Science Notes December 1, 2010 SOL 5.7 (b, c, d) Scientists are
advertisement

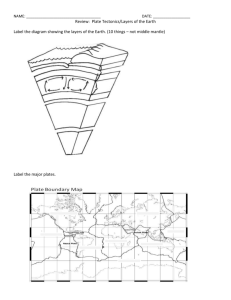
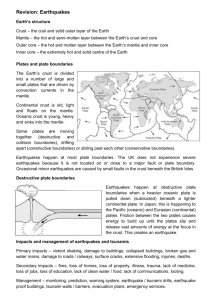
Science Notes December 1, 2010 SOL 5.7 (b, c, d) Scientists are able to study the Earth through fossil evidence. Fossils are the remains of plants and animals preserved in rocks. Fossils provide scientists with evidence about life on Earth, past and present. Fossils can also tell scientists how the Earth’s surface has changed over time, the age of the Earth, and how plants and animals lived long ago in their environments. Fossils are found mostly in sedimentary rocks. Sedimentary rocks are formed when small pieces of rock, called sediments, are dropped by water, wind, or ice and build up in layers. These layers eventually harden and turn into rock. In addition to pieces of rock, sediments also contain materials that were once living organisms. Many fossils form when plants and animals die and are quickly buried by clay, sand and other sediments. The Earth is made up of four layers; crust, mantle, outer core, and inner core. Each of these layers is unique and possesses their own distinctive characteristics. The crust is the outer layer of the Earth. It is the coolest and the thinnest compared to the other layers. It is approximately 3 to 25 miles thick and is mainly composed of lakes, oceans, rivers, plants, and soil. The crust is the layer on which we live. The mantle is located beneath the crust. Even though no one has been able to dig through the crust to the mantle, scientists think they know what it is like. The mantle is approximately 1800 miles thick, which makes it the largest layer. The temperatures are very hot, so hot, that the rocks that are found there flow (imagine watching your food on the conveyor belt in the checkout line at Walmart!). There are also pockets of magma that sometimes erupt through the Earth’s crust. When this magma reaches the surface, it is called lava. Under the mantle is the core. The core is divided into two parts. The first part, right under the mantle is the outer core. This layer is about 1400 miles thick. This layer is composed of hot liquid nickel and iron. The temperatures are so hot that these materials are melted into a thick liquid state like pudding. The other part of the core is found at the very center of the Earth. It is called the inner core. The inner core, which is about 800 miles thick, is a solid ball of hot iron and nickel. This layer is the smallest and the hottest of all the layers. Temperatures and pressure increase from the crust to the inner core of the Earth. These two factors can cause the following events to happen: Magma from the mantle can erupt from a volcano Flowing rocks of the mantle can cause the crust to move and earthquakes to occur. Flowing rocks of the mantle can cause continents to move across the surface of the Earth. The extreme pressure and heat from the Earth can cause materials in the Earth to move or shift. This heat and pressure cause large continent-sized blocks called plates to move slowly about the Earth’s surface. They are not connected to one another, but move freely about. These plates can bump, push, and scrape past the other plates that are around them. The edges, or boundaries, of plates are called faults. Most volcanoes and earthquakes occur on these faults. Plates move in three main ways to form boundaries: Convergent Boundaries – Occur when plates push together; cause mountain ranges to rise up from the Earth’s surface (example - Appalachian Mountains); however, deep in the Earth’s oceans, these boundaries force plates downward instead of upward and deep trenches are formed. Divergent Boundaries – Occur when plates move apart from each other. These boundaries occur mostly on the ocean floors of the Earth. At these boundaries, magma rises up between the two separating plates forming volcanoes and mountain ranges deep under water called mid-ocean ridges. Most of Earth’s new crust comes from the magma that erupts from these divergent boundaries and the volcanoes they create. Transform Boundaries – Occur when plates slide past each other horizontally. These types of boundaries grind against each other causing earthquakes. One example of this boundary is located on the west coast of the U.S, which causes earthquakes in California (San Andreas Fault). The process of plate movement that moves the Earth’s continents is called continental drift. These movements, past and present, are responsible for the amazing geological features of our Earth’s ever-changing surface.