Southern Africa Physical Geography Physical features 1. The
advertisement

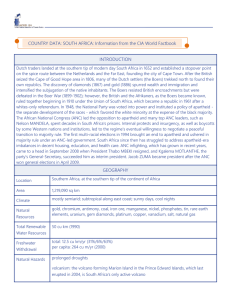
Southern Africa I. Physical Geography A. Physical features 1. The surface of southern Africa is a large plateau. 2. The Drakensberg and Inyanga are the steep peeks that form the plateau’s edges 3. Open grassland (the veld) at Kruger National Park contains lions, leopards, elephants, rhinos, hippos, baboons and antelope. Tourism/Safari B. Climate 1. Range from desert to cool uplands. Inland is dry and hot/Coast is seasonally wet and dry 2. Deserts a. Deserts include the Kalahari Desert and Namib Desert 3. Rivers a. The Orange and Limpopo Rivers are vital for transportation, trade and hydroelectric power. 4. Resources a. Rich in mineral resources like gold, diamonds, platinum, copper, uranium, coal and iron ore II. History and Culture A. The Khosian – 1. Hunter-Gatherers from 18,000 B.C. – Some of the oldest human fossils in the world. B. Bantu Migrations 1. Bantu speaking people moved from central to South Africa around 500 A.D. / Introduced iron tools and herding to southern people C. Shona and Swahili. 1. Shona and Swahili speaking people built an empire along the coast of Zimbabwe and Mozambique D. Madagascar 1. Influences from Asia/Malagasy is official language E. Mozambique 1. Portuguese set it up as an outpost for slave trade F. Colonialism 1. Dutch, Portuguese and British colonized and controlled the area. Used people as slaves 2. British took over South Africa and fought Boers and Zulu people G. Resources 1. Diamonds, Gold and Colonies a. Diamonds and gold were found in the 1860’s and the British took them from the area. b. Railroads were built to move goods 2. Fighting between British and Boers/ Became British colony in 1920 III. South Africa Today A. South Africa 1. Racial Divisions 2. African National Congress was formed to defend the rights of Black South Africans 3. Apartheid (“apartness”) was the policy of the South African government 4. Whites owned most good farmland, went to better schools, held better jobs 5. Blacks had to live in separate areas known as townships B. Pressure Against South Africa 1. Countries around the world put sanctions or penalties against South Africa. 2. Other countries of Southern Africa gained independence during the 1960’s, 70’s and 80’s while South Africa did not. 3. The End of Apartheid 4. Nelson Mandela, who was jailed for 26 years for protesting apartheid, was released in 1990 and by 1994 he became Africa’s first black President. He ended Apartheid. C. South Africa’s Economy 1. Most businesses are still owned and run by whites 2. Change has been slow 3. Energy resources include coal, uranium, and hydroelectric power 4. Mineral resources are gold, diamonds D. South Africa’s Future 1. It strives for equal education and economic opportunities 2. Crime and AIDS must be controlled IV. Other Southern African Countries A. Namibia 1. Live in the savannas and cooler highlands 2. Many of German descent/Christian/English is official language 3. Jobs are in mining of mineral resources like diamonds, copper, zinc and lead 4. Fishing the coast of the Atlantic Ocean B. Botswana 1. Belongs to the Organization of African Unity/Success story 2. Good government uses resources for profit (Diamonds and copper) 3. No ethnic tensions/79 percent belong to the Tswana group 4. Most are Christian C. Zimbabwe 1. Gained independence in 1980/Struggle with distribution of wealth 2. Export tobacco, corn, sugar and beef. Many mineral resources 3. AIDS is an epidemic there D. Mozambique 1. Many Bantu ethnic groups/Civil War/Mix of Christian and Muslim 2. Portuguese is official language 3. Zambezi River offers energy, trade, transportation and minerals E. Madagascar 1. Former French colony/Asian influences/Very poor 2. Exports coffee, sugar, vanilla, and cloves 3. 4th largest island in the world