Yu, J. et al. Greatwall kinase: a nuclear protein required for proper chromosome condensation and mitotic progression in Drosophila. J Cell Biol 164, 487-92 (2004). Ura, S., Masuyama, N., Graves, J. D. & Gotoh, Y. MST1-JNK promotes apoptosis via caspase-dependent and independent pathways. Genes Cells 6, 519-30 (2001). Bardin, A. J. & Amon, A. Men and sin: what's the difference? Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 2, 815-26 (2001). Chen, X. et al. Cyclin D-Cdk4 and cyclin E-Cdk2 regulate the Jak/STAT signal transduction pathway in Drosophila. Dev Cell 4, 179-90 (2003). Schumacher, S., Gryzik, T., Tannebaum, S. & Muller, H. A. The RhoGEF Pebble is required for cell shape changes during cell migration triggered by the Drosophila FGF receptor Heartless. Development 131, 2631-40 (2004). Persad, S. & Dedhar, S. The role of integrin-linked kinase (ILK) in cancer progression. Cancer Metastasis Rev 22, 375-84 (2003). 6 61. 62. 63. 64. 65. 66. 67. 68. 69. 70. 71. 72. 73. 74. 75. 76. 77. 78. 79. 80. 81. Harrison, J. C., Bardes, E. S., Ohya, Y. & Lew, D. J. A role for the Pkc1p/Mpk1p kinase cascade in the morphogenesis checkpoint. Nat Cell Biol 3, 417-20 (2001). Oldham, S. & Hafen, E. Insulin/IGF and target of rapamycin signaling: a TOR de force in growth control. Trends Cell Biol 13, 79-85 (2003). Deak, M., Clifton, A. D., Lucocq, L. M. & Alessi, D. R. Mitogen- and stress-activated protein kinase-1 (MSK1) is directly activated by MAPK and SAPK2/p38, and may mediate activation of CREB. Embo J 17, 4426-41 (1998). Soloaga, A. et al. MSK2 and MSK1 mediate the mitogen- and stress-induced phosphorylation of histone H3 and HMG-14. Embo J 22, 2788-97 (2003). Vermeulen, L., De Wilde, G., Van Damme, P., Vanden Berghe, W. & Haegeman, G. Transcriptional activation of the NF-kappaB p65 subunit by mitogen- and stressactivated protein kinase-1 (MSK1). Embo J 22, 1313-24 (2003). Jin, Y. et al. JIL-1: a novel chromosomal tandem kinase implicated in transcriptional regulation in Drosophila. Mol Cell 4, 129-35 (1999). Enslen, H., Brancho, D. M. & Davis, R. J. Molecular determinants that mediate selective activation of p38 MAP kinase isoforms. Embo J 19, 1301-11 (2000). Uddin, S., Ah-Kang, J., Ulaszek, J., Mahmud, D. & Wickrema, A. Differentiation stage-specific activation of p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase isoforms in primary human erythroid cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 101, 147-52 (2004). Zhang, H., Li, Z., Viklund, E. K. & Stromblad, S. P21-activated kinase 4 interacts with integrin alpha v beta 5 and regulates alpha v beta 5-mediated cell migration. J Cell Biol 158, 1287-97 (2002). Jaffer, Z. M. & Chernoff, J. p21-activated kinases: three more join the Pak. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 34, 713-7 (2002). Wada, T. & Penninger, J. M. Stress Kinase MKK7: Savior of Cell Cycle Arrest and Cellular Senescence. Cell Cycle 3, 577-9 (2004). Pang, K. M. et al. The minibrain kinase homolog, mbk-2, is required for spindle positioning and asymmetric cell division in early C. elegans embryos. Dev Biol 265, 127-39 (2004). Peng, C. Y. et al. C-TAK1 protein kinase phosphorylates human Cdc25C on serine 216 and promotes 14-3-3 protein binding. Cell Growth Differ 9, 197-208 (1998). Burwinkel, B. et al. Muscle glycogenosis with low phosphorylase kinase activity: mutations in PHKA1, PHKG1 or six other candidate genes explain only a minority of cases. Eur J Hum Genet 11, 516-26 (2003). Pullen, N. et al. Phosphorylation and activation of p70s6k by PDK1. Science 279, 70710 (1998). Radimerski, T. et al. dS6K-regulated cell growth is dPKB/dPI(3)K-independent, but requires dPDK1. Nat Cell Biol 4, 251-5 (2002). Chen, Z. et al. ASK1 mediates apoptotic cell death induced by genotoxic stress. Oncogene 18, 173-80 (1999). Searle, J. S., Schollaert, K. L., Wilkins, B. J. & Sanchez, Y. The DNA damage checkpoint and PKA pathways converge on APC substrates and Cdc20 to regulate mitotic progression. Nat Cell Biol 6, 138-45 (2004). Janssens, S. & Beyaert, R. Functional diversity and regulation of different interleukin-1 receptor-associated kinase (IRAK) family members. Mol Cell 11, 293-302 (2003). Barr, F. A., Sillje, H. H. & Nigg, E. A. Polo-like kinases and the orchestration of cell division. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 5, 429-40 (2004). Ferrara, N., Gerber, H. P. & LeCouter, J. The biology of VEGF and its receptors. Nat Med 9, 669-76 (2003). 7 82. 83. 84. 85. 86. 87. 88. 89. 90. 91. 92. 93. 94. 95. 96. 97. 98. 99. 100. Gupta, T. & Schupbach, T. Two signals are better than one: border cell migration in Drosophila. Dev Cell 1, 443-5 (2001). Kosako, H. et al. Rho-kinase/ROCK is involved in cytokinesis through the phosphorylation of myosin light chain and not ezrin/radixin/moesin proteins at the cleavage furrow. Oncogene 19, 6059-64 (2000). Lane, H. A., Fernandez, A., Lamb, N. J. & Thomas, G. p70s6k function is essential for G1 progression. Nature 363, 170-2 (1993). Montagne, J. et al. Drosophila S6 kinase: a regulator of cell size. Science 285, 2126-9 (1999). Yntema, H. G. et al. A novel ribosomal S6-kinase (RSK4; RPS6KA6) is commonly deleted in patients with complex X-linked mental retardation. Genomics 62, 332-43 (1999). Roux, P. P., Ballif, B. A., Anjum, R., Gygi, S. P. & Blenis, J. Tumor-promoting phorbol esters and activated Ras inactivate the tuberous sclerosis tumor suppressor complex via p90 ribosomal S6 kinase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 101, 13489-94 (2004). Palmer, A., Gavin, A. C. & Nebreda, A. R. A link between MAP kinase and p34(cdc2)/cyclin B during oocyte maturation: p90(rsk) phosphorylates and inactivates the p34(cdc2) inhibitory kinase Myt1. Embo J 17, 5037-47 (1998). Schwab, M. S. et al. Bub1 is activated by the protein kinase p90(Rsk) during Xenopus oocyte maturation. Curr Biol 11, 141-50 (2001). Hudson, J. W. et al. Late mitotic failure in mice lacking Sak, a polo-like kinase. Curr Biol 11, 441-6 (2001). Purnapatre, K., Piccirillo, S., Schneider, B. L. & Honigberg, S. M. The CLN3/SWI6/CLN2 pathway and SNF1 act sequentially to regulate meiotic initiation in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Genes Cells 7, 675-91 (2002). Thomas, J. H. & Wieschaus, E. src64 and tec29 are required for microfilament contraction during Drosophila cellularization. Development 131, 863-71 (2004). Pedraza, L. G., Stewart, R. A., Li, D. M. & Xu, T. Drosophila Src-family kinases function with Csk to regulate cell proliferation and apoptosis. Oncogene 23, 4754-62 (2004). Li, H. H., Li, A. G., Sheppard, H. M. & Liu, X. Phosphorylation on Thr-55 by TAF1 mediates degradation of p53: a role for TAF1 in cell G1 progression. Mol Cell 13, 86778 (2004). Maile, T., Kwoczynski, S., Katzenberger, R. J., Wassarman, D. A. & Sauer, F. TAF1 activates transcription by phosphorylation of serine 33 in histone H2B. Science 304, 1010-4 (2004). Li, J., Xia, F. & Li, W. X. Coactivation of STAT and Ras is required for germ cell proliferation and invasive migration in Drosophila. Dev Cell 5, 787-98 (2003). Brunn, G. J. et al. Phosphorylation of the translational repressor PHAS-I by the mammalian target of rapamycin. Science 277, 99-101 (1997). Zhang, H., Stallock, J. P., Ng, J. C., Reinhard, C. & Neufeld, T. P. Regulation of cellular growth by the Drosophila target of rapamycin dTOR. Genes Dev 14, 2712-24 (2000). Bowers, A. J., Scully, S. & Boylan, J. F. SKIP3, a novel Drosophila tribbles ortholog, is overexpressed in human tumors and is regulated by hypoxia. Oncogene 22, 2823-35 (2003). Mata, J., Curado, S., Ephrussi, A. & Rorth, P. Tribbles coordinates mitosis and morphogenesis in Drosophila by regulating string/CDC25 proteolysis. Cell 101, 511-22 (2000). 8 101. 102. 103. 104. Lew, D. J. & Kornbluth, S. Regulatory roles of cyclin dependent kinase phosphorylation in cell cycle control. Curr Opin Cell Biol 8, 795-804 (1996). Xia, H. et al. LATS1 tumor suppressor regulates G2/M transition and apoptosis. Oncogene 21, 1233-41 (2002). Remm, M., Storm, C. E. & Sonnhammer, E. L. Automatic clustering of orthologs and in-paralogs from pairwise species comparisons. J Mol Biol 314, 1041-52 (2001). Altschul, S. F. et al. Gapped BLAST and PSI-BLAST: a new generation of protein database search programs. Nucleic Acids Res 25, 3389-402 (1997). 9