BY251
advertisement
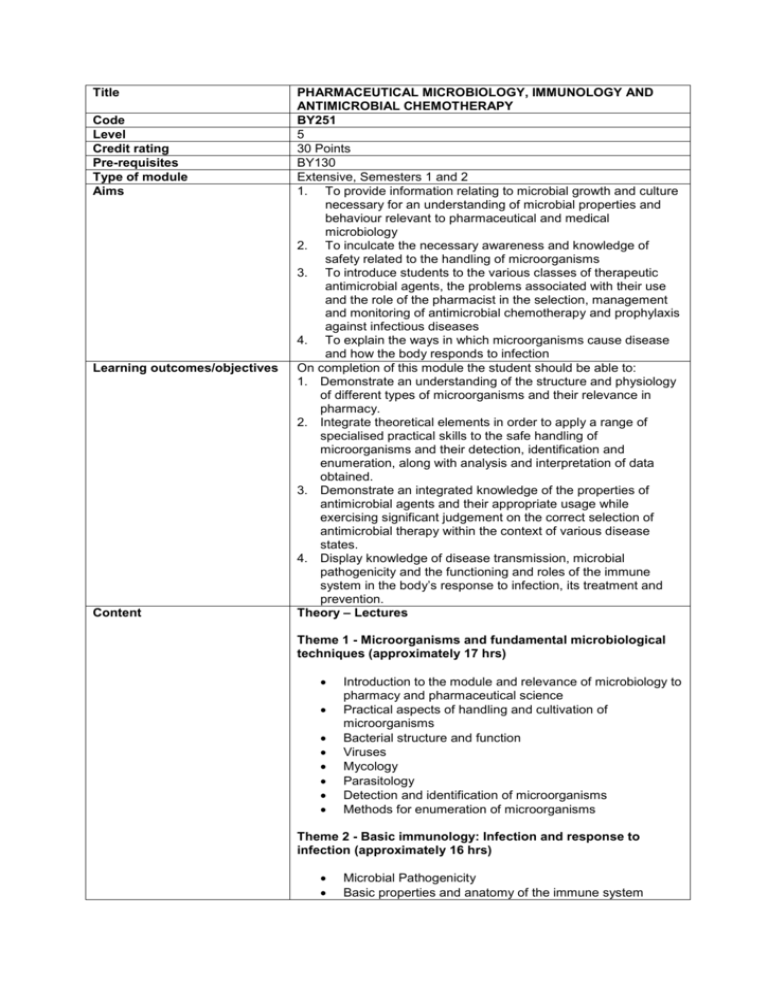
Title Code Level Credit rating Pre-requisites Type of module Aims Learning outcomes/objectives Content PHARMACEUTICAL MICROBIOLOGY, IMMUNOLOGY AND ANTIMICROBIAL CHEMOTHERAPY BY251 5 30 Points BY130 Extensive, Semesters 1 and 2 1. To provide information relating to microbial growth and culture necessary for an understanding of microbial properties and behaviour relevant to pharmaceutical and medical microbiology 2. To inculcate the necessary awareness and knowledge of safety related to the handling of microorganisms 3. To introduce students to the various classes of therapeutic antimicrobial agents, the problems associated with their use and the role of the pharmacist in the selection, management and monitoring of antimicrobial chemotherapy and prophylaxis against infectious diseases 4. To explain the ways in which microorganisms cause disease and how the body responds to infection On completion of this module the student should be able to: 1. Demonstrate an understanding of the structure and physiology of different types of microorganisms and their relevance in pharmacy. 2. Integrate theoretical elements in order to apply a range of specialised practical skills to the safe handling of microorganisms and their detection, identification and enumeration, along with analysis and interpretation of data obtained. 3. Demonstrate an integrated knowledge of the properties of antimicrobial agents and their appropriate usage while exercising significant judgement on the correct selection of antimicrobial therapy within the context of various disease states. 4. Display knowledge of disease transmission, microbial pathogenicity and the functioning and roles of the immune system in the body’s response to infection, its treatment and prevention. Theory – Lectures Theme 1 - Microorganisms and fundamental microbiological techniques (approximately 17 hrs) Introduction to the module and relevance of microbiology to pharmacy and pharmaceutical science Practical aspects of handling and cultivation of microorganisms Bacterial structure and function Viruses Mycology Parasitology Detection and identification of microorganisms Methods for enumeration of microorganisms Theme 2 - Basic immunology: Infection and response to infection (approximately 16 hrs) Microbial Pathogenicity Basic properties and anatomy of the immune system Properties of antigens and antibody structure B and T lymphocyte receptor genetics and clonal selection Immune receptor function Mechanisms of tolerance. Cellular and Humoral Immune responses The innate immune system Introduction to medical immunology Microbial evasion of the immune system Immunology of sepsis, endotoxin response, superantigens Immunology of drug allergy (antimicrobials) Immunology of vaccines Theme 3 - Treatment: Antimicrobial agents (approximately 22 hrs) Sites of action of antibacterials Classes of antibiotic Antifungal agents Antiviral agents Pharmacodynamics and pharmacokinetics of antimicrobials Resistance of organisms to antimicrobials Vaccines Theme 4 - Treatment: Clinical management of infection (approximately 15 hrs) Infection and sepsis: what it means to the practitioner Monitoring response to infection and treatment Basic principles of antimicrobial usage Antibacterial agents Management of infection: A review of major infections and their clinical management including Malaria and its treatments Antimicrobial stewardship Clinical case studies and sample exam questions Coursework (approximately 16 hrs) The coursework programme may include the following manipulative laboratory exercises and associated MCQ sheets: 1. 2. 3. 4. Sources of microbial contamination. Principles of microbial enumeration. Pharmacopoeial methods for the detection of specified organisms. Measurement of cell growth by turbidity Guided study Students are required to read and learn certain items of information which may be completed in advance of laboratory classes or to complement lecture materials. The requirements for laboratory classes are clearly presented in the module handbook on student central and may be examined by means of question sheets during the course of the laboratory session or on a pre-determined date. Further aspects of the theory syllabus which students will be expected to study on their own initiative will be detailed on student central and may include topics such as visual aspects of microbial identification and some antimicrobial therapeutic agents (for Teaching and learning strategies Learning support Assessment tasks Brief description of module content and/or aims (maximum 80 words) example those used to treat scabies and lice, aminoglycosides, tetracyclines and streptogramins). This module is delivered through lectures and coursework-based exercises. The 300 hours study time allocated to this module normally comprises: Approximately 70 hrs lecture contact time Approximately 16 hrs of lab-based coursework Approximately 214 hrs personal study and assessment time The personal study time should be divided between the guided study and independent reading and revision for assessments. Texts (current editions) Aulton, M. E. Aulton’s Pharmaceutics: The Design and Manufacture of medicines, Churchill Livingstone. Baird R. M. and Bloomfield S. F. Microbial Quality Assurance in Cosmetics, Toiletries and Non-sterile Pharmaceuticals. Taylor and Francis. Baird, R. M., Hodges, N. A. and Denyer, S. P. Handbook of Microbiological Quality Control: Pharmaceuticals and Medical Devices, Taylor and Francis. Bannister, B. A., Gillespie, S. H. and Jones, J. Infection: Microbiology and Management, Blackwell Science. British National Formulary. Collins, C. H., Lyne, P. M., Grange, J. M. and Falkinham, J. O. Collins and Lyne’s Microbiological Methods, Arnold. Denyer, S. P. and Baird, R. M. Guide to Microbiological Control in Pharmaceuticals and Medical Devices, CRC Press. Denyer, S. P., Hodges, N. A. and Gorman, S. Hugo and Russell’s Pharmaceutical Microbiology, Blackwell Publishing. Finch, R. G., Greenwood, D., Norrby, S. R. and Whitely, R. J. Antibiotic and Chemotherapy: Anti-infective Agents and Their Use in Therapy, Churchill Livingstone. Greenwood, D., Slack, R., Peutherer, J. and Barer, M. Medical Microbiology, A Guide to Microbial Infections: Pathogenesis, Immunity, Laboratory Diagnosis and Control, Churchill Livingstone. Murphy, K. M., Travers, P. and Walport, M. Janeway’s Immunobiology, Garland Science: Taylor and Francis. 1. An unseen examination consisting of MCQs and short answer questions based on Microbiology and Fundamental Microbiological Techniques (Theme 1, 20% of the module mark) [LO1 & 2] 2. An unseen examination consisting of MCQs and short answer questions based on Basic Immunology: Infection and Response to Infection (Theme 2, 20% of the module mark) [LO4] 3. An unseen examination consisting of MCQs, short answer questions and essay questions based on Treatment: Antimicrobial agents (Theme 3) and Treatment: Clinical management of infection (Theme 4) (40% of the module mark, [LO3] 4. Coursework (20% of the module mark, [aspects of LO1 & 2] This module builds in part upon the information contained in BY130 Essential Cell Biology and Biochemistry module providing students with a more in-depth understanding of the structure and function of microorganisms. It contains features of microbiology which are of practical concern to pharmacy. Furthermore, it extends knowledge of how infections develop, the scope and appropriate use of agents available for the treatment of such infections and the role of the body’s immune system in the response to and prevention of Area examination board to which module relates Module team/authors/coordinator Semester offered, where appropriate Site where delivered Date of first approval Date of last revision Date of approval of this version Version number Replacement for previous module Field for which module is acceptable and status in that field Course(s) for which module is acceptable and status in that course School home External examiner infection. Biology and Biomedical Sciences Dr. Lara Barnes (module leader) and other members of the School of Pharmacy and Biomolecular Sciences 1 and 2 Moulsecoomb 2008 2008 2009 2 BY226 & PY237 Pharmacy, Compulsory MPharm, Compulsory Pharmacy and Biomolecular Sciences Gavin Knight